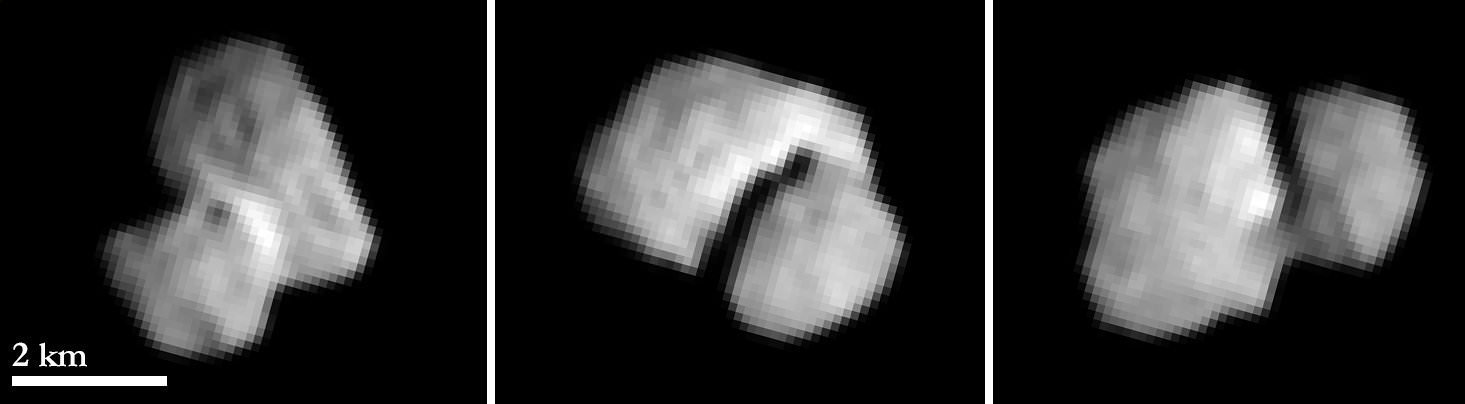
Rosetta’s “rubber duckie” comet appears to be wearing a collar! New images of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko from the spacecraft, which is speeding towards an orbit of the comet next month, show that the “neck” region of the nucleus appears to be brighter than the rest.
Last week, images from the spacecraft revealed that the comet likely has a “contact binary” nucleus, meaning that there are two parts of the nucleus that are just barely joined together under low gravity. There are many theories for why this happened, but it will take a closer examination to begin to come up with answers. The shape of the nucleus reminds many of a rubber duckie.
As for why the “neck” region appears brighter, that’s not known right now. There could be different grains in that region of the nucleus, or it could be some feature of the surface. Or perhaps it is a different type of material there. The scientists plan to get more spectral information from this region in the coming weeks, which could reveal what elements are there.
“Even though the images taken from a distance of 5500 kilometers are still not highly resolved, the scientists feel remotely reminded of comet 103P/Hartley,” stated the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research.
“This body was visited in a flyby by NASA’s EPOXI mission in 2010. While Hartley’s ends show a rather rough surface, its middle is much smoother. Scientists believe this waist to be a gravitational low: since it contains the body’s center of mass, emitted material that cannot leave the comet’s gravitational field is most likely to be re-deposited there.”
Rosetta is expected to arrive at the comet on August 6, and to send out its spider-like lander (Philae) in November. The spacecraft will remain with the comet through its closest approach to the sun in 2015, between the orbits of Earth and Mars.

If it indicates a higher contration of ice, it could be a good hint about the reason why the comet got shaped that way and why some comet so easily dislocate. Some zones might melt through much more easily and dig ravines until the comet breaks or collapse to a new stable shape.