Supermassive Black Holes are Nature’s confounding behemoths. It’s difficult for Earth-bound minds to comprehend their magnitude and power. Astrophysicists have spent decades studying them, and they’ve made progress. But one problem still baffles even them: the Final Parsec Problem.
New research might have solved the problem, and dark matter plays a role in the solution.
Supermassive Black Holes (SMBHs) can be billions of times more massive than our Sun. Evidence shows that they may reside at the center of all large galaxies. The Milky Way has one and it’s named Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*).
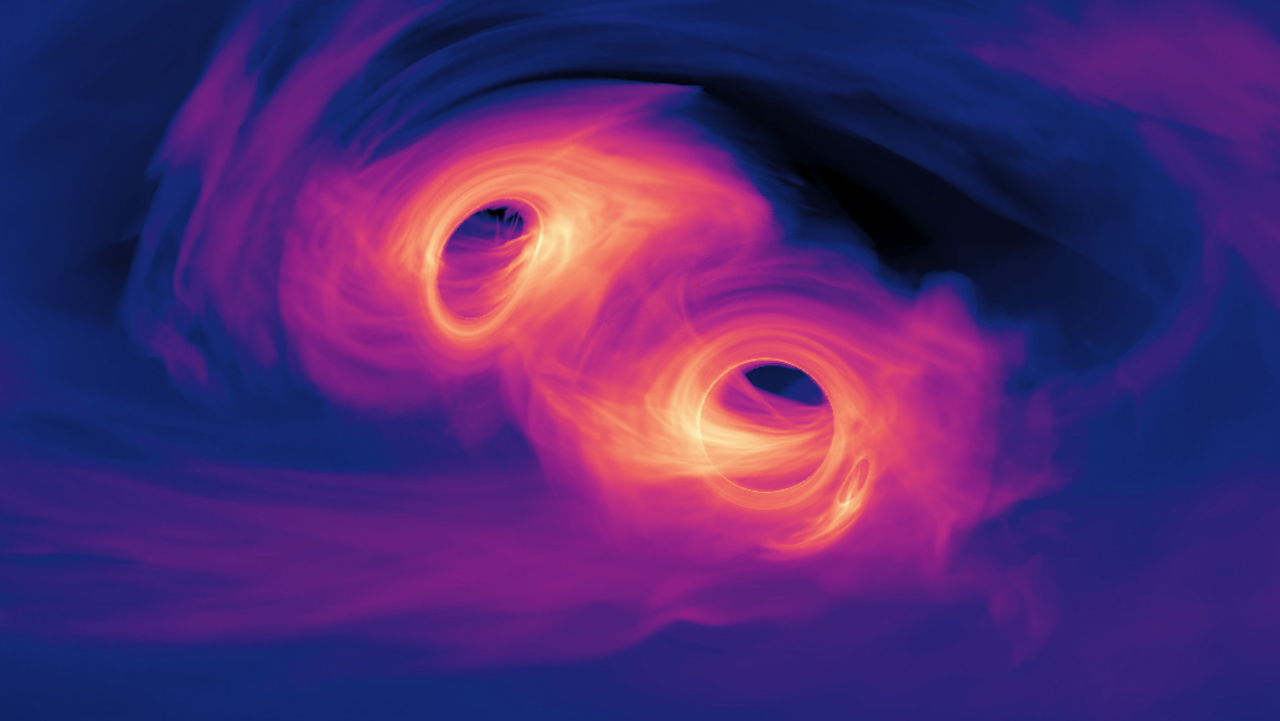
SMBHs grow so massive by merging with other SMBHs when their host galaxies merge. But there’s a problem. Astrophysicists don’t understand how the two SMBHs can close the final parsec that separates them.
When black holes merge, they begin as a binary object. They spiral around each other, each carrying their own momentum. To merge, the black holes need to shed energy. To do this, they shed energy to the surrounding gas and dust which then dissipates. But when they get about three light-years away from one another, or about one parsec, there simply isn’t enough gas and dust to absorb the necessary energy.
Yet SMBHs do merge, so somehow, nature overcomes the Final Parsec Problem (FPP).
New research published in the journal Physical Review Letters presents a solution to the FPP. The research is titled “Self-Interacting Dark Matter Solves the Final Parsec Problem of Supermassive Black Hole Mergers.” The first author is Gonzalo Alonso-Álvarez, a Postdoctoral Fellow in the Department of Physics at the University of Toronto, Canada.
“Our work is a new way to help us understand the particle nature of dark matter.”
Gonzalo Alonso-Álvarez, Department of Physics, University of Toronto
There’s no question that stellar-mass black holes can merge. LIGO/Virgo has sensed the gravitational waves coming from many mergers between stellar-mass black holes, which is direct evidence that black holes can merge. However, evidence for SMBH mergers is elusive.
In 2023, scientists announced the detection of a persistent background hum of gravitational waves. That detection came from the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav.) NANOGrav gathered gravitational wave data for 15 years using pulsar timing.
Different groups of researchers hypothesized that the hum comes from the mergers of SMBHs. In one paper, researchers said the hum comes from hundreds of thousands of pairs of merging SMBHs. Somehow, these SMBHs are overcoming the FPP.
In their new paper, Alonso-Álvarez and his co-researchers show how dark matter allows SMBHs to merge despite the Final Parsec Problem. “We show that including the previously overlooked effect of dark matter can help supermassive black holes overcome this final parsec of separation and coalesce,” said Alonso-Álvarez. “Our calculations explain how that can occur, in contrast to what was previously thought.”
Astrophysicists have been working on the FPP for a long time. Different researchers have developed different models to try to explain how SMBHs merge, and those models include dark matter. However, previous merger models showed that the dark matter near the spiralling black holes is thrown clear of the merger area by the gravity created by the inspiralling holes. Without that dark matter to absorb energy, the pair of SMBHs can’t overcome the FPP.
But in this new research, dark matter interacts with itself and ‘spikes’ instead of being dispersed. Dark matter spikes are theoretical concentrations of dark matter around a black hole. As an SMBH grows, it draws regular matter towards itself. The same process could lead to a spike in dark matter around the black hole. Its density remains high enough that it can absorb enough energy for the pair of SMBHs to continue their inspiralling. Eventually, they overcome the FPP and coalesce into one.

It all depends on dark matter self-interacting.
“The possibility that dark matter particles interact with each other is an assumption that we made, an extra ingredient that not all dark matter models contain,” said Alonso-Álvarez. “Our argument is that only models with that ingredient can solve the final parsec problem.”
Physicists aren’t certain that dark matter can interact with itself, though. The Standard Model says that dark matter interacts primarily through gravity. But newer evidence is accumulating that it can interact with itself, and physicists call this the Self-Interacting Dark Matter theory.
Other research has looked at dark matter spikes near merging black holes. According to that research, dynamical friction between the black holes and the DM spike could dissipate the spike. However, this new research argues that only SIDM can effectively move the heat outwards and replenish the DM spike. Contrary to collisionless dark matter, an SIDM spike maintains itself and allows the inspiralling black holes to shed enough energy and cross the final parsec problem.
More support for this hypothesis comes from the nature of the background gravitational wave hum that scientists announced in 2023. It was measured by pulsar timing and the waves displayed a softening at low frequencies. According to Alonso-Álvarez, their model predicts this phenomenon, lending credence to their work.
“A prediction of our proposal is that the spectrum of gravitational waves observed by pulsar timing arrays should be softened at low frequencies,” said co-author Professor James Cline from McGill University and the CERN Theoretical Physics Department in Switzerland. “The current data already hint at this behavior, and new data may be able to confirm it in the next few years.”
This research reaches beyond SMBH mergers to the nature of dark matter itself. The self-interactions the researchers modelled can help explain the shape of dark matter haloes around galaxies.
“Our work is a new way to help us understand the particle nature of dark matter,” said Alonso-Álvarez. “We found that the evolution of black hole orbits is very sensitive to the microphysics of dark matter and that means we can use observations of supermassive black hole mergers to better understand these particles.”
“Despite astrophysical uncertainties about their detailed nature, there is no doubt that dark matter spikes exist around supermassive black hole binaries and thus contribute to the dynamical friction accelerating the decay of their orbit,” the authors write in the conclusion of their paper.
“We found that the final parsec problem can only be solved if dark matter particles interact at a rate that can alter the distribution of dark matter on galactic scales,” said Alonso-Álvarez. “This was unexpected since the physical scales at which the processes occur are three or more orders of magnitude apart. That’s exciting.”

The excellent article seem to cover all the pertinent points. But there is recent context that makes the work itself even more pertinent.
The simpler CDM model makes a better fit to observations on cosmological scales. But as the article notes here they show for the first time that the more particle physics generic SIDM provides a better fit to pulsar timing array data of the gravitational wave background from mergers, while avoiding conflict with other data.
So that is promising, combined with the recent find that black hole mergers is a part of a most likely and robust self consistent model dynamically generated pathway for early galaxy supermassive black holes. Supermassive black holes are now observed to have formed with early galaxies and then have been a more significant part of galaxy mass. The heavy seed and superEddington growth scenario seems both robustly observed by self consistent models now. [From Seeds to Supermassive Black Holes: Capture, Growth, Migration, and Pairing in Dense Protobulge Environments, Yanlong Shi et al 2024 ApJL 969 L31.] This pathway to formation would conveniently explain both how gas clouds magnetic fields are collected to strong fields and then how they can dominate over thermal forces allowing for superEddington growth in dense clouds. It may even explain the mysterious red dots:
“The late-stage system appears remarkably similar to recently observed high-redshift “little red dots.” This scenario can provide an explanation for rapid SMBH formation, growth, and mergers in high-redshift galaxies.”
Moreover, the star massed seed growth and merger path in early dense gas clusters is consistent with other black hole formation pathways and much more likely than direct collapse scenarios.
“The formation of [dynamically generated heavy] seeds is 100,000 times more likely than heavy seeds produced via direct collapse and are therefore more likely to explain the overall MBH population.”
[The seeds that formed the garden of massive black holes, Pranav Satheesh, Astrobites, Jun 14, 2024.]