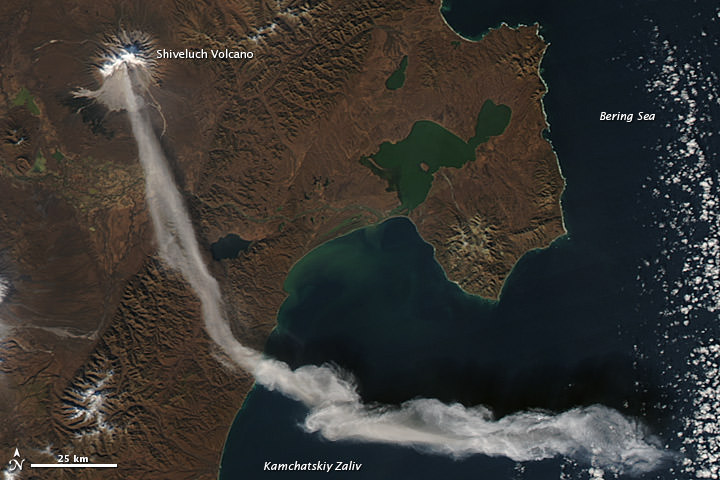
The Shiveluch volcano as seen by the Aqua satellite on October 6, 2012. Credit: NASA
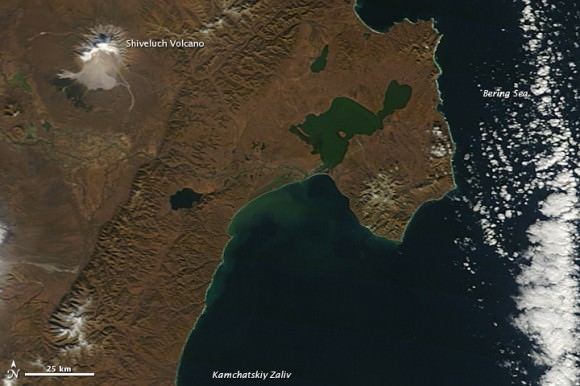
It’s almost like this volcano has an on/off switch. The Shiveluch Volcano in the northern Russian peninsula of Kamchatka had been quiet, and an earlier image taken by NASA’s Terra satellite (below) at about noon local time (00:00 UTC) on October 6, 2012, showed a quiet volcano with no activity. But just two hours later when the Aqua satellite passed over the area, the volcano had erupted and sent a plume of ash over about 90 kilometers (55 miles). Later, a local volcanic emergency response team reported that the ash plume from Shiveluch reached an altitude of 3 kilometers (9,800 feet) above sea level, and had traveled some 220 kilometers (140 miles) from the volcano summit.
The same volcano seen by the Terra satellite just two hours earlier on the same day. Credit: NASA
Shiveluch is one the biggest and most active volcanoes in this region and rises 3,283 meters (10,771 feet) above sea level. NASA’s Earth Observatory website says Shiveluch is a stratovolcano composed of alternating layers of hardened lava, compacted ash, and rocks ejected by previous eruptions. It has had numerous eruptions the past 200 years, but has been active during much of its life – estimates are the volcano is 60,000 to 70,000 years old.
The beige-colored expanse of rock on the volcano’s southern slopes (visible in both images) is due to an explosive eruption that occurred in 1964. Another eruption started in 1999 and lasted for over 10 years.
Source: NASA Earth Observatory