[/caption]
NASA’s solar powered Jupiter bound Juno orbiter has captured her first image – a beautiful portrait of the Earth & Moon – since the probe blasted off from the home planet.
Juno lifted off 25 days ago at 12: 25 p.m. on August 5 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft snapped the portrait with the onboard JunoCam camera on August 26 after journeying some 6 million miles (9.66 million km) from Earth and while traveling at a velocity of 77,600 miles per hour (124,900 kilometers per hour) relative to the sun.
“The image of the Earth Moon system is a rather unique perspective that we can get only by stepping outside of our home planet,” said Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator, in an exclusive interview with Universe Today. Bolton is from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio.
“On our way to Jupiter, we’ve looked back at home and managed to take this amazing image.”
“Earth looking much like any other planet or star from a distance is glorious as this somewhat average looking “star” is home to all of humanity. Our companion, the moon, so beautiful and important to us, stands out even less.”
“We appear almost average and inconspicuous, yet all of our history originates here. It makes one wonder just how many other planets or solar systems might contain life like ours,” Bolton told me.

The Juno team commanded the probe to take the image as part of the checkout phase of the vehicles instruments and subsystems.
“The JunoCam instrument turn on and check out were planned activities. The instrument is working great and in fact, all the instruments that we’ve turned on thus far have been working great,” Bolton added.
So far the spacecraft is in excellent health and the team has completed the checkout of the Waves instrument and its two Flux Gate Magnetometer sensors and deployment of its V-shaped electric dipole antenna.
“We have a couple more instruments still to do,” Bolton noted.
The team reports that Juno also performed its first precession, or reorientation maneuver, using its thrusters and that the first trajectory control maneuver (TCM-1) was cancelled as unnecessary because of the extremely accurate targeting provided by the Atlas V rocket.
The portrait shot is actually not Juno’s last photo of her home.
The 8000 pound (3,600 kilogram) probe will fly by Earth once more on October 9, 2013 for a gravity assisted speed boost of 16,330 MPH (7.3 km/sec) to accelerate Juno past the asteroid belt on its long journey to the Jovian system.

JunoCam will collect new photos and the other science instruments will make measurements as Juno cartwheels past Earth during the slingshot to Jupiter.
Juno is on a 5 year and 1.7 Billion mile (2.8 Billion km) trek to the largest planet in our solar system. When she arrives at Jupiter on July 4, 2016, Juno will become the first polar orbiting spacecraft at the gas giant.
During a one year science mission – entailing 33 orbits lasting 11 days each – the probe will plunge to within about 3000 miles (5000 km) of the turbulent cloud tops and collect unprecedented new data that will unveil the hidden inner secrets of Jupiter’s genesis and evolution.
The goal is to find out more about the planets origins, interior structure and atmosphere, observe the aurora, map the intense magnetic field and investigate the existence of a solid planetary core.
“This is a remarkable sight people get to see all too rarely,” said Bolton in a NASA statement about the Earth-Moon photo. “This view of our planet shows how Earth looks from the outside, illustrating a special perspective of our role and place in the universe. We see a humbling yet beautiful view of ourselves.”
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the Juno mission. The spacecraft was designed and built by Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver.

NASA's Juno spacecraft and its spent Centaur upper rocket stage are captured in this telescope view as they move across the field of stars. The five-minute, timed exposure was acquired on Aug. 5 11:18pm Eastern time (Aug. 6 at 3:18 UTC) when Juno was at a distance of about 195,000 miles (314,000 kilometers) from Earth. The images were taken remotely by amateur astronomer Scott Ferguson using Global Rent-a-Scope's GRAS-016 Takahashi Widefield Refractor, which is located in Nerpio, Spain. Credit: Scott Ferguson
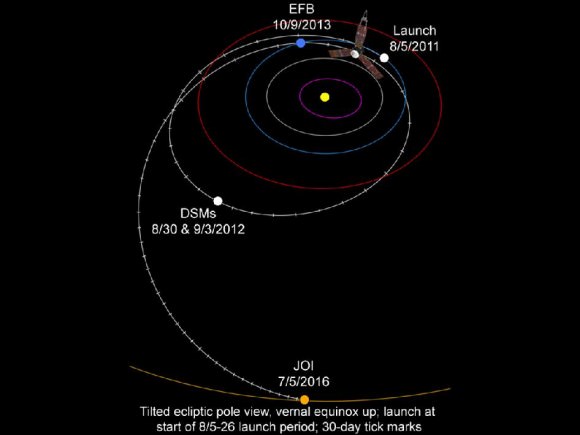
This graphic shows Juno's trajectory, or flight path, from Earth to Jupiter. The spacecraft travels around the Sun, to a point beyond the orbit of Mars where it fires its main engine a couple of times. These deep space maneuvers set up the Earth flyby maneuver that occurs approximately two years after launch. The Earth flyby gives Juno the boost in velocity it needs to coast all the way to Jupiter. Juno arrives at Jupiter in July 2016. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Read my continuing features about Juno
Juno Blasts off on Science Trek to Discover Jupiter’s Genesis
Juno Jupiter Orbiter poised at Launch Pad for Aug. 5 Blastoff
JUNO Orbiter Mated to Mightiest Atlas rocket for Aug. 5 Blastoff to Jupiter
Solar Powered Jupiter bound JUNO lands at Kennedy Space Center
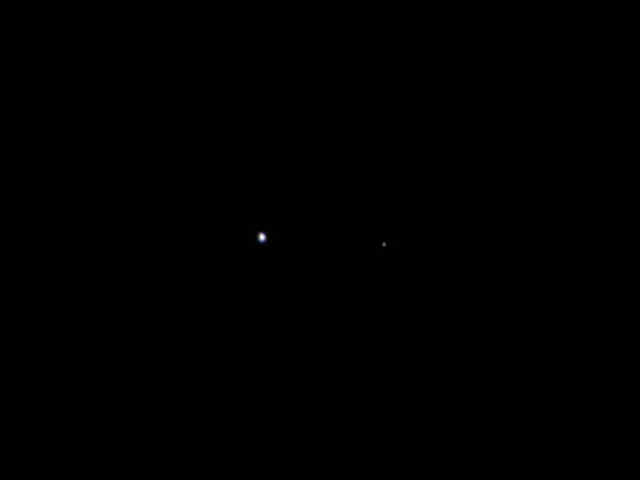


“This is a remarkable sight people get to see all too rarely… This view of our planet shows how Earth looks from the outside, illustrating a special perspective of our role and place in the universe. We see a humbling yet beautiful view of ourselves.”– Scott Bolton.
Humbling indeed. “Only” 6-million miles out, and our homeworld becomes an insignificant planetary disk ( elegantly attended by its faithful companion ), with its life history, encompassed by the aging Solar System’s huge volume.
In framing turn, what is that large measure of space ( the Sun’s domain of light-hours ) in comparison to the enormous expanse of our ancient star-strewn Galaxy?
And beyond that gravity-bound System’s scale, what are those two lost dots of reflected light ( now vanished in an ocean of stellar night ) in comparison to the space-chamber that is the realm of the Local Group? Who can fathom the magnitudes of size which expand out from there into receding, galaxy-clustering space-time?
Dimly attempting to grasp the depths of it all can give one a “special perspective of our role and place in the universe”, as our great world disappears in scaled-up space.
“Juno will become the first polar orbiting spacecraft at the gas giant.” Some exciting, new perspective views of that Gas Giant, and its company of worlds, this may provide!
Only 5000 km above the cloud tops! I know the Juno Cam is mostly for PR to reach out to the public, but I can’t wait myself for the images to come in. Hopefully it will allow a look down that reveals the different layer decks, something akin to what you can see on certain occassions from an airliner.
And the aliens are sending a probe to earth as we speak.
Please don’t mention aliens and probing, together in the same sentence! The repressed memories start to come back. ouch! lol
Sweet*]
Hmm, they mention Juno is going at a speed of 77,600 mph, that makes it the fastest man made object to date wiith Voyager 1 in second place at 29,160 pmh, right? If so, that is awesome. I wonder what kind of speeds we will achieve in the near future.
The velocity is relative to the heliocentric coordinate system. This velocity is equal to the velocity of the Earth around the sun v = 29.5km/sec plus the escape velocity from Earth at about 10km/sec. The velocity of the spacecraft is of course not oriented along the Earth’s orbital velocity. The angle is about 45-deg and so the vector addition gives a total velocity in the heliocentric system as
V =~ 29.5km/sec + cos(45)10km/sec =~ 37km/sec,
which is 133500km/hr or 80,000 mi/hr, which is pretty close. All spacecraft that we send out into the solar system follows more or less this sort of rule.
LC
How can one see this image and still deny the existence of a Creator? I guess I will never understand that!
Evolution my ass, this is the picture of our insignificance and nothingness!!!
And how exactly can you see the work of the “Creator” in this picture? And even find a reason to defy evolution.I guess i will never understand simple minded people.
“How can one see this image and still deny the existence of a Creator?”
Can you give me your address? I’d like to send you a ‘Get Well Soon’ card.
@ a post now past its expiration date as I was composing this reply… There were several other replies to that post which also seem to have expired (moder-vention)
Indeed, your ass, should you actually be the owner of one, is evolution along with human intervention via animal husbandry — please continue to display the open framed mind all of organizational religions.
On the other hand, non-dogmatic science being what it is, you might do better to embrace the simple truth and harmony of the methodology of physics and the physical sciences. Therein lies greater order for comprehension which does not require leaps of faith. Careful now, that leap you are taking might not be to solid ground, and who is there to catch you.
Mary -testable vs intractable-
As you can see from the historical view from space. Our spirit to dream is finally becoming reality we can see. The soul of the human race can travel the universe one mission at a time.