The Cassini mission to Saturn ended in September 2017, but the data it gathered during its 13 year mission is still yielding scientific results. On the heels of a newly-released global image of Saturn's moon Titan comes another discovery: Rainfall at Titan's north pole.
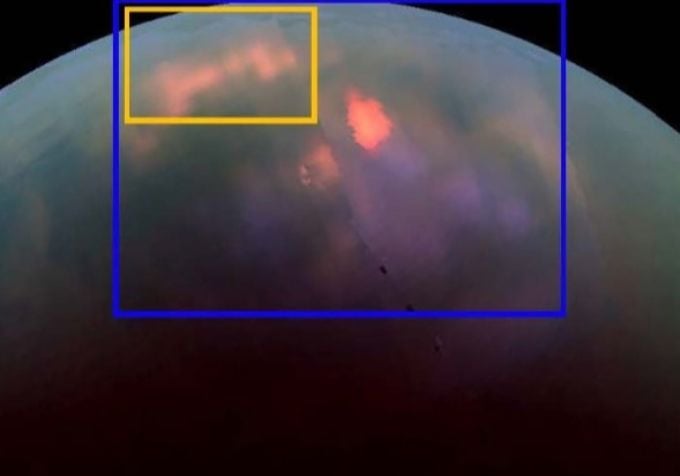
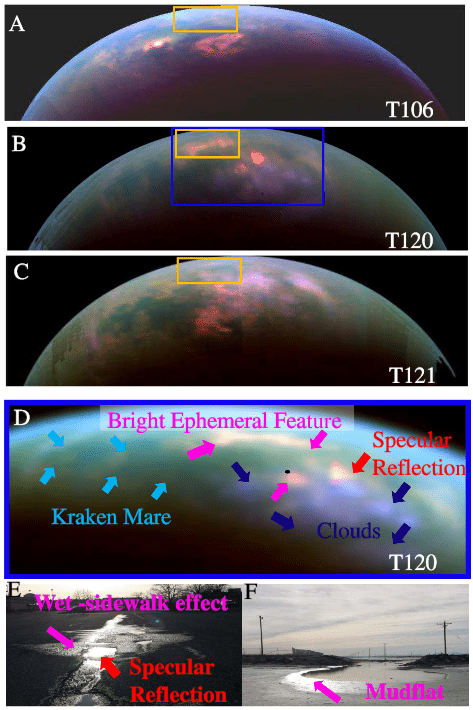
Climate models developed by scientists during Cassini's mission concluded that rain should fall in the north during Titan's summer. But scientists hadn't seen any clouds. Now, a team of scientists have published a paper centered on Cassini images that show light reflecting off a wet surface. They make the case that the reflecting light, called a Bright Ephemeral Flare (BEF) is sunlight reflecting from newly-fallen rain.
The rain on Titan is like no rain here on Earth. Titan is a frigid place, and the only thing that falls from the sky is methane. But it's still an intriguing discovery. It confirms what scientists expected to see after seeing rainfall on Titan's south pole during that region's summer in 2004. Also, Titan is the only Moon in our Solar System with any substantial atmosphere, so seeing it rain there is a unique event in the Solar System.
"The whole Titan community has been looking forward to seeing clouds and rains on Titan's north pole..."
Discovering and quantifying seasonal changes at Titan was one of Cassini's mission objectives. Titan is an intriguing object of study because it has seasonal flows of liquids on its surface, like Earth does.
In their paper, the scientists present a series of images from Cassini's VIMS (Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer) that show the appearance, then the disappearance, probably due to evaporation, of a BEF (Bright Ephemeral Feature.) The BEF is sunlight glinting off a wet surface feature.
"The whole Titan community has been looking forward to seeing clouds and rains on Titan's north pole, indicating the start of the northern summer, but despite what the climate models had predicted, we weren't even seeing any clouds," said Rajani Dhingra, a doctoral student in physics at the University of Idaho in Moscow, and lead author of the new study accepted for publication in Geophysical Research Letters, a journal of the American Geophysical Union.
The rainfall marks the beginning of summer at Titan's north pole. On Titan, the seasons last about seven Earth years. When Cassini arrived at Titan in 2004, it was summer at the south pole. At that time, the Sun was heating Titan's south pole, causing methane to evaporate and condense.
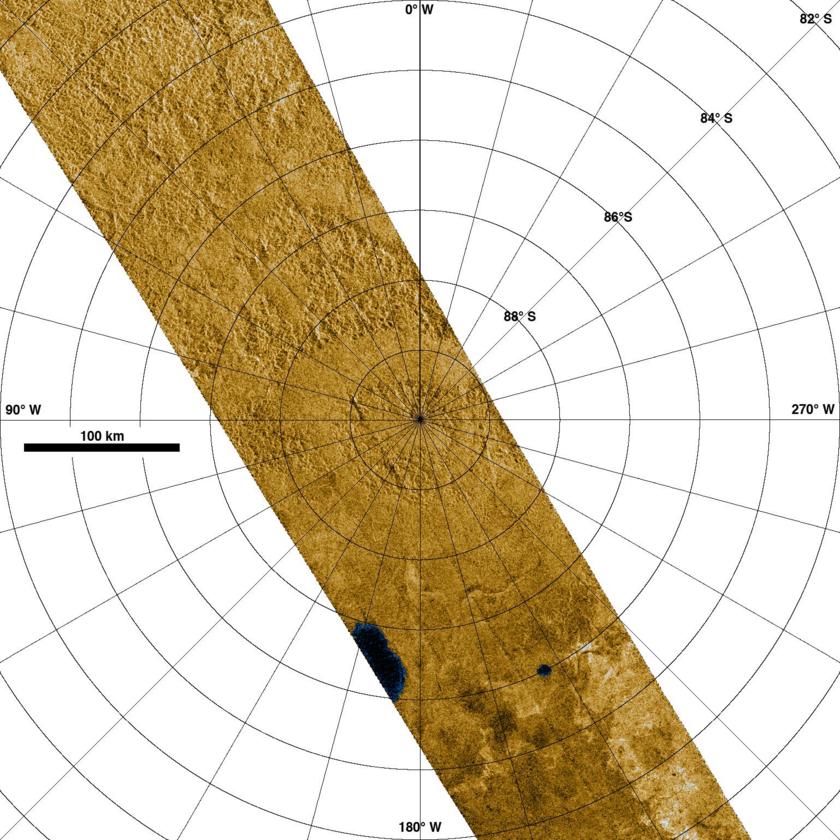
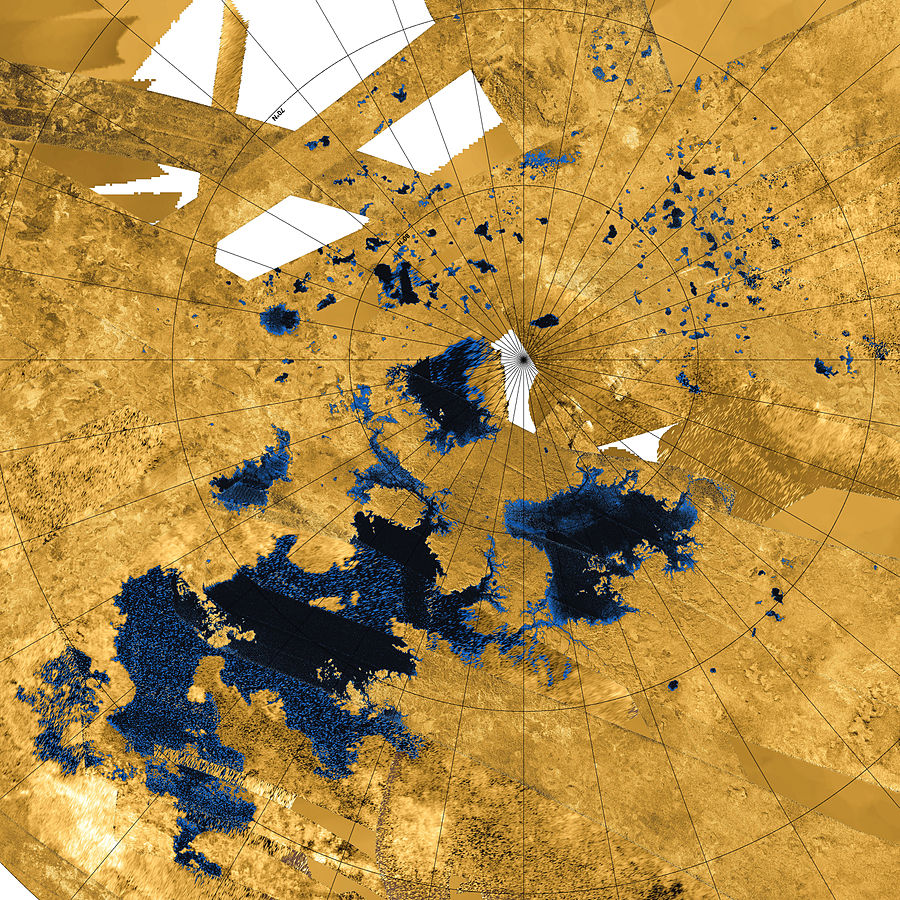
Titan's south pole is drier than the north. A Cassini image of the south pole region shows only two lakes, while the north pole region has dozens of lakes. This led scientists to believe that if there's clouds and rain at the relatively dry south, the north pole, with its abundance of liquid methane, must have clouds and rainfall during its summer, too.
After finding rain at the south pole in 2004, scientists created climate models of Titan that said similar weather would occur at the north pole in the years leading up to the summer solstice, in 2017. But 2016 came and went, and there was still no sign of the expected weather.
With this discovery, it looks like summer has finally arrived at Titan's north pole. Scientists are hopeful that finally seeing it there will help them build a more complete model of the climate on one of our Solar System's most interesting worlds.
Sources:
- Research Paper: Observational evidence for summer rainfall at Titan’s north pole
- Press Release: Titan, rainfalls at the north pole
- NASA Solar System Exploration: Titan
- Planetary Society: Titan's South Pole
- Wikipedia: Lakes of Titan
 Universe Today
Universe Today