Don’t let them pass you by. Right now and continuing through July, the biggest and brightest asteroids will be running on nearly parallel tracks in the constellation Virgo and so close together they’ll easily fit in the same binocular field of view. The twofer features Ceres (biggest) and Vesta (brightest) which are also the prime targets of NASA’s Dawn Mission. Now en route to a Ceres rendezvous next February, Dawn orbited Vesta from July 2011 to September 2012 and sent back spectacular photos of two vast impact basins, craters stained black by carbon-rich asteroids and parallel troughs that stretch around the 330-mile-wide world like rubber bands.
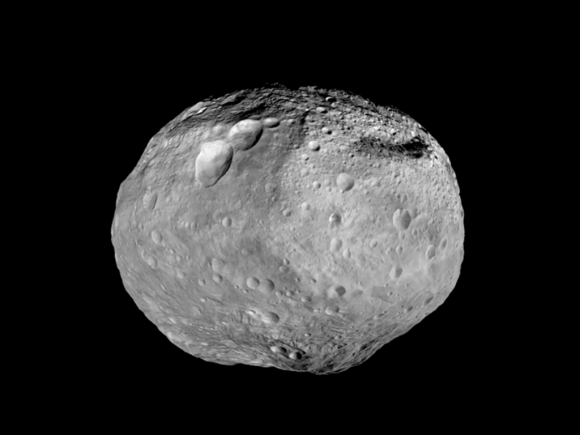

Astronomers used Dawn’s gravity data to discover Vesta is more like a planet than anyone had supposed. Deep beneath its crust, composed of lighter minerals, lies a denser iron core. Most asteroids were too small to generate enough interior heat through the decay of radioactive elements to melt and “differentiate” into core, mantle and crust like the terrestrial planets. Thanks to our new understanding, you’ll hear Vesta referred to as a ‘baby planet’.
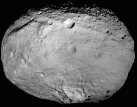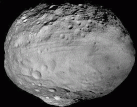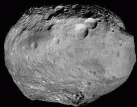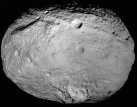
Studies of its crustal rocks showed a match to a clan of basaltic meteorites called howardites, eucrites and diogenites. Many of these formerly volcanic rocks that trace their origin to Vesta are found in numerous private and institutional collections. With a little homework, you can even buy a slice of Vesta on eBay, making for one of the least expensive sample return missions ever undertaken.
Dawn’s Greatest Hits at Vesta – A quick summary of key discoveries accompanied by electric guitar
While Vesta is a rocky body, Ceres shows telltale signs of water and iron-rich clay. Like Vesta, it also appears to have cooked itself into denser core and lighter crust. Because Ceres is less dense than Earth, astronomers believe water ice may be buried beneath its dusty crust.

Earlier this year, astronomers working with the Herschel Space Telescope announced the discovery of plumes of water vapor blasting from two regions on the dwarf planet’s surface. While Ceres is an asteroid it’s also a member of a select group of dwarf planets, bodies large enough to have crunched themselves into spheres through their own gravity but not big enough to clear the region they orbit of smaller asteroids.

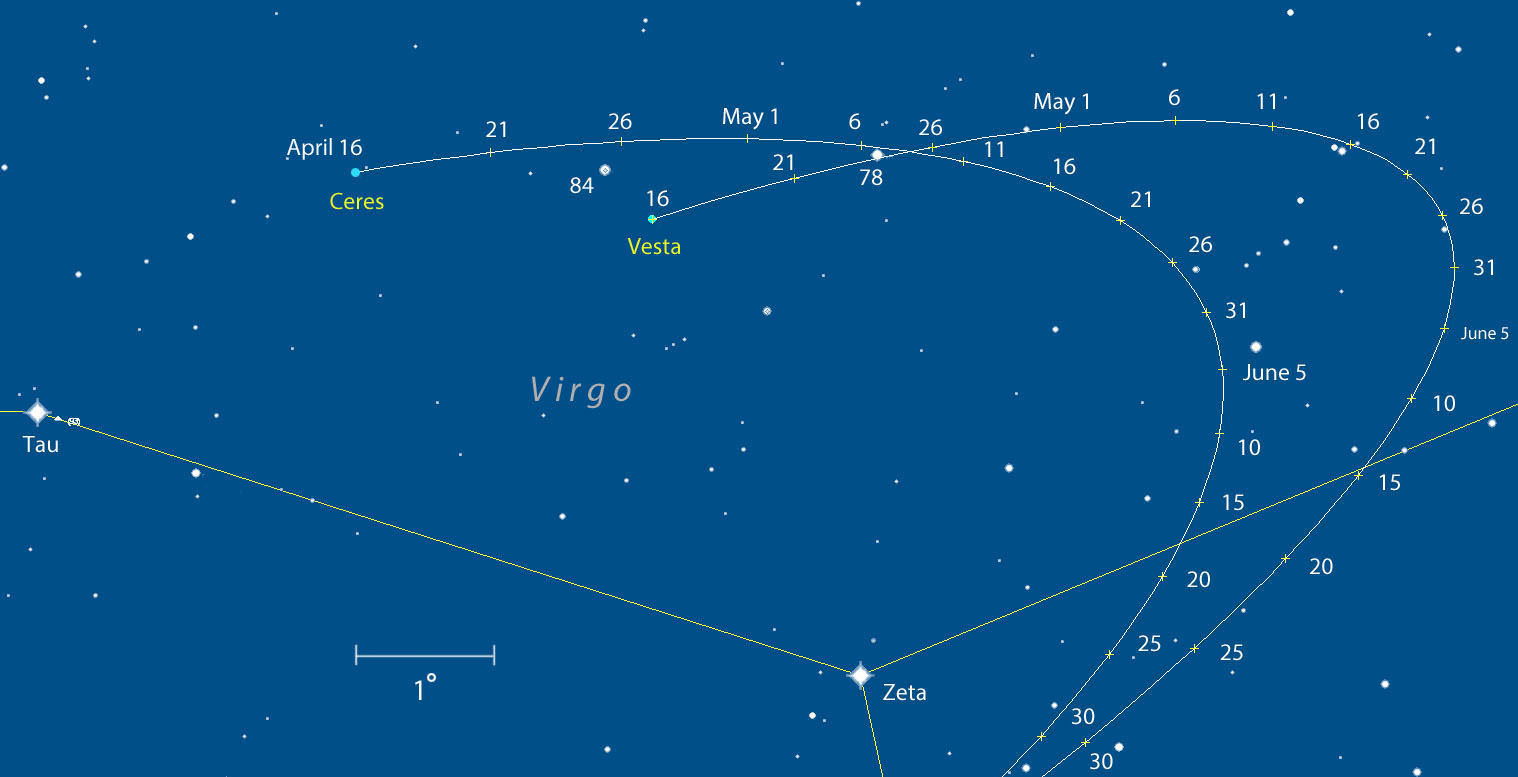
Ceres and Vesta will be gradually drawing closer in the coming weeks and months until on July 5 only 10 arc minutes (one-third the diameter of a full moon) will separate them. They’ll also be fading, but not so much that binoculars won’t show them throughout this excellent dual apparition. Vesta will only dim to magnitude +7 by July 1, Ceres to 8.4. Come mid-June I’ll return with a detailed map showing how best to see the dynamic duo during their close conjunction.
Sure, both Ceres and Vesta look exactly like stars even in large amateur telescopes, but sampling photons from real asteroids while listening to the sound of frogs on a spring night is my idea of a good time. Maybe yours too. Good luck!

2015 will be a great year for space exploration. Ceres and Pluto!