NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) orbiter is oh-so-close to its destination after a 10-month journey. It's scheduled to arrive in orbit Sunday (Sept. 21) around 9:50 p.m. EDT (1:50 a.m. UTC) if all goes well, but there are a few things that need to happen, in order, first.
One big obstacle is already out of the way. MAVEN controllers had expected to do final engine burn tweaks to put it on the right trajectory, but the mission is so on-target that it won't be needed.
"#MAVEN orbit insertion sequence has been activated on the s/c. No additional ground intervention is needed to enter #Mars' orbit on Sunday," the official account tweeted yesterday (Sept. 18).
So what does the sequence entail? MAVEN will need to turn on its six thruster engines for a 33-minute braking maneuver to slow it down. This will allow the gravity of Mars to "capture" the spacecraft into an elliptical or oval-shaped orbit.
Should that all go safely, MAVEN still has a lot of work to do before being ready to capture information about the upper atmosphere of the Red Planet. All spacecraft go through a commissioning phase to ensure their instruments are working correctly and that they are in the correct orbit and orientation to do observations.
As such, controllers will spend about six weeks moving MAVEN into a more circular orbit and testing out its instruments. Usually this period is done without interruption, but NASA wants to
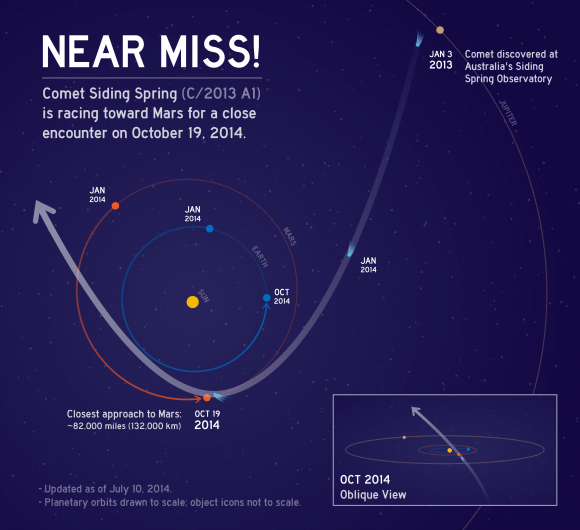
capture information when Comet Siding Spring comes whizzing by Mars
Oct. 19.
Controllers are interested in learning about the comet and its effect on the upper atmosphere, so they will stop the commissioning to make those measurements. MAVEN will also be oriented in such a way that its solar panels are protected as much as possible from the dust, although scientists now believe the risk of strikes is very low.
[caption id="attachment_114353" align="alignnone" width="580"]
This graphic depicts the orbit of comet C/2013 A1 Siding Spring as it swings around the sun in 2014. On Oct. 19, 2014 the comet will have a very close pass at Mars. Its nucleus will miss Mars by about 82,000 miles (132,000 kilometers). Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech[/caption]
MAVEN is expected to work at Mars for a year, but investigators are hoping it will be for longer so that the atmosphere can be tracked through more of a solar cycle. The Sun's activity is a major influencer on the atmosphere and the "stripping" of molecules from it over time, which could have thinned Mars' atmosphere in the ancient past.
The spacecraft will also serve as a backup communications and data relay for the Opportunity and Curiosity rovers on the surface, which might be needed if some of the older NASA Mars spacecraft that fulfill that function experience technical difficulties.
 Universe Today
Universe Today