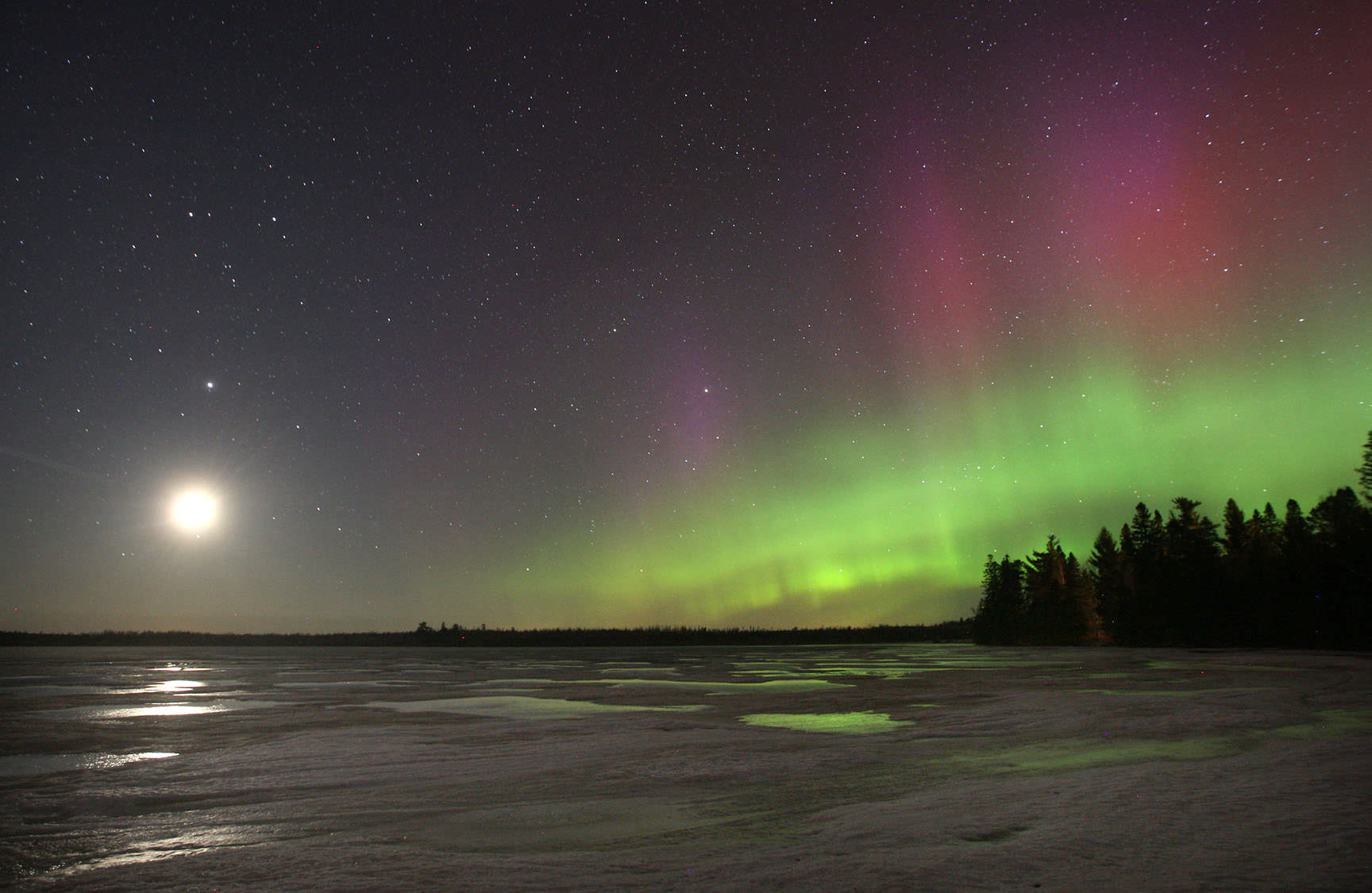
Expect the unexpected when it comes to northern lights. Last night beautifully illustrated nature’s penchant for surprise. A change in the “magnetic direction” of the wind of particles from the sun called the solar wind made all the difference. Minor chances for auroras blossomed into a spectacular, night-long storm for observers at mid-northern latitudes.
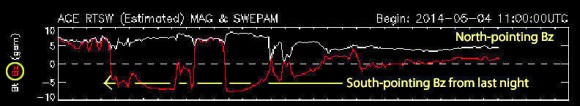
Packaged with the sun’s wind are portions of its magnetic field. As that material – called the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) – sweeps past Earth, it normally glides by, deflected by our protective magnetic field, and we’re no worse for the wear. But when the solar magnetic field points south – called a southward Bz – it can cancel Earth’s northward-pointing field at the point of contact, opening a portal. Once linked, the IMF dumps high-speed particles into our atmosphere to light up the sky with northern lights.

Spiraling down magnetic field lines like firefighters on firepoles, billions of tiny solar electrons strike oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the thin air 60-125 miles up. When the excited atoms return back to their normal rest states, they shoot off niblets of green and red light that together wash the sky in multicolor arcs and rays. Early yesterday evening, the Bz plot in the ACE satellite data dipped sharply southward (above), setting the stage for a potential auroral display.

Nothing in the space weather forecast would have led you to believe northern lights were in the offing for mid-latitude skywatchers last night. Maybe a small possibility of a glow very low on the northern horizon. Instead we got the full-blown show. Nearly every form of aurora put in an appearance from multi-layered arcs spanning the northern sky to glowing red patches, crisp green rays and the bizarre flaming aurora. “Flames” look like waves or ripples of light rapidly fluttering from the bottom to the top of an auroral display. Absolutely unearthly in appearance and yet only 100 miles away.
VLF Auroral Chorus by Mark Dennison
I even broke out a hand-held VLF (very low frequency) radio and listened to the faint but crazy cosmic sounds of electrons diving through Earth’s magnetosphere. When my electron-jazzed brain finally hit the wall at 4 a.m., flames of moderately bright aurora still rippled across the north.
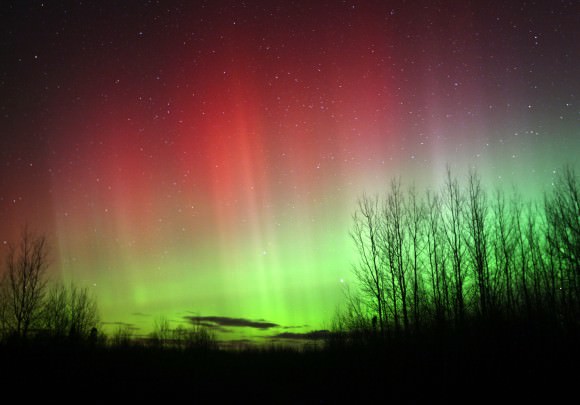


So what about tonight? Just like last night, there’s only a 5% chance of a minor storm. Take a look anyway – nature always has a surprise or two up her sleeve.

