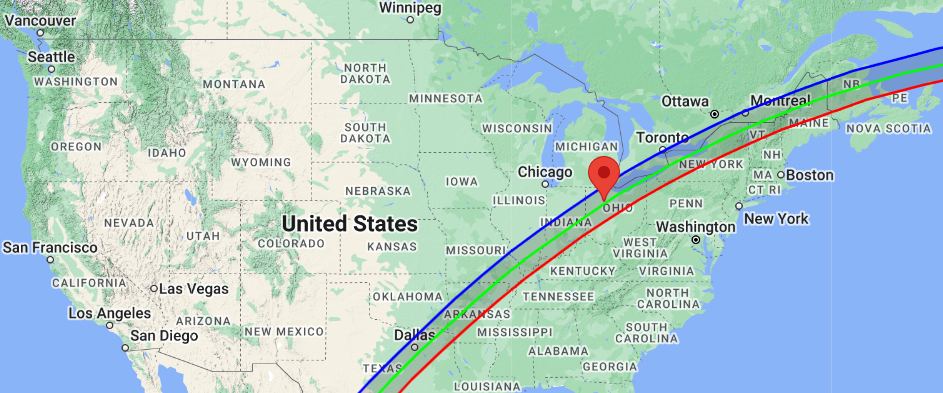
You had to be in the right part of North America to get a great view of the recent solar eclipse. But a particular telescope may have had the most unique view of all. Even though that telescope is in Hawaii and only experienced a partial eclipse, its images are interesting.
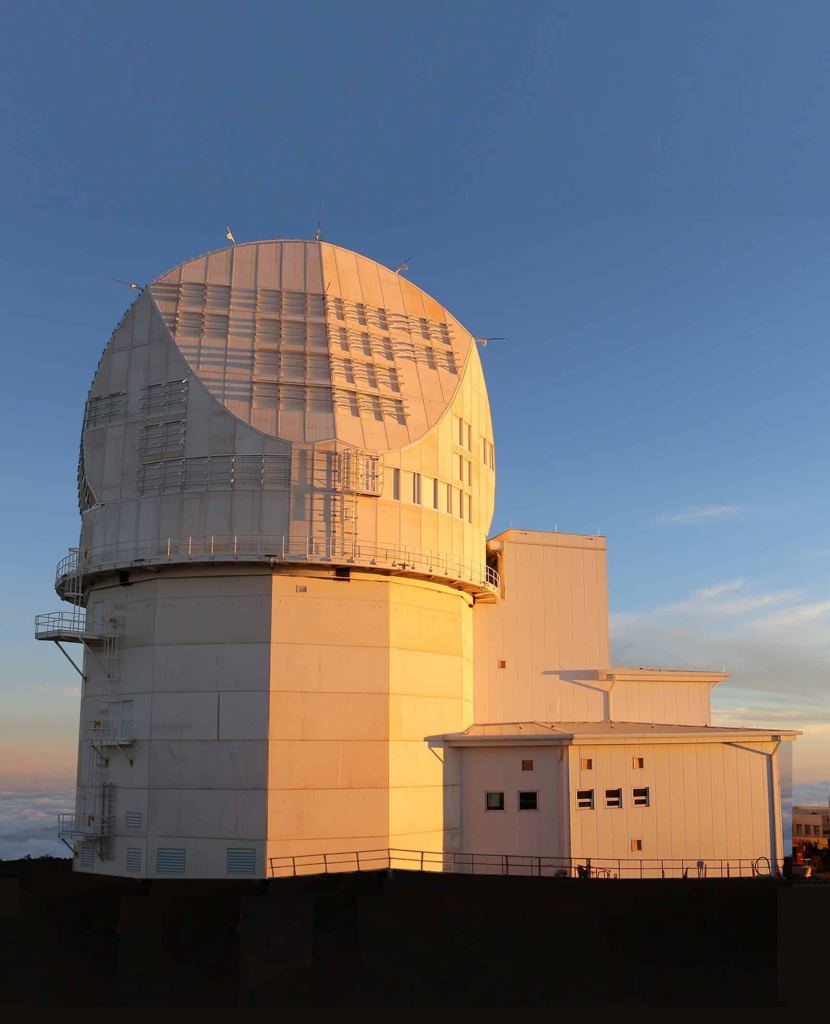
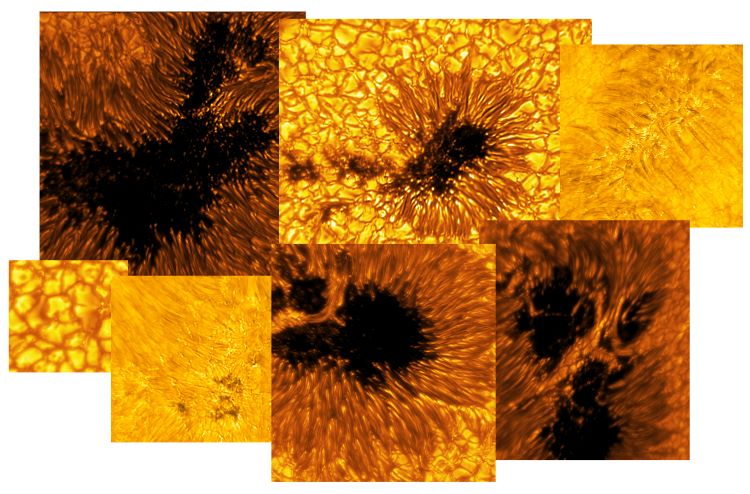
The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (DKIST) is at the Haleakala Observatory in Hawaii. With its four-meter mirror, it's the largest solar telescope in the world. It observes in visible to near-infrared light, and its sole target is the Sun. It can see features on the Sun's surface as small as 20 km (12 miles.) It began science operations in February 2022, and its primary objective is to study the Sun's magnetic fields.
Though seeing conditions weren't perfect during the eclipse and the eclipse was only partial when viewed from Hawaii, the telescope still gathered enough data to create a movie of the Moon passing in front of the Sun. The bumps on the Moon's dark edge are lunar mountains.
via GIPHY
"The team's primary mission during Maui's partial eclipse was to acquire data that allows the characterization of the Inouye's optical system and instrumentation," shares National Solar Observatory scientist Dr. Friedrich Woeger.
The Moon plays a critical role in measuring the telescope's performance. Its edge is well-known and as a dark object in front of the Sun, it acts as a unique tool to measure the Inouye telescope's performance and to understand the data it collects. Since the telescope has to correct for Earth's turbulent atmosphere with adaptive optics, the Moon's known qualities help researchers work with the telescope's optical elements.
"With the Inouye's high order adaptive optics system operating, the blurring due to the Earth's atmosphere was greatly reduced, allowing for extremely high spatial resolution images of the moving lunar edge," said Woeger. "The appearance of the edge is not straight but serrated because of mountain ranges on the Moon!" This serrated dark edge covers the granular convection pattern that governs the "surface of the Sun."
The Inouye Solar Telescope studies the Sun's magnetic fields, which drive space weather. What we see in the video is visually interesting, but there's a lot of data behind it.
It'll take several months to analyze all of the data it gathered during the eclipse.
 Universe Today
Universe Today