[/caption]
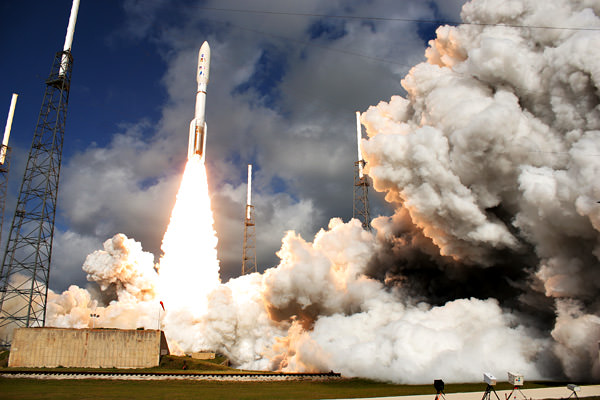
Atop a towering inferno of sparkling flames and billowing ash, Humankinds millennial long quest to ascertain “Are We Alone ?” soared skywards today (Nov. 26) with a sophisticated spaceship named ‘Curiosity’ – NASA’s newest, biggest and most up to date robotic surveyor that’s specifically tasked to hunt for the ‘Ingredients of Life’ on Mars, the most ‘Earth-like’ planet in our Solar System.
‘Mars Trek – Curiosity’s Search for Undiscovered Life’ zoomed to the heavens with today’s (Nov. 26) pulse pounding blastoff of NASA’s huge Curiosity Mars rover mounted atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 10:02 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Curiosity’s noble goal is to meticulously gather and sift through samples of Martian soil and rocks in pursuit of the tell-tale signatures of life in the form of organic molecules – the carbon based building blocks of life as we know it – as well as clays and sulfate minerals that may preserve evidence of habitats and environments that could support the genesis of Martian microbial life forms, past or present.
The Atlas V booster carrying Curiosity to the Red Planet vaulted off the launch pad on 2 million pounds of thrust and put on a spectacular sky show for the throngs of spectators who journeyed to the Kennedy Space Center from across the globe, crowded around the Florida Space Coast’s beaches, waterways and roadways and came to witness firsthand the liftoff of the $2.5 Billion Curiosity Mars Science Lab (MSL) rover.

The car sized Curiosity rover is the most ambitious, important and far reaching science probe ever sent to the Red Planet – and the likes of which we have never seen or attempted before.
“Science fiction is now science fact,” said Doug McCuistion, director of the Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters at the post launch briefing for reporters at KSC. “We’re flying to Mars. We’ll get it on the ground… and see what we find.”
“’Ecstatic’ – in a word, NASA is Ecstatic. We have started a new Era in the Exploration of Mars with this mission – technologically and scientifically. MSL is enormous, the equivalent of 3 missions frankly.”
“We’re exactly where we want to be, moving fast and cruising to Mars.”

NASA is utilizing an unprecedented, rocket powered precision descent system to guide Curiosity to a pinpoint touch down inside the Gale Crater landing site, with all six wheels deployed.
Gale Crater is 154 km (96 mi) wide. It is dominated by layered terrain and an enormous mountain rising some 5 km (3 mi) above the crater floor which exhibits exposures of minerals that may have preserved evidence of ancient or extant Martian life.
“I hope we have more work than the scientists can actually handle. I expect them all to be overrun with data that they’ve never seen before.”
“The first images from the bottom of Gale Crater should be stunning. The public will see vistas we’ve never seen before. It will be like sitting at the bottom of the Grand Canyon,” said McCuistion.
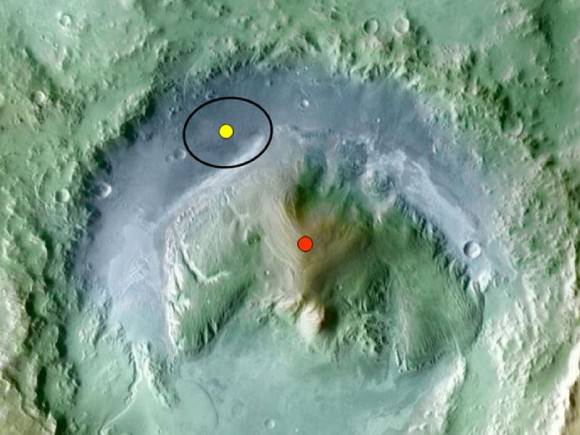
Color coding in this image of Gale Crater on Mars represents differences in elevation. The vertical difference from a low point inside the landing ellipse for NASA's Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory (yellow dot) to a high point on the mountain inside the crater (red dot) is about 3 miles (5 kilometers). Credit: NASA
The 197 ft tall Atlas booster’s powerful liquid and solid fueled engines ignited precisely on time with a flash and thunderous roar that grew more intense as the expanding plume of smoke and fire trailed behind the rapidly ascending rockets tail.
The Atlas rockets first stage is comprised of twin Russian built RD-180 liquid fueled engines and four US built solid rocket motors.
The engines powered the accelerating climb to space and propelled the booster away from the US East Coast as it majestically arced over in between broken layers of clouds. The four solids jettisoned 1 minute and 55 seconds later. The liquid fueled core continued firing until its propellants were expended and dropped away at T plus four and one half minutes.
The hydrogen fueled Centaur second stage successfully fired twice and placed the probe on an Earth escape trajectory at 22,500 MPH.

The Atlas V initially lofted the spacecraft into Earth orbit and then, with a second burst from the Centaur, pushed it out of Earth orbit into a 352-million-mile (567-million-kilometer) journey to Mars.
MSL spacecraft separation of the solar powered cruise stage stack from the Centaur upper stage occurred at T plus 44 minutes and was beautifully captured on a live NASA TV streaming video feed.
“Our spacecraft is in excellent health and it’s on its way to Mars,” said Pete Theisinger, Mars Science Laboratory Project Manager from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California at the briefing. “I want to thank the launch team, United Launch Alliance, NASA’s Launch Services Program and NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for their help getting MSL into space.”

“The launch vehicle has given us a first rate injection into our trajectory and we’re in cruise mode. The spacecraft is in communication, thermally stable and power positive.”
“I’m very happy.”
“Our first trajectory correction maneuver will be in about two weeks,” Theisinger added.
“We’ll do instrument checkouts in the next several weeks and continue with thorough preparations for the landing on Mars and operations on the surface.”
Curiosity is a 900 kg (2000 pound) behemoth. She measures 3 meters (10 ft) in length and is nearly twice the size and five times as heavy as Spirit and Opportunity, NASA’s prior set of twin Martian robots.
NASA was only given enough money to build 1 rover this time.
“We are ready to go for landing on the surface of Mars, and we couldn’t be happier,” said John Grotzinger, Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist from the California Institute of Technology at the briefing. “I think this mission will be a great one. It is an important next step in NASA’s overall goal to address the issue of life in the universe.”

Curiosity is equipped with a powerful 75 kilogram (165 pounds) array of 10 state-of-the-art science instruments weighing 15 times more than its predecessor’s science payloads.

A drill and scoop located at the end of the robotic arm will gather soil and powdered samples of rock interiors, then sieve and parcel out these samples into analytical laboratory instruments inside the rover. A laser will zap rocks to determine elemental composition.
“We are not a life detection mission.”
“It is important to distinguish that as an intermediate mission between the Mars Exploration Rovers, which was the search for water, and future missions, which may undertake life detection.”
“Our mission is about looking for ancient habitable environments – a time on Mars which is very different from the conditions on Mars today.”
“The promise of Mars Science Laboratory, assuming that all things behave nominally, is we can deliver to you a history of formerly, potentially habitable environments on Mars,” Grotzinger said at the briefing. “But the expectation that we’re going to find organic carbon, that’s the hope of Mars Science Laboratory. It’s a long shot, but we’re going to try.”
Today’s liftoff was the culmination of about 10 years of efforts by the more than 250 science team members and the diligent work of thousands more researchers, engineers and technicians spread around numerous locations across the United States and NASA’s international partners including Canada, Germany, Russia, Spain and France.
“Scientists chose the site they wanted to go to for the first time in history, because of the precision engineering landing system. We are going to the very best place we could find, exactly where we want to go.”
“I can’t wait to get on the ground,” said Grotzinger.

Complete Coverage of Curiosity – NASA’s Next Mars Rover launched 26 Nov. 2011
Read continuing features about Curiosity by Ken Kremer starting here:
Mars Trek – Curiosity Poised to Search for Signs of Life
Curiosity Rover ‘Locked and Loaded’ for Quantum Leap in Pursuit of Martian Microbial Life
Science Rich Gale Crater and NASA’s Curiosity Mars Rover in Glorious 3-D – Touchdown in a Habitable Zone
Curiosity Powered Up for Martian Voyage on Nov. 26 – Exclusive Message from Chief Engineer Rob Manning
NASA’s Curiosity Set to Search for Signs of Martian Life
Curiosity Rover Bolted to Atlas Rocket – In Search of Martian Microbial Habitats
Closing the Clamshell on a Martian Curiosity
Curiosity Buttoned Up for Martian Voyage in Search of Life’s Ingredients
Assembling Curiosity’s Rocket to Mars
Encapsulating Curiosity for Martian Flight Test
Dramatic New NASA Animation Depicts Next Mars Rover in Action
Packing a Mars Rover for the Trip to Florida; Time Lapse Video
Test Roving NASA’s Curiosity on Earth


Good article, but … aaagh, I was reminded of the James Webb type cost overruns when checking up on the science payload weight. [I thought there was a huge weight reduction at some point, but it must have been the planned european rover.]
More to the point, and I didn’t know this, the redevelopment of RTGs, since the old technology had been lost, wasn’t all too successful. Apparently it looses capacity at shocks such as EDL, and the mission has recently and perhaps silently been scaled back in scope. (As of 2011.)
“More Recent Concerns. Project managers stated that the expected performance of the rover’s power generation system, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG), has been reduced. Thermoelectric modules inside the MMRTG, which was developed and provided to NASA by the Department of Energy, convert heat (thermal energy) from the decay of a radioisotope (plutonium-238 dioxide) into electricity. Project managers attribute some of the MMRTG’s performance degradation to the natural radioactive decay that occurred during the 2-year launch delay. However, unexpected temporary reductions in the system’s power output were also noted during testing that simulated the vibration and shock that MSL will experience during its entry, descent, and landing on Mars.
Department of Energy officials stated that the power degradation issue is unlikely to cause a catastrophic failure. However, as a cautionary measure, MSL Project managers have reduced the mission’s performance capabilities to processing 28 rather than 74 soil and rock samples and to traversing 4.5 kilometers rather than 20 kilometers.”
Curiosity wouldn’t be able to climb that mountain straight up under that regime (5 km ascent)! I assume performance capabilities is under some minimum mission requirements (“cautionary” case), but it isn’t really reassuring. I hope the RTG will survive to make the usual long lived mission profiles that we are getting used to! Already 2 out of the original 14 years of RTG capacity have been lost. :-/
Scientists ideally wants to do one at least 37 km traverse. That is ~ 10 times “the mission’s performance capabilities” in the cautionary case.
For climate and mineralogical purposes, sure.
Venus has historically been seen as most Earth-like I believe, being our “twin” in size and dense atmosphere, and perhaps in later days in geology. (Crustal ‘plate’ with hot spots like the one building the Hawaiian island chain, is the latest suspicion, IIRC.)