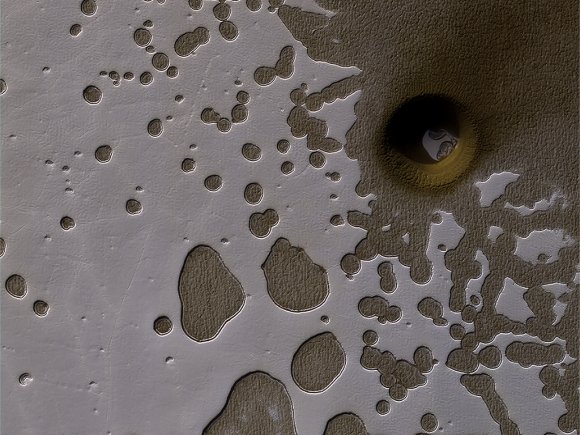

During late summer in the Southern hemisphere on Mars, the angle of the sunlight as it strikes the surface brings out some subtle details on the planet’s surface.
In this image, the HiRISE camera on board NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) captured an area of frozen carbon dioxide on the surface. Some of the carbon dioxide ice has melted, giving it a swiss-cheese appearance. But there is also an unusual hole or crater on the right side of the image, with some of the carbon dioxide ice clearly visible in the bottom of the pit.
NASA scientists are uncertain what exactly caused the unusual pit. It could be an impact crater, or it could be a collapsed pit caused by melting or sublimation of sub-surface carbon dioxide ice.
MRO has been in orbit around Mars for over 10 years, and has completed over 50,000 orbits. The MRO has two cameras. The CTX camera is lower resolution, and has imaged over 99% of the Martian surface. HiRISE is the high-resolution camera that is used to closely examine areas and objects of interest, like the unusual surface pit in this image.
More Reading:

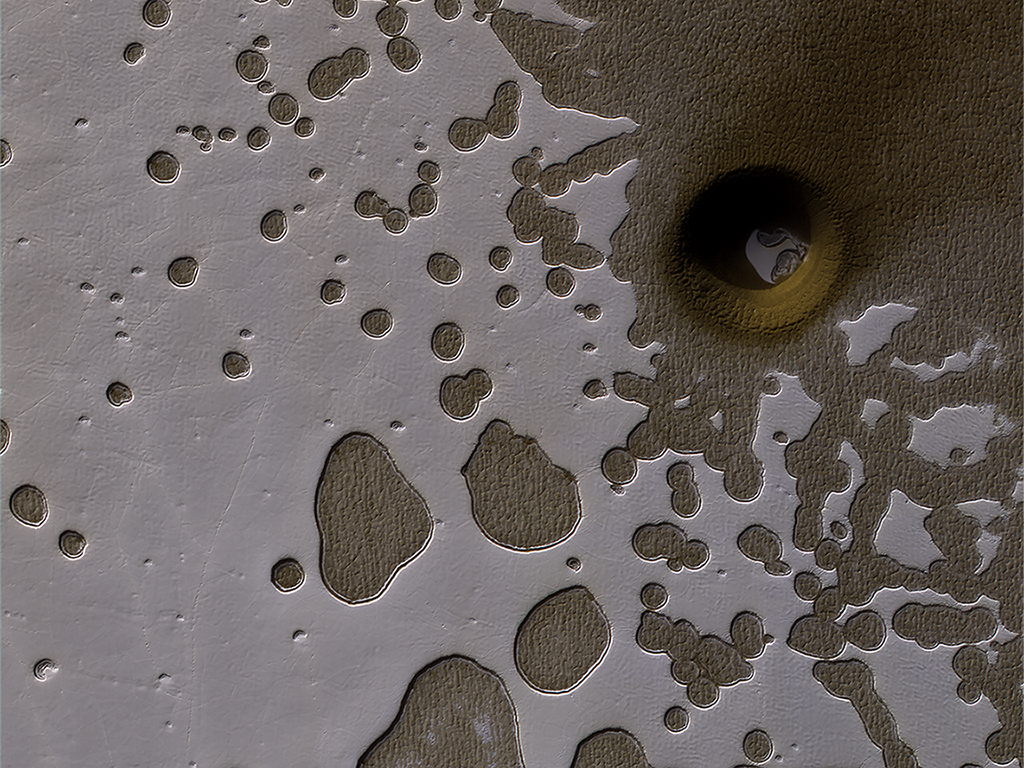
The brown dust blowing away to the upper right in the Photo, certainly suggests collapse, or some other surface phenomenon. An impact normally would be more dish shaped, and not cylindrical. I am thinking about the NASA high velocity impact tests as a model.
This topography has been replicated using arc mode plasma in many plasma physics labs across the country. There is a convincing presentation available on U Tube by Wal Thornhill which summarizes these findings and their specific application to Mars topographic and geologic observations.