[/caption]
The giant Asteroid Vesta is among the most colorful bodies in our entire solar system and it appears to be much more like a terrestrial planet than a mere asteroid, say scientists deciphering stunning new images and measurements of Vesta received from NASA’s revolutionary Dawn spacecraft. The space probe only recently began circling about the huge asteroid in July after a four year interplanetary journey.
Vesta is a heavily battered and rugged world that’s littered with craters and mysterious grooves and troughs. It is the second most massive object in the Asteroid Belt and formed at nearly the same time as the Solar System some 4.5 Billion years ago.
“The framing cameras show Vesta is one of the most colorful objects in the solar system,” said mission scientist Vishnu Reddy of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany. “Vesta is unlike any other asteroid we have visited so far.”
Scientists presented the new images and findings from Dawn at the American Geophysical Union meeting this week in San Francisco.
Dawn is the first man-made probe to go into orbit around Vesta.
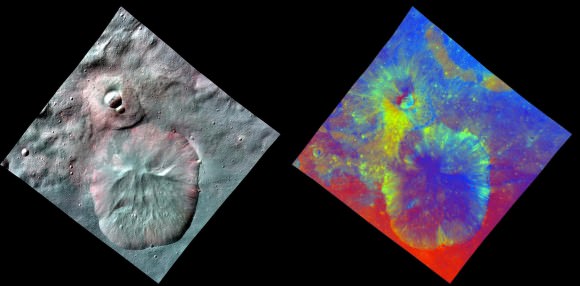
This image of Oppia Crater combines two separate views of the giant asteroid Vesta obtained by Dawn's framing camera. The far-left image uses near-infrared filters where red is used to represent 750 nanometers, green represents 920 nanometers and blue represents 980 nanometers. The image on the right is an image with colors assigned by scientists, representing different rock or mineral types on Vesta. The data reveal a world of many varied, well-separated layers and ingredients. The reddish color suggests a steep visible spectral slope, and areas of fresh landslides in the inner walls of the crater show deeper green colors. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
“Vesta is a transitional body between a small asteroid and a planet and is unique in many ways,” Reddy said. “We do not know why Vesta is so special.”
Although many asteroids look like potatoes, Reddy said Vesta reminds him more of an avocado.
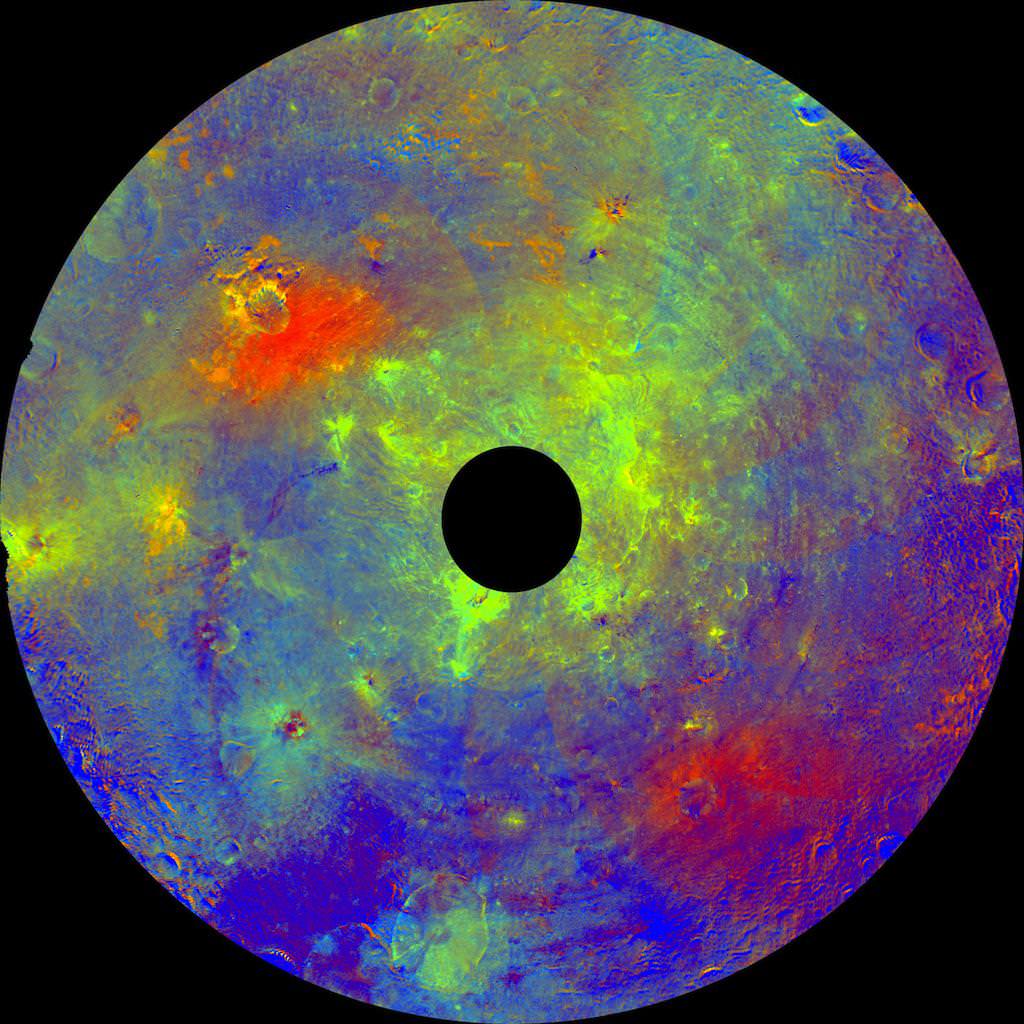
Asteroid Vesta is revealed as a ‘rainbow-colored palette’ in a new image mosaic (above) showcasing this alien world of highly diverse rock and mineral types of many well-separated layers and ingredients.
Researchers assigned different colors as markers to represent different rock compositions in the stunning new mosaic of the asteroid’s southern hemisphere.
The green areas in the mosaic suggest the presence of the iron-rich mineral pyroxene or large-sized particles, according to Eleonora Ammannito, from the Visible and Infrared (VIR) spectrometer team of the Italian Space Agency. The ragged surface materials are a mixture of rapidly cooled surface rocks and a deeper layer that cooled more slowly.
What could the other colors represent?
“The surface is very much consistent with the variability in the HED (Howardite-Eucritic-Diogenite) meteorites,” Prof. Chris Russell, Dawn Principal Investigator (UCLA) told Universe Today in an exclusive interview.
“There is Diogenite in varying amounts.”
“The different colors represent in part different ratios of Diogenite to Eucritic material. Other color variation may be due to particle sizes and to aging,” Russell told me.
No evidence of volcanic materials has been detected so far, said David Williams, Dawn participating scientist of Arizona State University, Tucson.
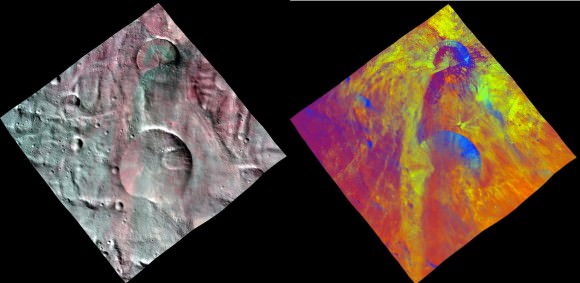
The fresh impact craters in this view are located in the south polar region, which has been partly covered by landslides from the adjacent crater. This would suggest that a layer of loose material covers the Vesta surface. This image combines two separate views of the giant asteroid Vesta obtained by Dawn’s framing camera. The far-left image uses near-infrared filters where red is used to represent 750 nanometers, green represents 920 nanometers and blue represents 980 nanometers. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
Before Dawn arrived, researchers expected to observe indications of volcanic activity. So, the lack of findings of volcanism is somewhat surprising. Williams said that past volcanic activity may be masked due to the extensive battering and resultant mixing of the surface regolith.
“More than 10,000 high resolution images of Vesta have been snapped to date by the framing cameras on Dawn,” Dr. Marc Rayman told Universe Today. Rayman is Dawn’s Chief Engineer from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif.
Dawn will spend a year in orbit at Vesta and investigate the asteroid at different altitudes with three on-board science instruments from the US, Germany and Italy.
The probe will soon finish spiraling down to her lowest mapping orbit known as LAMO (Low Altitude Mapping Orbit), approximately 130 miles (210 kilometers) above Vesta’s surface.
“Dawn remains on course to begin its scientific observations in LAMO on December 12,” said Rayman.
The German Aerospace Center and the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research provided the Framing Camera instrument and funding as international partners on the mission team. The Visible and Infrared Mapping camera was provided by the Italian Space Agency.
In July 2012, Rayman and the engineering team will fire up Dawn’s ion propulsion system, break orbit and head to Ceres, the largest asteroid and what a number of scientists consider to be a planet itself.
Ceres is believed to harbor thick caches of water ice and therefore could be a potential candidate for life.
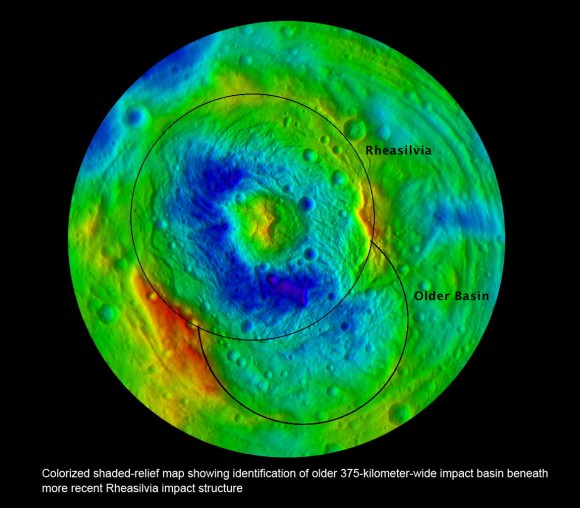
Colorized shaded-relief map showing location of 375-kilometer-wide Older impact basin that is overlapping with the more recent 500 km (300 mi) wide Rheasilvia impact structure at asteroid Vesta’s South Pole. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
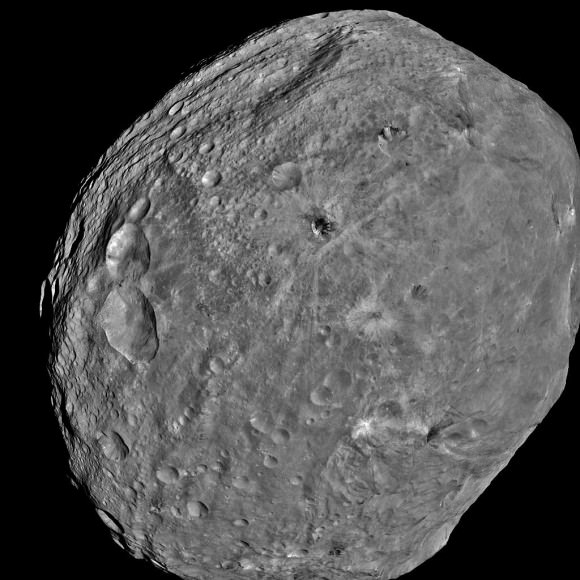

NASA's Dawn spacecraft obtained this image of the giant asteroid Vesta with its framing camera on July 24, 2011. It was taken from a distance of about 3,200 miles (5,200 kilometers). Before Dawn, Vesta was just a fuzzy blob in the most powerful telescopes. Dawn entered orbit around Vesta on July 15, and will spend a year orbiting the body before firing up the ion propulsion system to break orbit and speed to Ceres, the largest Asteroid. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
Read continuing features about Dawn by Ken Kremer starting here:
Vrooming over Vivid Vestan Vistas in Vibrant 3 D – Video
NASA Planetary Science Trio Honored as ‘Best of What’s New’ in 2011- Curiosity/Dawn/MESSENGER
Dawn Discovers Surprise 2nd Giant South Pole Impact Basin at Strikingly Dichotomous Vesta
Amazing New View of the Mt. Everest of Vesta
Dramatic 3 D Imagery Showcases Vesta’s Pockmarked, Mountainous and Groovy Terrain
Rheasilvia – Super Mysterious South Pole Basin at Vesta
Space Spectacular — Rotation Movies of Vesta
3 D Alien Snowman Graces Vesta
NASA Unveils Thrilling First Full Frame Images of Vesta from Dawn
Dawn Spirals Down Closer to Vesta’s South Pole Impact Basin
First Ever Vesta Vistas from Orbit – in 2D and 3D
Dawn Exceeds Wildest Expectations as First Ever Spacecraft to Orbit a Protoplanet – Vesta

Why would bodies with so little gravity collect so many craters? Earth would deflect and suck in many random rocks partially due to our atmosphere but would Vesta’s scars be solely due to chance? The escape velocity must be relatively miniscule! Is there an algorithm that would allow scientists to calculate the present and past density of the asteroid belt due to this number of impacts?
For the same reason that your car’s windshield has a nice insect collection splatted on it.
…and why when I dropped a plate of curry on the floor on Sunday I found 10’s of specs of curry sauce on my cat’s face hours later.
Well, keep in mind that the geology on Vesta isn’t really capable of eroding evidence of impacts as fast as something like a planet, or even our moon, as it literally is just a rock. The little heat it once might have had due to radioactive decay in its core is long gone, meaning that molten face-lifts like those that occurred on the moon are out of the question. But towering over all these is the sheer amount of time Vesta has had to collect impact craters. Remember, gravity isn’t the thing that “sucks” impactors in to cause the collision, at least not in the ranges of gravitational potency of the terrestrial planets. Gravity from larger bodies in a system chiefly serves to stir up the debris still in the system, shooting rocks in all sorts of directions. Vesta was one of the biggest innocent by-standers when the planets started throwing their fits in the early solar system, and has never been able to heel the scars… poor thing.
God sure knows how to make asteroids very interesting. That goes for dinosaurs as well.
Dawn uses filters centered at 430, 540, 650, 750, 830, 920, 980 nm – are those bands related to something, like specific minerals, rocks? And does some such bands could be used for false color Moon images?
A bona fide transitional protoplanet like Mars, I take it.
“Williams said that past volcanic activity may be masked due to the extensive battering and resultant mixing of the surface regolith.”
IIRC the regolith is estimated to be tens of times deeper, tens or hundreds of meters against meters for the Moon.