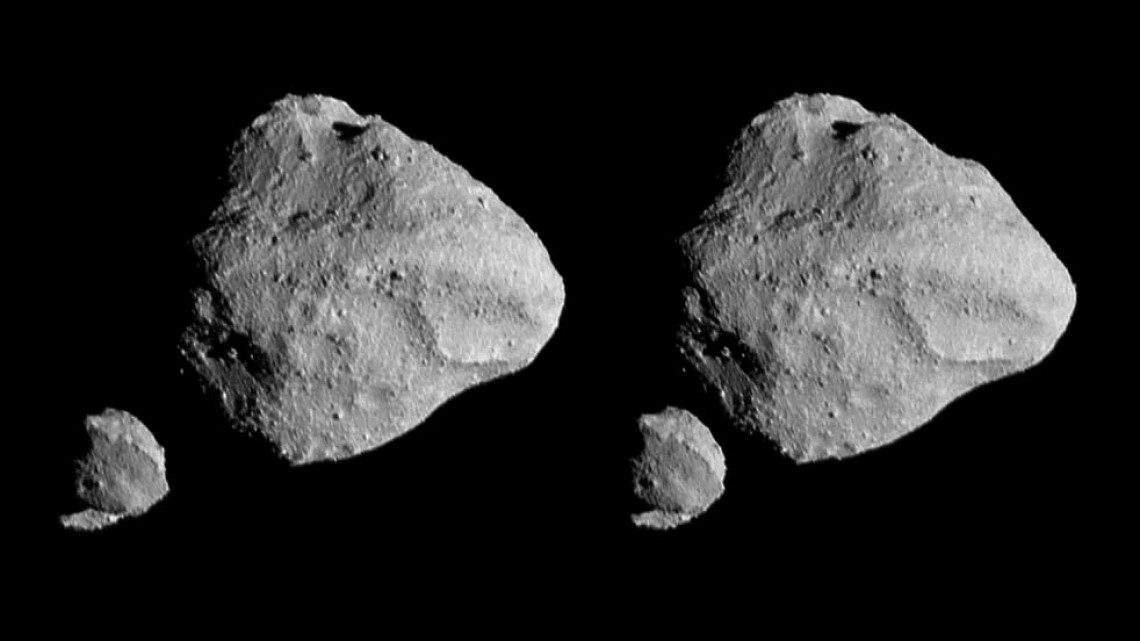
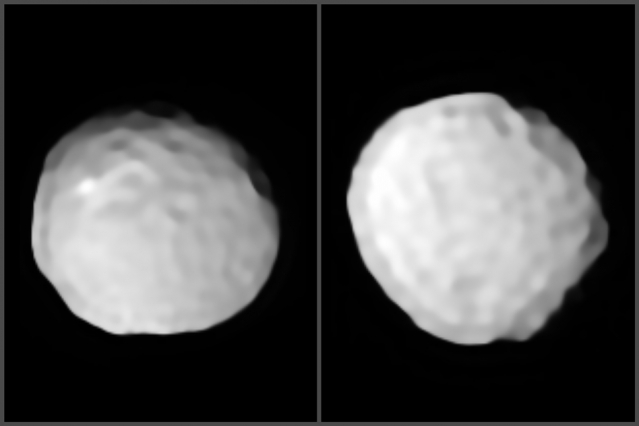
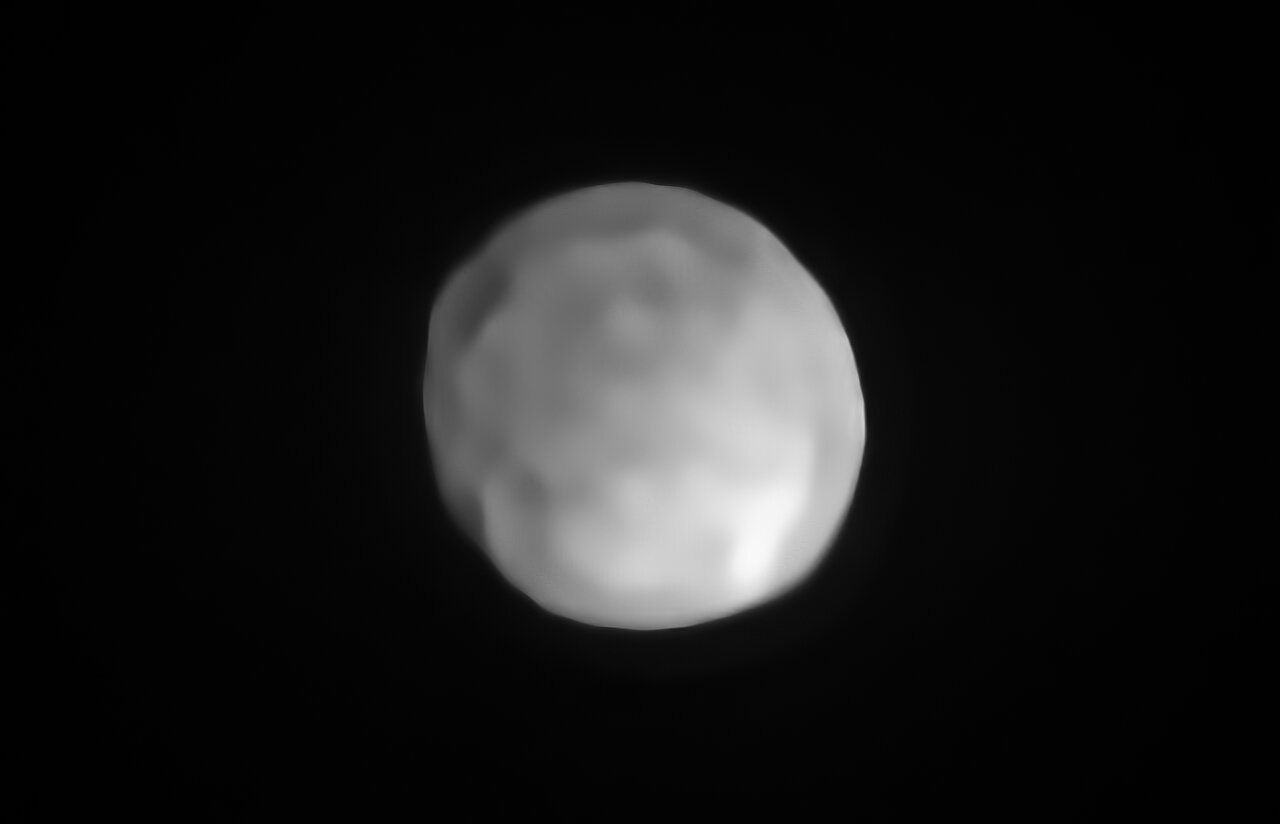
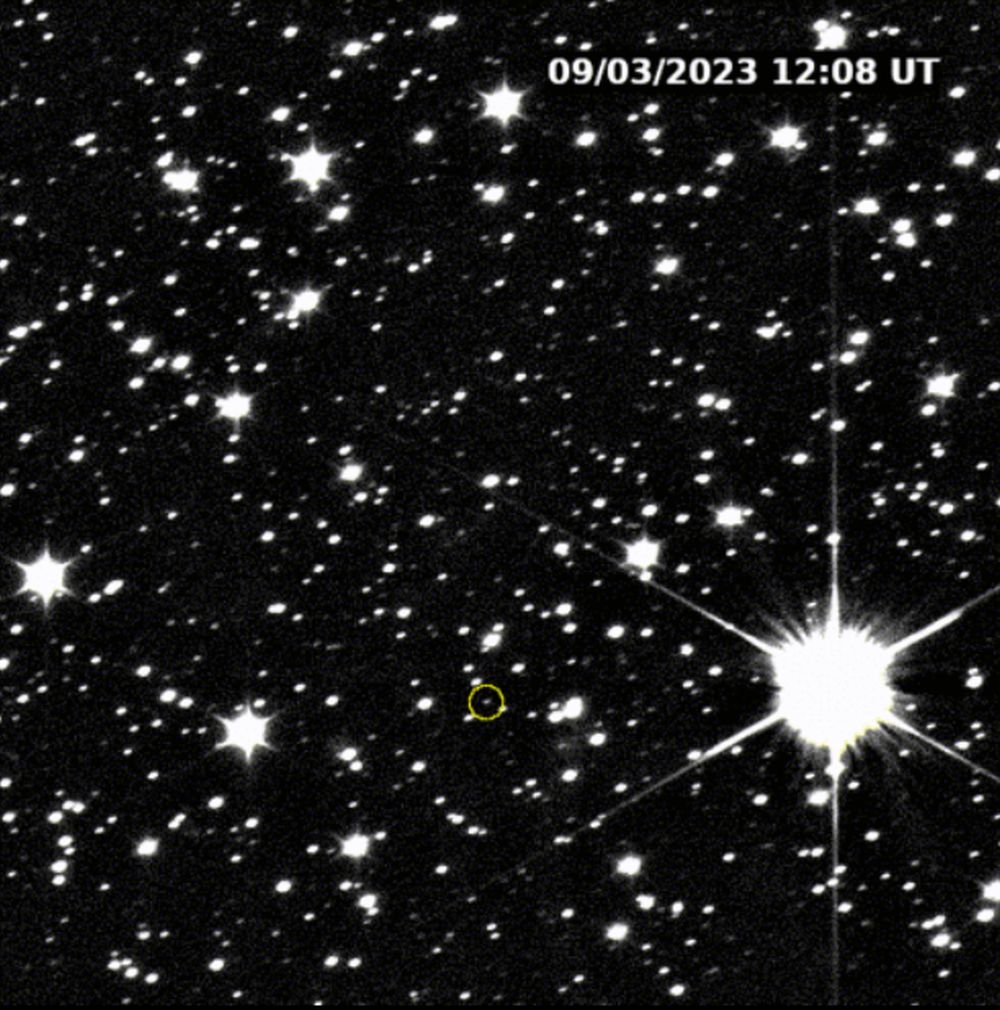
Last November, NASA’s Lucy mission conducted a flyby of the asteroid Dinkinish, one of the Main Belt asteroids it will investigate as it makes its way to Jupiter. In the process, the spacecraft spotted a small moonlet orbiting the larger asteroid, now named Selam (aka. “Lucy’s baby”). The moonlet’s name, an Ethiopian name that means “peace,” pays homage to the ancient human remains dubbed “Lucy” (or Dinkinish) that were unearthed in Ethiopia in 1974. Using novel statistical calculations based on how the two bodies orbit each other, a Cornell-led research team estimates that the moonlet is only 2-3 million years old.
Continue reading “Dinkinesh's Moonlet is Only 2-3 Million Years Old”Dinkinesh's Moonlet is Only 2-3 Million Years Old