India’s inaugural voyager to the Red Planet, the Mars Orbiter Mission or MOM, has just celebrated 100 days and 100 million kilometers out from Mars on June 16, until the crucial Mars Orbital Insertion (MOI) engine firing that will culminate in a historic rendezvous on September 24, 2014.
MOM is cruising right behind NASA’s MAVEN orbiter which celebrated 100 days out from Mars on Friday the 13th of June. MAVEN arrives about 48 hours ahead of MOM on September 21, 2014.
After streaking through space for some ten and a half months, the 1,350 kilogram (2,980 pound) MOM probe will fire its 440 Newton liquid fueled main engine to brake into orbit around the Red Planet on September 24, 2014 – where she will study the atmosphere and sniff for signals of methane.
Working together, MOM and MAVEN will revolutionize our understanding of Mars atmosphere, dramatic climatic history and potential for habitability.
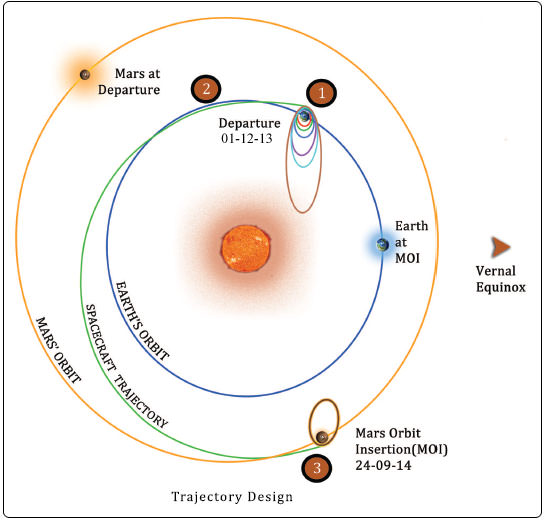
The do or die MOI burn on September 24, 2014 places MOM into an 377 km x 80,000 km elliptical orbit around Mars.
MOM was designed and developed by the Indian Space Research Organization’s (ISRO) at a cost of $69 Million and marks India’s maiden foray into interplanetary flight.
But before reaching Mars, mission navigators must keep the craft meticulously on course on its heliocentric trajectory from Earth to Mars through a series of in flight Trajectory Correction Maneuvers (TMSs).
The second TCM was just successfully performed on June 11 by firing the spacecraft’s 22 Newton thrusters for a duration of 16 seconds. TCM-1 was conducted on December 11, 2013 by firing the 22 Newton Thrusters for 40.5 seconds. Two additional TCM firings are planned in August and September 2014.
To date the probe has flown about 70% of the way to Mars, traveling about 466 million kilometers out of a total of 680 million kilometers (400 million miles) overall, with about 95 days to go. One way radio signals to Earth take approximately 340 seconds.
MOM reached the halfway mark to Mars on April 9, 2014.

ISRO reports the spacecraft and its five science instruments are healthy. It is being continuously monitored by the Indian Deep Space Network (IDSN) and NASA JPL’s Deep Space Network (DSN).
MOM’s journey began with a picture perfect blast off on Nov. 5, 2013 from India’s spaceport at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, atop the nations indigenous four stage Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) which placed the probe into its initial Earth parking orbit.
A series of six subsequent orbit raising maneuvers ultimately culminated with a liquid fueled main engine firing on Dec. 1, 2013 for the Trans Mars Injection(TMI) maneuver that successfully placed MOM on a heliocentric elliptical trajectory to the Red Planet.
If all goes well, India will join an elite club of only four who have launched probes that successfully investigated the Red Planet from orbit or the surface – following the Soviet Union, the United States and the European Space Agency (ESA).

Both MAVEN and MOM’s goal is to study the Martian atmosphere, unlock the mysteries of its current atmosphere and determine how, why and when the atmosphere and liquid water was lost – and how this transformed Mars climate into its cold, desiccated state of today.
Together, MOM and MAVEN will fortify Earth’s invasion fleet at Mars. They join 3 current orbiters from NASA and ESA as well as NASA’s pair of sister surface rovers Curiosity and Opportunity.
Although they were developed independently and have different suites of scientific instruments, the MAVEN and MOM science teams will “work together” to unlock the secrets of Mars atmosphere and climate history, MAVEN’s top scientist told Universe Today.
“We have had some discussions with their science team, and there are some overlapping objectives,” Bruce Jakosky told me. Jakosky is MAVEN’s principal Investigator from the University of Colorado at Boulder.
“At the point where we [MAVEN and MOM] are both in orbit collecting data we do plan to collaborate and work together with the data jointly,” Jakosky said.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing MOM, MAVEN, Opportunity, Curiosity, Mars rover and more planetary and human spaceflight news.

…………….
Learn more about NASA’s Mars missions, upcoming sounding rocket and Orbital Sciences Antares ISS launch from NASA Wallops, VA in July and more about SpaceX, Boeing and commercial space and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations.
June 25: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Launch (July 10) and Suborbital Rocket Launch (June 26) from Virginia” & “Space mission updates”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, evening