[/caption]
(Editor’s Note: Ken Kremer is at the Kennedy Space Center for Universe Today covering the flight of Endeavour)
Astronauts Robert Behnken and Nicholas Patrick completed the second of their three spacewalks (EVAs) planned for the STS-130 mission early this Sunday morning Feb 14 at 3:14 AM EST. The pair worked essentially as plumbers today during the spacewalk which began at 9:20 PM Saturday night. They successfully accomplished all their assigned tasks overnight by connecting crucial Tranquility feed lines to the International Space Station (ISS).
“It was an extremely exciting and successful day on the International Space Station, one that I’m very proud of,” said Flight Director Bob Dempsey. “The team has been working for over two years to make today happen. And it did, and it was extremely successful and I’m very pleased with the way it has gone. Everything was accomplished as we had planned.”
The main goal of EVA 2 was to route four newly redesigned ammonia coolant lines from the new Tranquility life support module to the Destiny laboratory module thereby hooking Tranquility into the space stations existing cooling system. Tranquility could not be fully activated and powered up for use by the ISS crew until fulfilling this essential plumbing job to install the custom built ammonia lines.
Behnken and Patrick spent the first half of EVA-2 connecting the four external ammonia jumper hoses which convey ammonia that works as a coolant to dissipate heat generated by the electronics and systems inside the module. The set up is comprised of two independent loops (A and B) with two lines each, a supply and a return line. The 16 ft long flex lines were also routed through brackets on the Unity node to which Tranquility is attached on the left side.
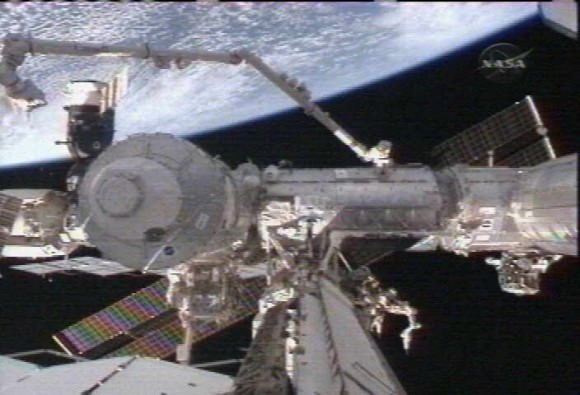
After connecting the four jumper hoses the astronauts methodically wrapped them with a long sheet of protective multi layer insulation, or MLI. During the EVA, the astronauts then flipped open the control valves for one of the two external loops (A) and successfully initiated the flow of ammonia coolant though the newly installed set of custom hoses. The second “B” loop will be activated on the third, and last, spacewalk of the STS 130 mission.

With coolant flowing as intended, another team of astronauts inside the ISS began powering up and fully activating the stations newest room for the first time. They turned on the interior lights, ventilation, air conditioning, computers and other life support and environmental control systems which this room was specifically designed to house.
The Italian-built module was constructed at a cost of some $400 million and then officially handed over by ESA to NASA in exchange for shuttle launch services lofting ESAs Columbus science laboratory to the ISS. Tranquility is now integrated into the massive orbiting complex which is greater than 90% complete.
Once again the highly trained and professional astronauts made an extremely difficult job look relatively easy. The only problem was quite minor. Patrick reported that a small quantity of ammonia of leaked out of a reservoir as he uncapped a connector on the Unity module before he could hook up the jumper hose. He said that ammonia particles, which had solidified in the cold vacuum of space, splashed onto the exterior of his spacesuit. This spray of ammonia automatically qualifies as a contamination incident although Patrick did not find any particles actually adhering to his suit. The pair had been trained for exactly this occurrence since a tiny leakage of this type was not entirely unexpected. The spacewalk continued as planned.
Since ammonia is highly toxic, the spacewalkers took care to “bake out” their suits and test for any residual contamination when they arrived back at the airlock at the conclusion of the EVA. None was detected and they ingressed the station as planned.
The final tasks of EVA 2 involved outfitting the nadir docking port of Tranquility for the relocation of the Cupola module to another berthing port and installing exterior handrails.
The Story behind the Urgently Redesigned Ammonia Hoses
The road to this point was very uncertain until the final days before blast off. In early January the original set of ammonia jumper hoses failed during preflight testing when they ruptured under high pressure during qualification testing in early January.
NASA and contractor teams had to work quite swiftly to redesign and construct four new custom ammonia hoses. The arduous task was only completed a few days before the then targeted launch date of Feb. 7. Otherwise a significantly curtailed mission involving only partial activation of Tranquility or a launch delay or would have been necessitated.
At the Kennedy Space Center press site I spoke with Eric Howell of Boeing in detail about the intense effort to construct and certify the hoses for the External Active Thermal Control System (EATCS). I had the opportunity to inspect the flexible metal hoses and their individual components first hand and hold and touch them with my own hands. I was quite surprised to find that they were rather sharp and easily capable of causing a deadly air leak gash into a spacewalkers glove.
“The 1 inch diameter hoses are constructed of Inconel, which is resistant to a highly corrosive substance like ammonia. The flexible, convoluted tube is covered by a metal braid which carries the entire load and provides all the strength to maintain the tubes integrity and prevent it from bursting. The individual strands of wire are 1/11,000 inch in diameter,” Howell explained to me.
“Normally it takes about 9 months to design and test the ammonia hoses. We had to get this job done in about 25 days. There was a weld quality issue with the original set of flight hoses. The weld was separating (yielding) from the metal braid carriers under pressure testing with nitrogen. To fix the hose bursting problem, we changed the design of the weld and the welding process to obtain a full depth of penetration.”
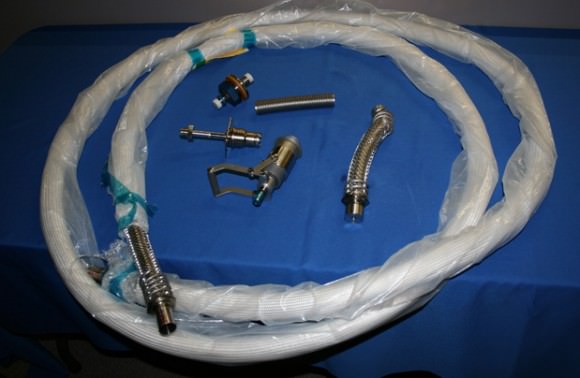
“The hoses are designed to operate at 500 psi. To qualify for flight they are tested for 25 cycles at 2000 psi (4 x operating pressure). The original hoses burst at 1600 psi. So we redesigned the hoses and modified the nut collar at the end which we found was too short.”
“We constructed four new multi-segmented hoses built by splicing together 3 to 5 shorter segments which we found lying around in storage throughout several NASA centers. Each of the original hoses that failed were constructed from two segments. The outer metal braid was then covered by a fiberglass sleeve to provide thermal protection. The new hoses were rush shipped from NASA Marshall Spaceflight Center in Huntsville, Ala on Jan 29 after a final checkout for approval by the Endeavour spacewalkers who were quite concerned,” Howell concluded.

Cupola Relocation and Extra day in Space
Transfer of the Cupola, which had been scheduled for this evening (Sunday, Feb 14) has been put on hold pending resolution of a clearance issue on Tranquilities end docking port to which Cupola is currently attached. The astronauts were unable to attach a protective cover onto the port from inside Tranquility. Several protruding bolts are interfering with attempts to lock the cover in place. The cover shields the port from debris and extreme temperatures when nothing is attached to it.
The astronauts did receive other very good news today when NASA managers decided to extend the STS 130 flight by one day bringing it to14 days in all and thus allowing a total of 9 days of joint docked operations with Endeavour at the orbiting outpost.
The extra flight day will permit Endeavour’s crew additional time to move the space toilet, water recycling, oxygen generation and exercise equipment into the now activated Tranquility. Those relocations had been on hold pending the repairs to the urine recycling system conducted earlier in the flight, and enough run time on the system to generate needed samples for return to Earth for analysis. Landing at the Kennedy Space Center is now targeted for 10:24 PM on Feb 21, weather permitting.
Update: NASA gave the go ahead late this afternoon (Feb 14) to start relocating Cupola late this evening. Watch for a report upon completion sometime overnight.
Earlier STS 130/ISS and SDO articles by Ken Kremer
Tranquility attached to Space Station
Sky on Fire as Endeavour Blasts to Space
Orion can Launch Safely in 2013 says Lockheed
Russian Cargo Freighter Docks at ISS; 1 Day to Endeavour launch
Endeavour astronauts arrive at Cape for launch of Tranquility
ISS Crew Twitpics from Orbit; Live Streaming Video Soon !
Path clear for STS 130 to attach Tranquility module
Endeavour aiming for on time launch with coolant hose fix ahead of schedule
STS 130 flight pressing forward to launch as NASA resolves coolant hose leak
STS-130 Shuttle flight facing delay due to Payload technical glitch
Shuttle Endeavour Rolled to Pad; Countdown to the Final Five Begins

