Are there waves on Titan’s lakes and seas? Cassini scientists say that the best chance of answering this question is with the May 23 flyby of Titan, when the Cassini spacecraft will be just 970 km (603 miles) over Titan’s biggest ‘lake,’ the northern sea named Ligeia Mare.
Lakes, seas, and rivers were discovered on Titan by Cassini in 2005, and since then, scientists and space enthusiasts have been intrigued about the possibility of what could be found in these bodies of hydrocarbon liquid. Future potential missions such as paddleboats have even been proposed.
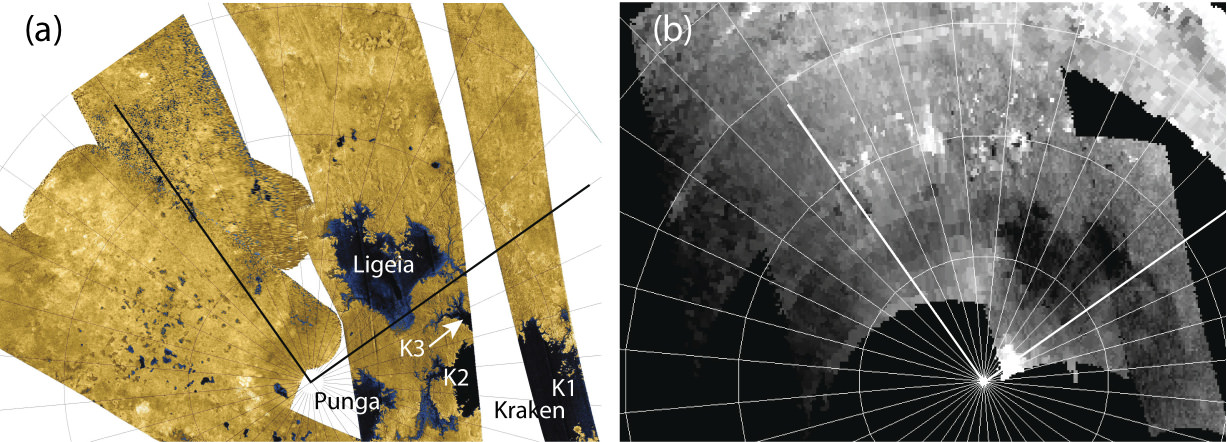
Lakes, seas and rivers of liquid hydrocarbons cover much of the Titan’s northern hemisphere. Additionally, these hydrocarbons may rain down on the surface. The questions is, are these frigid liquid bodies capable of producing wave action, or would they be a rigid type of frigid? With surface temperature at -178 degrees Celsius (-289 degrees Fahrenheit), Titan’s environment is too cold for life as we may know it, but its environment, rich in the building blocks of life, is of great interest to astrobiologists.
Additionally, new models of Titan’s atmosphere prediction that as the seasons change in Titan’s northern hemisphere, waves could ripple across the moon’s hydrocarbon seas, and possibly even hurricanes could begin to swirl over these areas, too. The model predicting waves tries to explain data from the moon obtained so far by Cassini.
“If you think being a weather forecaster on Earth is difficult, it can be even more challenging at Titan,” said Scott Edgington, Cassini’s deputy project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. “We know there are weather processes similar to Earth’s at work on this strange world, but differences arise due to the presence of unfamiliar liquids like methane. We can’t wait for Cassini to tell us whether our forecasts are right as it continues its tour through Titan spring into the start of northern summer.”
For the flyby on May 23, the altimetry data that will be collected by the radar instrument could show whether the surface of that sea is thick like molasses or as thin as liquid water on Earth.
In addition, radar will look for changes in small northern lakes last observed in previous flybys, the T-16 and T-19 flybys.
This flyby is a carefully planned sibling of the following flyby; the combination of the data from T-91 and T-92 will provide stereo views of the same geography, which will tell us about the depth of the lake walls.
Stay tuned! See the Cassini flyby page for more info, and read more about the new models of Titan’s atmosphere here.


Very exciting, I can’t wait for the pictures from Cassini’s flyby tomorrow to come in. Surf’s up!
Titan has no geothermal energy? Not even from being stretched as it passes by Jupiter?
Saturn!