A team of astronomers has found two Super-Earths orbiting a red dwarf about 114 light-years away. The star, named LP 890-9, is the second coolest star found that hosts planets. Both the planets are likely temperate, and one of them “… is the second-most favourable habitable-zone terrestrial planet known so far,” according to the paper presenting the results.
There’s a challenging problem in our hunt for Earth-like exoplanets. Three-quarters of the exoplanets we’ve found were detected with the transit method, where planets pass in front of their stars, causing a dip in starlight that spacecraft like Kepler and TESS can see. This means that giant Jupiter-size planets orbiting bright stars are easiest to detect because there’s lots of starlight and a massive world that creates a more detectable dip.

Finding giant planets the size of Jupiter means we’re finding uninhabitable gas giants, many so close to their stars that they’re hot Jupiters. But we’re more interested in finding Earth-like planets, planets in the same size range as Earth that orbit in their star’s habitable zone. These planets are smaller and don’t block as much light, making them difficult to detect.
The desire to find Earth-like planets led to the development of the Search for habitable Planets EClipsing ULtra-cOOl Stars (SPECULOOS.) It’s a project at the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Paranal Observatory in Chile. SPECULOOS is a survey of about 1700 M dwarfs (red dwarfs) using the transit method to spot planets similar to Earth.
Since M dwarfs are cooler than stars like our Sun, the habitable zone is closer to the star. So Earth-like planets in these stars’ habitable zones are closer to their stars and easier to detect when transiting. They’re also easier to study, and astronomers can make more precise measurements of their properties, like their masses, radii, orbital parameters, and in the future, their atmospheres. Studying the atmospheres of nearby Earth-like planets is a critical goal because that’s where we can find traces of biological activity.
SPECULOOS has paid dividends since its inception in 2017, and the new findings are from the SPECULOOS survey.
The paper is “Two temperate super-Earths transiting a nearby late-type M dwarf” and was published in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics. The lead author is Laetitia Delrez, a Postdoctoral Researcher in Astrophysics at the University of Liège, Belgium.
The star in this study is an Ultra-Cool Dwarf (UCD) about 104 light years away named LP 890-9 (TOI-4306, SPECULOOS-2). The planets are temperate super-Earths called LP 890-9 b and LP 890-9 c.
The planet closest to the star, LP 890-9 b, is about 30% larger than Earth, has an orbital period of 2.73 days and is 0.019 au away from the star. The second planet, LP 890-9 c, is slightly larger than the first planet, takes longer to orbit with a period of 8.46 days and is 0.040 au from the star. That means that both planets fit well inside Mercury’s orbit around the Sun for comparison.

But while Mercury suffers under the relentless onslaught of the Sun’s powerful radiation, things are much different in this remote system. The star is far cooler than the Sun, which explains why both planets are in the temperate zone.
Francisco J. Pozuelos is a researcher at the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia and one of the main co-authors of the paper. He explains what the second planet in the system, LP 890-9 c, is like according to SPECULOOS and follow-up observations with other telescopes. “Although this planet orbits very close to its star, at a distance about 10 times shorter than that of Mercury around our Sun, the amount of stellar irradiation it receives is still low and could allow the presence of liquid water on the planet’s surface, provided it has a sufficient atmosphere,” Pozuelos said.
“This is because the star LP 890-9 is about 6.5 times smaller than the Sun and has a surface temperature half that of our star. This explains why LP 890-9c, despite being much closer to its star than the Earth is to the Sun, could still have conditions that are suitable for life.“

LP 890-9 c is a juicy target for the JWST. JWST has a powerful spectroscopic capability that it can use to study the planet’s atmosphere. It’s already studied another exoplanet, WASP-39b, and given us our most detailed understanding of an exoplanet’s atmosphere yet. But it’s a hot Jupiter, unlike the super-Earth detected by SPECULOOS.
LP 890-9 c is second only to the famous TRAPPIST-1 planets, found with SPECULOOS’s precursor mission, as a desirable, potentially habitable terrestrial exoplanet. Comparisons with Earth are inevitable, but each planet has so much detail that the comparison only goes so far. “This comparison does not, however, consider the fact that LP 890-9c is located close to the inner boundary of the habitable zone and could therefore have an atmosphere that is particularly rich in water vapour, which would then boost its atmospheric signals,” explains lead author Delrez. “Moreover, models often differ as to the exact position of this inner boundary of the habitable zone depending on the characteristics of the star. The discovery of LP 890-9c, therefore, offers a unique opportunity to better understand and constrain the habitability conditions around the smallest and coolest stars in our solar neighbourhood.”
How do these planets compare to other exoplanets around cool dwarf stars? The team plotted them on a chart with other exoplanets around similar stars found in NASA’s Exoplanet Archive. They restricted the data to planets around stars with a surface temperature lower than 3600 Kelvin. (The Sun’s surface temperature is 5778 K.)

It’s important to point out in all discussions of potentially-habitable exoplanets that we have little idea if any of these planets are remotely habitable. The term habitable is relative. Hot Jupiters are in no way habitable, so they’re never referred to as potentially habitable. But the term “habitable zone” does have utility. “The habitable zone (HZ) is a concept that can be used to prioritize detected rocky exoplanets for follow-up observations,” the authors explain.
It’s also important to point out that a habitable zone’s size is determined by several things. “The width and distance of the HZ region depend in a first approximation on the incident stellar flux and the atmospheric composition of the planet,” the authors write. The concentration of greenhouse gases is an essential factor. It also depends on the planet’s surface because, as the authors point out, “Cool stars warm an Earth-like planet’s surface more effectively than hotter stars,” which might be counterintuitive.
Another factor to consider is the potential habitability of planets around red dwarf stars. Some evidence shows they can flare violently, with each flare producing a stream of powerful particles that can strip atmospheres from planets. And while red dwarfs aren’t as bright as stars like our Sun, they can produce more harmful UV and X-rays. Other research shows that the violent flares only come from their poles, which would spare orbiting planets. There are huge questions about the habitability around red dwarfs that has nothing to do with the habitable zone or a planet’s atmosphere.
On the other hand, it looks as if LP 890-9 is a relatively calm star. “LP 890-9 is a relatively low-activity late-type M dwarf,” the authors explain. They say the star is relatively young for a red dwarf, only about 7 billion years. Red dwarfs can last for tens of billions of years, with the smallest ones lasting trillions. Other red dwarf stars had seemed calm before follow-up observations showed otherwise.
LP 890-9 and its planets are excellent candidates for follow-up studies, so we’ll probably learn more about its properties, not just its activity level, in the future. The paper shows the expected strength and reliability of future observations of planets in the system.
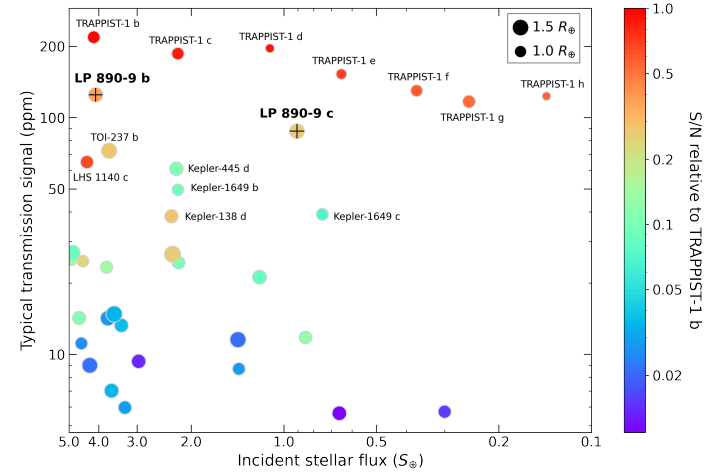
while LP 890-9 c stands out as the second-most favourable habitable-zone terrestrial planet after the TRAPPIST-1 planets. Image Credit: Delrez et al. 2022.
The JWST is working its way through its list of targets, and one of its four main science objectives concerns exoplanet atmospheres. Its observations have already provided the basis for one study, where it found carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of WASP-39b, the first time we’ve ever detected it on an exoplanet.
Hopefully, the powerful space telescope will eventually point its spectrograph at these planets and reveal their secrets.
“The discovery of this remarkable system offers another rare opportunity to study temperate terrestrial planets around our smallest and coolest neighbours,” the authors conclude.


To better grok the planet HZ plot, the last part of the paper caption reads:
“The inner (Recent Venus) and outer (Early Mars) boundaries of the empirical (optimistic) HZ are shown as solid red and blue lines, respectively (Kopparapu et al. 2014 and Sect. 8.3). The dashed green line shows an alternative conservative inner edge limit from 3D models (Leconte et al. 2013). The outer edge of the HZ in 3D models agrees with incident stellar flux for Early Mars insulation. We note that the three limits shown do vary with the stellar effective temperature, but this is not obvious on this plot due to the log-scale of the x-axis.”