
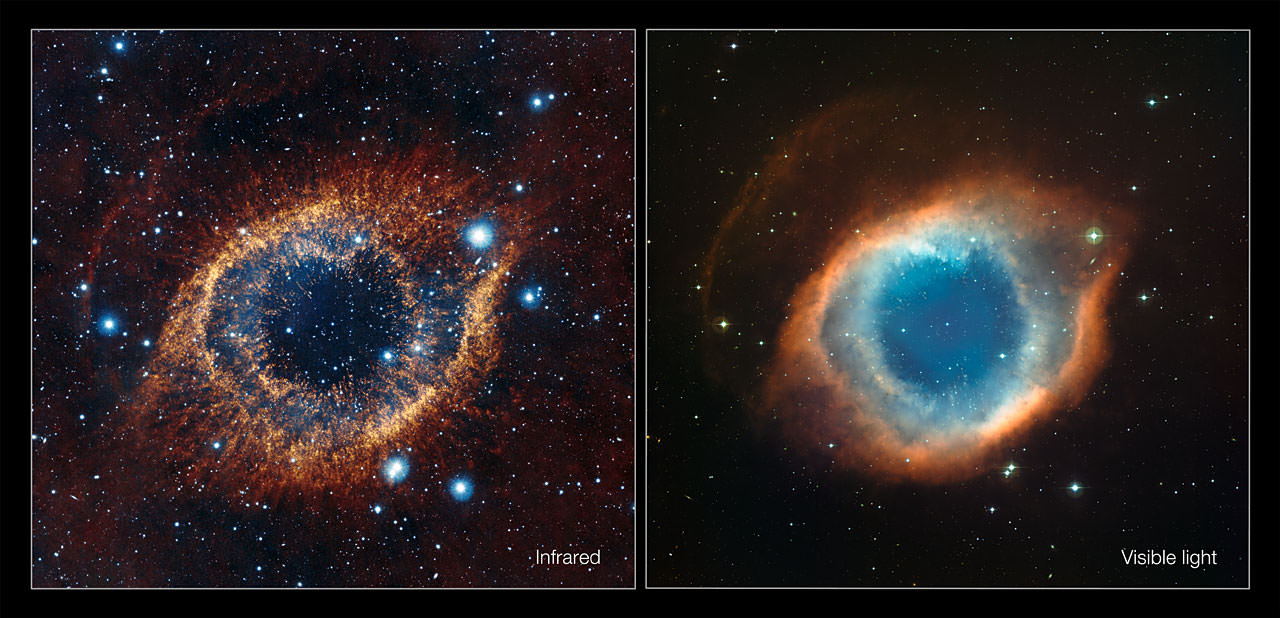
This comparison shows a new view of the Helix Nebula acquired with the VISTA telescope in infrared light (left) and the more familiar view in visible light from the MPG/ESO 2.2-metre telescope (right). The infrared vision of VISTA reveals strands of cold nebular gas that are mostly obscured in visible light images of the Helix. Credit: ESO/VISTA/J. Emerson. Acknowledgment: Cambridge Astronomical Survey Unit
[/caption]
Who is looking at who here? A brand new image of the Helix Nebula (breathlessly called the “Eye of God” in viral email messages) was taken by ESO’s VISTA telescope, at the Paranal Observatory in Chile. In infrared light — compared previous images of the Helix Nebula taken in visible light — the “eye” appears to have put on a colored contact lens, changing the color from blue to brown. What infrared really reveals are strands of cold gases within the nebula, as well as highlighting a rich background of stars and galaxies.
The Helix Nebula is a planetary nebula, and is located in the constellation Aquarius, about 700 light-years away from Earth. This strange object formed when a star like the Sun was in the final stages of its life. In fact, our own Sun might look like this one day, several billion years from now.
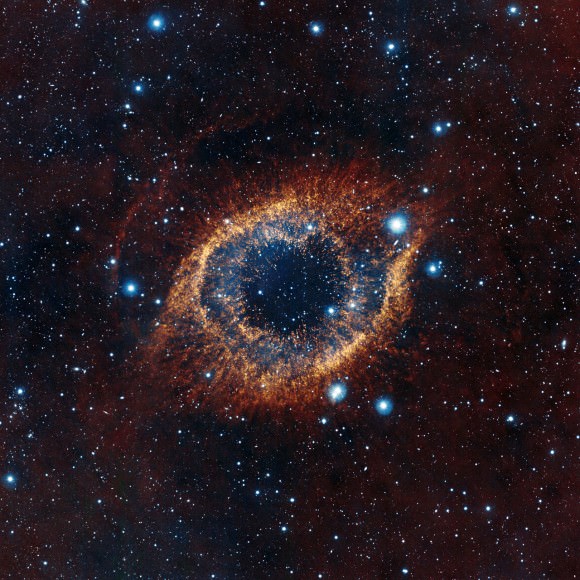


The Helix Nebula is a huge cavern of glowing gases. The main ring of the Helix is about two light-years across, roughly half the distance between the Sun and the nearest star. However, material from the nebula spreads out from the star to at least four light-years. This is particularly clear in this infrared view since red molecular gas can be seen across much of the image.
At its center is a dying star which has ejected masses of dust and gas to form tentacle-like filaments stretching toward an outer rim composed of the same material. Unable to hold onto its outer layers, the hot central star is slowly shedding shells of gas that became the nebula. It is evolving to become a white dwarf star and appears as the tiny blue dot seen at the center of the image.
The VISTA telescope also reveals fine structure in the nebula’s rings. The infrared light picks out how the cooler, molecular gas is arranged. The material clumps into filaments that radiate out from the center and the whole view resembles a celestial firework display – or a giant eye.
Source: ESO
Exoplanets come in a variety of forms and one particular type, the Hot Jupiters have…
Back in the 60’s and 70’s it was all about the Moon. The Apollo program…
NASA’s Curiosity Rover has been exploring Mars since 2012 and, more recently has found evidence…
Gas is the stuff of star formation, and most galaxies have enough gas in their…
The ISS's orbit is slowly decaying. While it might seem a permanent fixture in the…
What came first, galaxies or planets? The answer has always been galaxies, but new research…