[/caption]
Teams of Russian engineers are in a race against time to save the ambitious and unprecedented Phobos-Grunt sample return mission from crashing back to Earth following the post launch failure of the upper stage rocket firings essential to propel the probe onward to destination Mars and scooping up dirt and dust from the tiny moon Phobos.
Roscomos, the Russian Federal Space Agency says they have perhaps two weeks to salvage the spacecraft – now stuck in Earth orbit – before its batteries run out and its orbit would naturally decay leading to an ignominious and uncontrollable reentry and earthly demise. Vladimir Popovkin, head of Roscosmos Chief had initially indicated a survival time limited to only 2 days in a briefing to Russian media.
“I give them a good chance — better than even — of recovering the mission and making the Mars insertion burn in a day or two, said James Oberg, a renowned expert on Russian and US spaceflight in commentary to Universe Today.
But Oberg also told me that having such problems so early in the mission was not a good sign. It all depends on whether the root cause is related to a simple software patch or serious hardware difficulties.
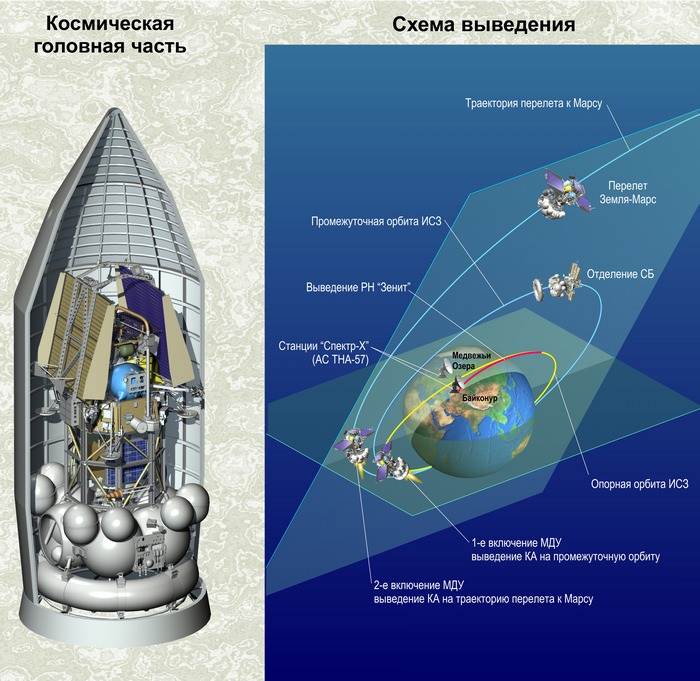
Following yesterday’s eerie midnight blastoff of Phobos-Grunt at 00:16 a.m. Moscow time atop an upgraded Zenit- 2SB booster and the apparently flawless performance of the first and second stages, the situation turned decidedly negative some 5 hours later when the pre-planned ignition burns of the Fregat upper stage failed to ignite twice.

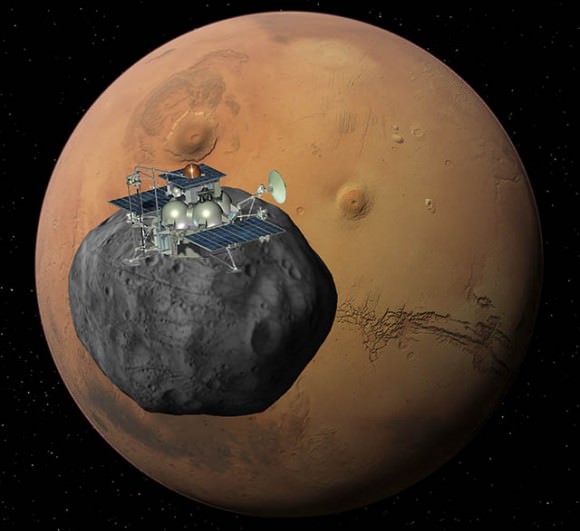
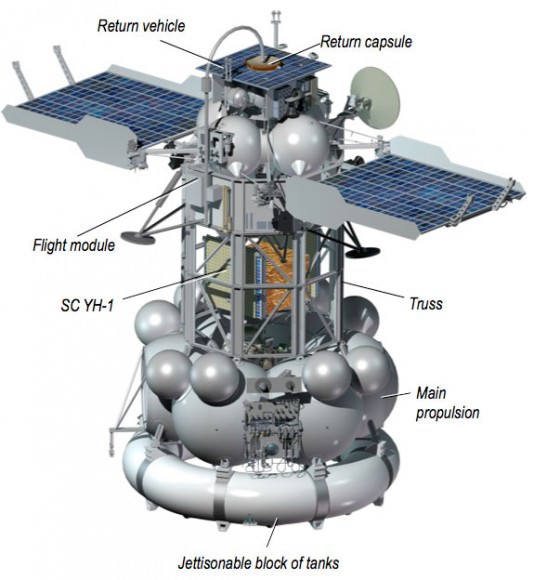
The 13,000 kg Phobos-Grunt (which means Phobos-Soil) spacecraft was to embark on an 11 month interplanetary cruise and arrive in the vicinity of Mars around October 2012, along with a piggybacked mini-satellite from China named Yinghuo-1, the nation’s first ever probe to orbit the Red Planet, and the Phobos-LIFE experiment from the Planetary Society.
“It has been a tough night for us because we could not detect the spacecraft [after the separation],” Vladimir Popovkin said according to the Ria Novosti Russian news agency. “Now we know its coordinates and we found out that the [probe’s] engine failed to start.”
“It is a complex trajectory, and the on-board computers could have simply failed to send a “switch on” command to the engine,” Popovkin added.
Fortunately, the engine ignition malfunction was one of the anticipated failure scenarios and a corrective action plan already exists for it – but only if it can be implemented to save the $163 million mission and Russian hopes to revive their long dormant interplanetary forays.
“But it’s an old old superstition that when leaving your house for a long voyage, if you trip on the door step, you better just lay down your suitcases and go back inside,” Oberg said.
“Seriously, on a mission so complex and innovative as this one is, with so much stuff that has to be done RIGHT the first time they’ve ever tried it, having this kind of error — even if it’s only a coding mishap — right at the start, is NOT a good omen about the quality of work on preparing the later steps,” Oberg warned.
The goal of the complicated and first of its-kind 3 year round trip mission is to deploy a lander to the surface of Phobos, grab up to 200 grams of pristine regolith and rocks, and then take off and sail back to Earth with the precious samples for analysis by the most scientifically advanced instruments available to humankind. Watch the detailed mission animation in my article here.
Another serious problem was a lengthy gap in tracking coverage and thus two way communications with the spacecraft which minimized and seriously delayed Russian controller’s ability to diagnose and correct the malfunction.
Roscosmos stated today that after two communications sessions all necessary parameters of the spacecrafts motion have been determined and they hoped to regain contact sometime Wednesday afternoon through a ground station at Baikonur and upload new software to orient the vehicle and commands for an engine firing at some point soon. Luckily the hydrazine filled propellant tank had not been jettisoned – or all would be lost.
It appears that the earliest day the Fregat engines can be fired is sometime Thursday. The Fregat would also journey all the way to Mars and conduct the critical braking maneuver to insert Phobos-Grunt and Yinghuo-1 into separate Mars orbits.
The engine ignition failure has left Phobos-Grunt stuck in an elliptical orbit ranging from about 207 by 347 kilometers and inclined 51 degrees. The engine firings would have placed the ship into a higher altitude elliptical orbit of 250 by 4150 km and then cruising to Mars.
The Russianspaceweb website reported that “the editor of this web site received a message from the director of Moscow-based Space Research Institute, IKI, Lev Zeleny, informing that tracking facilities of the US military provided significant help in establishing exact orbital parameters of the Phobos-Grunt spacecraft. This data was to be used during the previous night to send commands to the spacecraft as it was passing within range of ground control stations. Zeleny reassured that the mission team still had had “few days for reprogramming before the end of the Mars accessibility window for 2011.”
Alexey Kuznetsov, Head of the Roskosmos Press Office told me previously that, “The Phobos-Grunt launch window extends until November 25.” So theoretically, there is still some time to propel Phobos-Grunt to Mars but there are also many unknowns.
Further details will be reported as they emerge.
Meanwhile, NASA’s car sized Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Rover is posied atop an Atlas V rocket at her Florida launch pad awaiting a Nov. 25 liftoff.
Read Ken’s continuing features about Phobos-Grunt here:
Russia’s Bold Sample Return Mission to Mars and Phobos Blasts Off
Russian Mars Moon Sample Probe Poised to Soar atop Upgraded Rocket – VideoAwesome Action Animation Depicts Russia’s Bold Robot Retriever to Mars moon Phobos
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghuo-1 Encapsulated for Voyage to Mars and Phobos
Phobos and Jupiter Conjunction in 3 D and Amazing Animation – Blastoff to Martian Moon near
Russia Fuels Phobos-Grunt and sets Mars Launch for November 9
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghou-1 Arrive at Baikonur Launch Site to tight Mars Deadline
Phobos-Grunt: The Mission Poster
Daring Russian Sample Return mission to Martian Moon Phobos aims for November Liftoff

This is rather unfortunate. It might be that today is the do or die day.
One thing which might be telling is that this space mission, according to the above article, has a $163 million price tag. That is pretty cheap actually, and it does make me wonder if all the technical bases were covered.
LC
I don’t think batteries for launch suddenly extends to 2 weeks without the solar panels supplying some power. Which, as I said on the previous UT article, makes me think the deadline is the launch window closing in 2 weeks.
Oberg may have much accumulated experience on project overview, but I don’t think there is any such failure statistics out there.
If you look at a delivered (if software and scenario modifiable) product as a statistic assemblage, the traditional bathtub failure curve should hold. Modern complex systems modify it by having larger repeat failure and softer failures combined with less of wear out (see the improvement in Mars rover life time), but initial failures are always an issue. That is why rocket launchers usually fails at first, you are eradicating remaining bugs.
If it is a software function (even if only used once), it can be survivable. Unless it is a feet to metric conversion problem under EDL. :-/
I can agree with lcrowell that the cost indicates shortcuts like less thorough testing et cetera, and a case for concern. But that is a priori some estimate of error statistics, and I don’t think Oberg presented a valid a posteriori estimate.
the solar panels are deployed but they need to be pointed
I think we agree on that. First I thought the panels were pointed (star tracker succeeded), then I realized it wasn’t necessary to explain the difference between the 1st and 2nd time estimates. Presumably they have enough power for communication.
I think we agree on that. First I thought the panels were pointed (star tracker succeeded), then I realized it wasn’t necessary to explain the difference between the 1st and 2nd time estimates. Presumably they have enough power for communication.
Bad news – the probe is now reported as incommunicado due to a number of reasons, see the russianspaceweb. And yes, another design flaw seems to be one root cause, this time hardware related. (Low-gain antennas shielded by tanks.)
Let’s hope they succeed and it becomes the greatest success ever
It’s over.
It’s over.
I was hoping for the best but it’s beginning to look like the (empty) Phobos Soil Sample Recovery capsule just may be the only piece of hardware found that survives this mission and possibly ends up being displayed in a museum somewhere. How sad for science.
I was hoping for the best but it’s beginning to look like the (empty) Phobos Soil Sample Recovery capsule just may be the only piece of hardware found that survives this mission and possibly ends up being displayed in a museum somewhere. How sad for science.
I’m still amazed that we humans can send probes anywhere off the planet with accuracy. We are pretty clever monkeys.