The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation is one of the greatest discoveries of modern cosmology. Astrophysicist George Smoot once likened its existence to “seeing the face of God.” In recent years, however, scientists have begun to question some of the attributes of the CMB. Peculiar patterns have emerged in the images taken by satellites such as WMAP and Planck – and they aren’t going away. Now, in a paper published in the December 1 issue of The Astronomical Journal, one scientist argues that the existence of these patterns may not only imply new physics, but also a revolution in our understanding of the entire Universe.
Let’s recap. Thanks to a blistering ambient temperature, the early Universe was blanketed in a haze for its first 380,000 years of life. During this time, photons relentlessly bombarded the protons and electrons created in the Big Bang, preventing them from combining to form stable atoms. All of this scattering also caused the photons’ energy to manifest as a diffuse glow. The CMB that cosmologists see today is the relic of this glow, now stretched to longer, microwave wavelengths due to the expansion of the Universe.
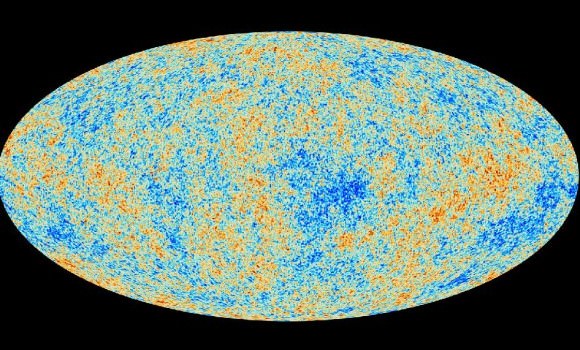
As any fan of the WMAP and Planck images will tell you, the hallmarks of the CMB are the so-called anisotropies, small regions of overdensity and underdensity that give the picture its characteristic mottled appearance. These hot and cold spots are thought to be the result of tiny quantum fluctuations born at the beginning of the Universe and magnified exponentially during inflation.

Given the type of inflation that cosmologists believe occurred in the very early Universe, the distribution of these anisotropies in the CMB should be random, on the order of a Gaussian field. But both WMAP and Planck have confirmed the existence of certain oddities in the fog: a large “cold spot,” strange alignments in polarity known as quadrupoles and octupoles, and, of course, Stephen Hawking’s initials.
In his new paper, Fulvio Melia of the University of Arizona argues that these types of patterns (Dr. Hawking’s signature notwithstanding) reveal a problem with the standard inflationary picture, or so-called ΛCDM cosmology. According to his calculations, inflation should have left a much more random assortment of anisotropies than the one that scientists see in the WMAP and Planck data. In fact, the probability of these particular anomalies lining up the way they do in the CMB images is only about 0.005% for a ΛCDM Universe.
Melia posits that the anomalous patterns in the CMB can be better explained by a new type of cosmology in which no inflation occurred. He calls this model the R(h)=ct Universe, where c is the speed of light, t is the age of the cosmos, and R(h) is the Hubble radius – the distance beyond which light will never reach Earth. (This equation makes intuitive sense: Light, traveling at light speed (c) for 13.7 billion years (t), should travel an equivalent number of light-years. In fact, current estimates of the Hubble radius put its value at about 13.4 billion light-years, which is remarkably close to the more tightly constrained value of the Universe’s age.)
R(h)=ct holds true for both the standard cosmological scenario and Melia’s model, with one crucial difference: in ΛCDM cosmology, this equation only works for the current age of the Universe. That is, at any time in the distant past or future, the Universe would have obeyed a different law. Scientists explain this odd coincidence by positing that the Universe first underwent inflation, then decelerated, and finally accelerated again to its present rate.
Melia hopes that his model, a Universe that requires no inflation, will provide an alternative explanation that does not rely on such fine-tuning. He calculates that, in a R(h)=ct Universe, the probability of seeing the types of strange patterns that have been observed in the CMB by WMAP and Planck is 7–10%, compared with a figure 1000 times lower for the standard model.
So, could this new way of looking at the cosmos be a death knell for ΛCDM? Probably not. Melia himself cites a few less earth-shattering explanations for the anomalous signals in the CMB, including foreground noise, statistical biases, and instrumental errors. Incidentally, the Planck satellite is scheduled to release its latest image of the CMB this week at a conference in Italy. If these new results show the same patterns of polarity that previous observations did, cosmologists will have to look into each possible explanation, including Melia’s theory, more intensively.

And red shift?
Not sure what you mean, but you might be confusing expansion with inflation.
There is clearly something fundamentally wrong with the current dark energy dark matter model, (yet it is also oddly right sometimes). I am glad to see others investigating some of the issues in Cosmology.
The paper is fairly simple too, which is another plus.
Can’t wait to see more of the Plank data!
So, if inflation didn’t happen, how do we explain the idea that there is more Universe outside of the Hubble Volume?
…Or is this person saying the Hubble Volume is all that exists?