Returning to the Moon has been the fevered dream of many scientists and astronauts. Ever since the Apollo Program culminated with the first astronauts setting foot on the Moon on July 20th, 1969, we have been looking for ways to go back to the Moon… and to stay there. In that time, multiple proposals have been drafted and considered. But in every case, these plans failed, despite the brave words and bold pledges made.
However, in a workshop that took place in August of 2014, representatives from NASA met with Harvard geneticist George Church, Peter Diamandis from the X Prize Foundation and other parties invested in space exploration to discuss low-cost options for returning to the Moon. The papers, which were recently made available in a special issue of New Space, describe how a settlement could be built on the Moon by 2022, and for the comparatively low cost of $10 billion.
Put simply, there are many benefits to establishing a base on the Moon. In addition to providing refueling stations that would shave billions off of future space missions – especially to Mars, which are planned for the 2030s – they would provide unique opportunities for scientific research and the testing of new technologies. But plans to build one have consistently been hampered by two key assumptions.

The first is that funding is the largest hurdle to overcome, which is understandable given the past 50 years of space mission costs. To put it in perspective, the Apollo Program would cost taxpayers approximately $150 billion in today’s dollars. Meanwhile, NASA’s annual budget for 2015 was approximately $18 billion, while its 2016 is projected to reach $19.3 billion. In the days when space exploration is not a matter of national security, money is sure to be more scarce.
The second assumption is that a presidential mandate to “return to the Moon to stay” is all that is needed overcome this problem and make the necessary budgets available. But despite repeated attempts, no mandate for renewed lunar or space exploration has resolved the issue. In short, space exploration is hampered by conventional thinking that assumes massive budgets are needed and that administrations simply need to make them available.
In truth, a number of advances that have been made in recent years are allowing for missions that would cost significantly less. This, and how a lunar base could be a benefit to space exploration and humanity, were the topics of discussion at the 2014 workshop. As NASA astrobiologist Chris McKay – who edited the New Space journal series – told Universe Today via email, one of the key benefits of a cost-effective base on the Moon is that it will bring other missions into the realm of affordability.
“I am interested in a long term research base on Mars – not just a short term human landing,” he said. “Establishing a research base on the Moon shows that we know how to do that and can do it in a sustainable way. We have to get away from the current situation where costs are so high that a base on the Moon, a human mission to Mars, and a human mission to an asteroid are all mutually exclusive. If we can drive the costs down by 10x or more then we can do them all.”

Central to this are several key changes that have taken place over the past decade. These include the development of the space launch business, which has led to an overall reduction in the cost of individual launches. The emergence of the NewSpace industry – i.e. a general term for various private commercial aerospace ventures – is another, which has been taking recent advances in technology and finding applications for them in space.
According to McKay, these and other technological developments will help resolve the budget issue. “Beyond the launch costs, they key to driving down the costs for a base on the Moon is to make use of technologies for sustainability being developed on Earth. My favorite examples are 3D printing, electric-cars, autonomous robots, and recycling toilets (like the blue diversion toilet).”
Alexandra Hall, the former Senior Director of the X Prize Foundation and one of the series’ main authors, also expressed the importance of emerging technologies in making this lunar base functional. As she told Universe Today via email, these will have significant benefits here on Earth, especially in the coming decades where rises in population will coincide with diminishing resources.
“The advances in life support and closed loop living necessary for sustaining life for long periods on the Moon will undoubtedly provide positive spin offs that benefit both the environment and our ability to live with changing climate and diminishing resources,” she said. “If we can figure out how to build structures with what’s already on the Moon, we can use that technology to help us create infrastructure and shelter solutions out of in-situ materials on Earth. If we can use rock that’s right there, perhaps we can avoid shipping asphalt and bricks across the world!”
Another important aspect of making a lunar base cost-effective was the potential for international partnerships, as well as those between the private and public sectors. As Hall explained it:
“While there will be commercial markets for the eventual fruits of our lunar exploration endeavors, the initial markets are likely to be dominated by governments. The private sector is best able to respond in ways that provide cost effective and competitive solutions when governments specify and commit to long term exploration goals. I believe that a Google Lunar XPRIZE win will flush out other private and commercial partners for pursuing a permanent settlement on the Moon, that could eclipse the need for significant government participation. Once a small company demonstrates that it is actually possible to get to the Moon and be productive, that allows others to start to plan new business and endeavors.”
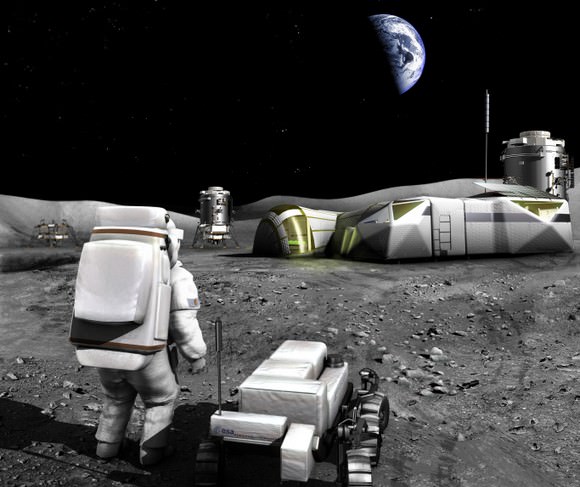
As for where this base will go and what it will do, that is described in the preface article, “Toward a Low-Cost Lunar Settlement“. In essence, the proposed lunar base would exist at one of the poles and would be modeled on the U.S. Antarctic Station at the South Pole. It would be operated by NASA or an international consortium and house a crew of about 10 people, a mix of staff and field scientists that would be rotated three times a year.
Activities on the base, which would be assisted by autonomous and remotely-operated robotic devices, would center on supporting field research, mainly by graduate students doing thesis work. Another key activity for the residents would be testing technologies and program precedents which could be put to use on Mars, where NASA hopes to be sending astronauts in the coming decades.

Several times over in the series, it is stressed that this can be done for the relatively low cost of $10 billion. This overall assessments is outlined in the paper titled “A Summary of the Economic Assessment and Systems Analysis of an Evolvable Lunar Architecture That Leverages Commercial Space Capabilities and Public–Private Partner“. As it concludes:
“Based on the experience of recent NASA program innovations, such as the COTS program, a human return to the Moon may not be as expensive as previously thought. The United States could lead a return of humans to the surface of the Moon within a period of 5–7 years from authority to proceed at an estimated total cost of about $10 billion (–30%) for two independent and competing commercial service providers, or about $5 billion for each provider, using partnership methods.”
Other issues discussed in the series are the location of the base and the nature of its life-support systems. In the article titled “Site Selection for Lunar Industrialization, Economic Development, and Settlement“, the case is made for a base located in either the northern or southern polar region. Written by Dennis Whigo, founder and CEO of Skycorp, the article identifies two potential sites for a lunar base, using input parameters developed in consultation with venture capitalists.
These include the issues of power availability, low-cost communications over wide areas, availability of possible water (or hydrogen-based molecules) and other resources, and surface mobility. According to these assessments, the northern polar region is a good location because of its ample access to solar power. The southern pole is also identified as a potential site (particularly in the Shackleton Crater) due to the presence of water ice.

Last, but certainly not least, the series explores the issue of economic opportunities that could have far-ranging benefits for people here on Earth. Foremost among these is the potential for creating space solar power (SSP), a concept which has been explored as a possible solution to humanity’s reliance on fossil fuels and the limits of Earth-based solar power.
Whereas Earth-based solar collectors are limited by meteorological phenomena (i.e. weather) and Earth’s diurnal cycle (night and day), solar collectors placed in orbit would be able to collect energy from the Sun around the clock. However, the issues of launch and wireless energy transmission costs make this option financially unattractive.
But as is laid out in “Lunar-Based Self-Replicating Solar Factory“, establishing a factory on the Moon could reduce costs by a factor of four. This factory could build solar power satellites out of lunar material, using a self-replicating system (SRS) able to construct replicas of itself, then deploy them into geostationary Earth orbit via a linear electromagnetic accelerator (aka. Mass Driver).
An overriding theme in the series is how a lunar base would present opportunities for cooperation, both between the private and public sectors and different nations. The ISS is repeatedly used an example, which has benefited greatly in the past decade from programs like NASA’s Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) – which has been very successful at acquiring cost-effective transportation service to the station.
It is therefore understandable why NASA and those companies that have benefited from COTS want to extend this model to the Moon – in what is often referred to as Lunar Commercial Orbital Transfer Services (LCOTS) program. Aside from establishing a human presence on the Moon, this endeavor is being undertaken with the knowledge that it will also push the development of technologies and capabilities that could lead to an affordable to Mars in the coming years.
It sure is an exciting idea: returning to the Moon and laying the groundwork for a permanent human settlement there. It is also exciting when considered in the larger context of space exploration, how a base on the Moon will help us to reach further into space. To Mars, to the Asteroid Belt, perhaps to the outer Solar System and beyond.
And with each step, the opportunities for resource utilization and scientific research will expand accordingly. It may sounds like the stuff of dreams; but then again, so did the idea of putting a man on the Moon before the end of the 1960s. If there’s one thing that particular experience taught us, it’s that setting foot on another world leaves lasting footprints!

Further Reading: New Space


My biggest worry is that whoever decides on the location of the moon base has watched too many Sci-Fi movies and decides to start a city in plain view of Earth near the moon’s equator. While this seems like a good idea, it’s actually one of the worse places for a base. It would be subject to extreme temperatures and radiation. And may not be near any water. One of the benefits to having a base on the moon is so that we can mine the moon’s resources to produce parts and supplies for future missions into deep space, like Mars. Deep under ground in a polar crater where the sun never shines might be one of the best places to build a base. We’ll see how much politics or smarts NASA has with locating the base.
None of these plans are built around an equatorial location. They selected the northern and southern poles as ideal locations. There’s abundant water in the Shackleton Crater and temperature variations are less at the poles. The LRO mission is also mapping radiation exposure for precisely this reason. And because the south pole is deeply cratered, it offers access to deeper layers of the Moon.
This is all very well but, these days, any legitimate large project must submit a “Risk Analysis” that forces proponents to systematically and honestly examine the proposed undertaking through a lens that isn’t entirely constructed from brittle rosy-tinted material. There a countless reasons for NOT going to the Moon or to Mars, but these are never considered during the course of NASA “workshops”, or in the articles that then appear on Universe Today. The reasons are scientific, technological, political, budgetary, environmental, ethical, etc. The fact that the “let’s move out into space” concept has not been subjected to a serious Risk Analysis simply illustrates that it is not meant to be taken seriously. Let’s face it – there will be no moon base by 2022 (six years from now!!!) or, probably, any time in this century. It’s fun to look at lurid illustrations and to fantasize about walking around on the Moon. But it won’t happen, at least not in any current lifetime. For now, it’s not worth doing, it’s too expensive, it’s too dangerous, there are too many higher priorities, and there isn’t enough support from the public.
Actually, risk analysis is a major factor in any such consideration. In fact, none of these assessments would ever get off the ground if they were ignoring the inherent risks, as you claim they were. In all the research papers, radiation, supplies, transport, construction, resources, and health and safety were considered at length. Perhaps you should read them to get a better idea of what was actually considered.
If that’s the case, why aren’t they mentioned in the article (which is, frankly, just another breathless puff-piece)?
Anyway, Risk Analysis is not just about things that could go wrong. It’s also about cost/benefit and alternatives. Thus, for example, it is often claimed that a lunar base would be great for doing high-end science (e.g., using various kinds of telescopes). I am convinced that such claims would never survive a serious/honest analysis. The ISS is a great example of this: the claims were grandiose, the cost has been gigantic, and the scientific payoff minimal. Suppose you had a few hundred billion dollars (the real cost of a lunar base) to spend on fundamental research (dark matter/energy, GUTs, etc.). Would you spend any of it on a trip to the Moon? Of course not!
Frankly, I didn’t see the need to bring them up since they are common knowledge. It is only the rather ignorant assumption that these concerns “never come up” in mission planning that would demand I list them. And as I said, if you would actually read the articles provided and cited, you would see that risk assessments is a central part of the entire planning process.
And cost-benefit? You mean like how they detailed at length how much such a base would cost, and what potential commercial benefits there would be? It is clear you are speaking out of ignorance on this point, much like your assessment of the ISS’ benefits for scientific research.
LRO has imaged dozens of collapsed lava tubes on the Moon and MRO has seen similar on Mars. We really should focus on locating and exploring these features. Which ones might be developed or enhanced and used for habitat shielding? Which ones are close to resources or aquafirs?
Yes.. we need a high power ground penetrating radar orbiting the Moon AND Mars!
Addendum: Lunar and Martian surface suits should incorporate a conductive mesh providing Faraday grounding and the ability to deguass the suit to remove dust.