At first glance, you wouldn’t think Hawaii has any connection at all with asteroid 2004 BL86, the one that missed Earth by 750,000 miles (1.2 million km) just 3 days ago. One’s a tropical paradise with nightly pig roasts, beaches and shave ice; the other an uninhabitable ball of bare rock untouched by floral print swimsuits.
But Planetary Science Institute researchers Vishnu Reddy and Driss Takir would beg to differ.
Using NASA’s Infrared Telescope Facility on Mauna Kea, Hawaii they discovered that the speedy “space mountain” has a composition similar to the very island from which they made their observations – basalt.
“Our observations show that this asteroid has a spectrum similar to V-type asteroids,” said Reddy. “V-type asteroids are basalt, similar in composition to lava flows we see in Hawaii.
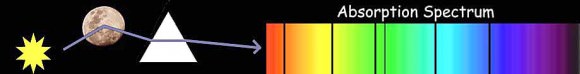
The researchers used a spectrograph to study infrared sunlight reflected from 2004 BL86 during the flyby. A spectrograph splits light into its component colors like the deli guy slicing up a nice salami. Among the colors are occasional empty spaces or what astronomers call absorption lines, where minerals such as olivine, pyroxene and plagioclase on the asteroid’s surface have removed or absorbed particular slices of sunlight.
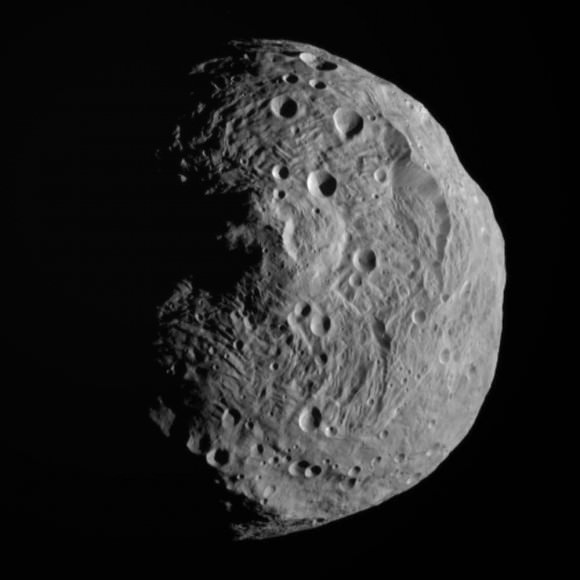

These are the same materials that not only compose earthly basalts – all that dark volcanic rock that underlies Hawaii’s reefs and resorts – but also Vesta, considered the source of V-type asteroids. It’s thought that the impact that hollowed out the vast Rheasilvia crater at Vesta’s south pole blasted chunks of mama asteroid into space to create a family of smaller siblings called vestoids.
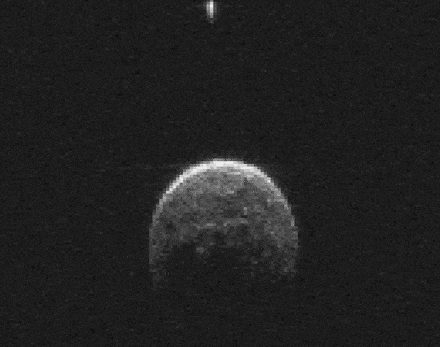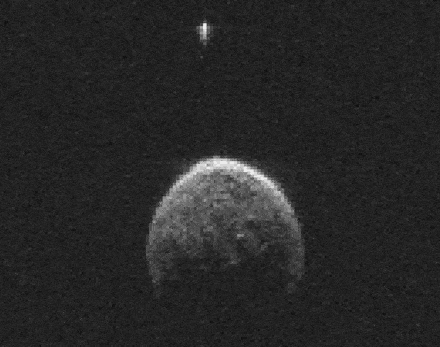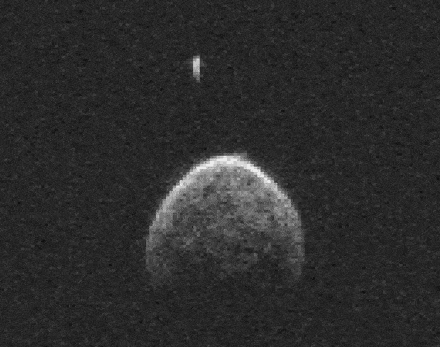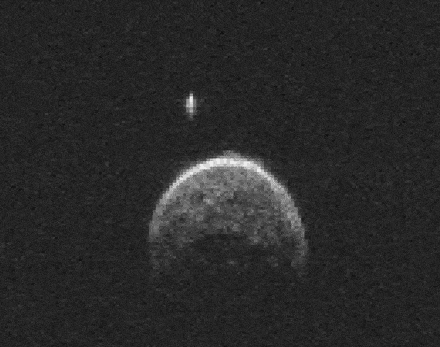
So it would appear that 2004 BL86 could be a long-lost daughter born through impact and released into space to later be perturbed by Jupiter into an orbit that periodically brings it near Earth. Close enough to watch in wonder as it inches across the field of view of our telescopes like it did earlier this week.
The little moonlet may or may not be related to Vesta, but its presence makes 2004 BL86 a binary asteroid, where each object revolves about their common center of gravity. While the asteroid is unlikely to become future vacation destination, there will always be Hawaii to satisfy our longings for basalt.
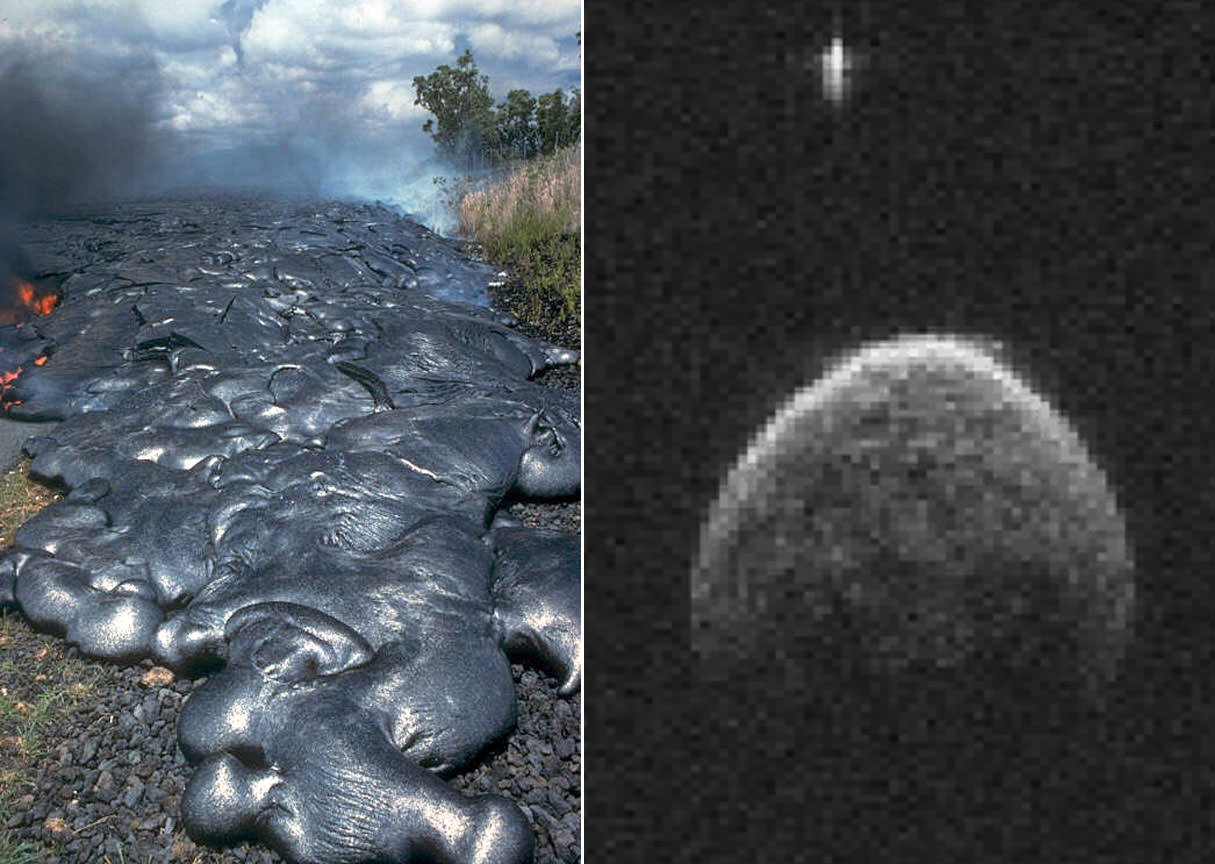


Bob, do you have any information about the orbital period of the small moon around the asteroid?
Hi Tihomir,
I’ve asked but not yet gotten an answer. Will post here and in the story when I do.
Tihomir,
Just found out. It’s 13.80 hours +/-0.05 hour
Thanks Bob – is the info from the Goldstone radar guys?
Tihomir,
Yes it is.
Thanks Bob!
I always find it hard to interpret radar images. They look nearly like photographs and that’s enough to throw off my intuition. Are there ways of transforming radar imagery into, say, 3d models?
This sphere shaped Vestoid 204 BL86 was probably molten after the impact on Vesta and being liquid before it hardened into the solid basalt it is today is probably the reason why it is an almost perfect sphere (like a hardened raindrop) Thanks Bob yet another great topic…
UFOs,
I think you make a good point and one I wondered about myself.
Earlier you mentioned you were going to attempt a viewing of this asteroid.. Any luck?
http://www.universetoday.com/118187/big-asteroid-2004-bl86-buzzes-earth-on-january-26-how-to-see-it-in-your-telescope/