When a supermassive black hole consumes a star, it doesn’t just swallow it whole. It shreds the star, ripping it apart bit by bit before consuming the remains. It’s a messy process known as a tidal disruption event (TDE). Astronomers occasionally catch a glimpse of TDEs, and one recent one has helped solve a mystery about a type of transient X-ray source.
Continue reading “A Black Hole has Destroyed a Star, and Used the Wreckage to Pummel Another Star”Satellites are Tracking the Ongoing Sea Level Rise Swamping Pacific Island Nations

The small island nations of the South Pacific are facing the harsh reality of sea level rise. Within 50 years they will be swamped by rising seas linked to climate change. That’s part of a stark forecast from a sea level change science team at NASA and leading universities.
Continue reading “Satellites are Tracking the Ongoing Sea Level Rise Swamping Pacific Island Nations”Exoplanet Discovered in a Binary System Could Explain Why Red Dwarfs Form Massive Planets
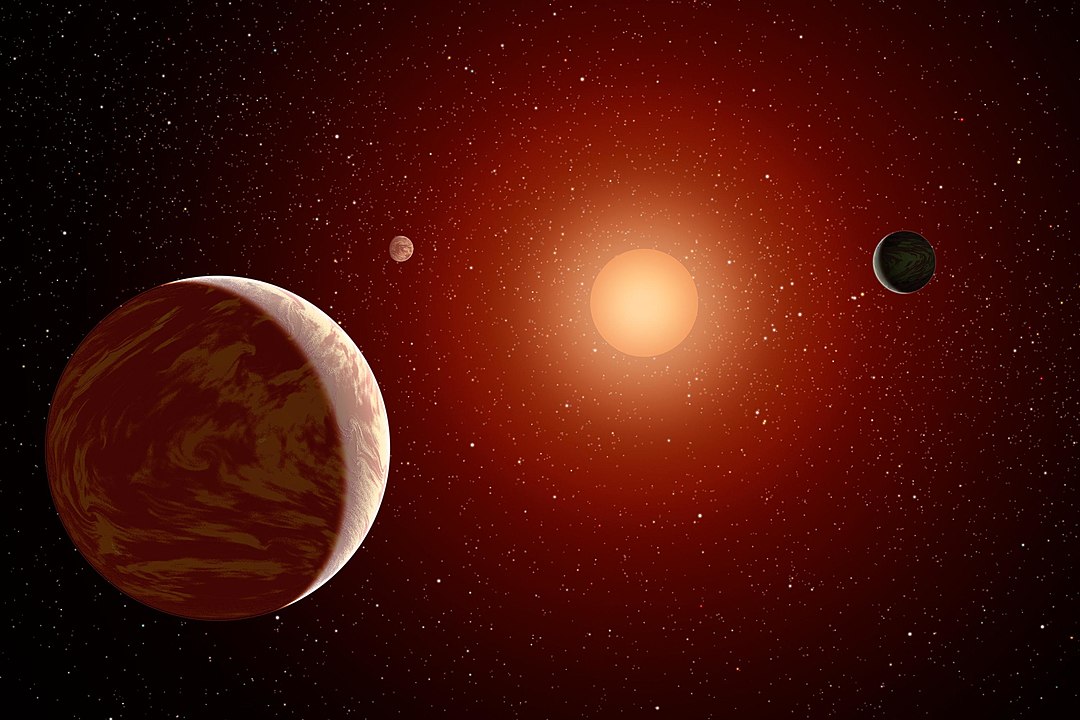
In recent years, the number of known extrasolar planets (aka. exoplanets) has grown exponentially. To date, 5,799 exoplanets have been confirmed in 4,310 star systems, with thousands more candidates awaiting confirmation. What has been particularly interesting to astronomers is how M-type (red dwarf) stars appear to be very good at forming rocky planets. In particular, astronomers have detected many gas giants and planets that are several times the mass of Earth (Super-Earths) orbiting these low-mass, cooler stars.
Consider TOI-6383A, a cool dwarf star less than half the mass of the Sun that orbits with an even smaller, cooler companion – the red dwarf star TOI-6383B. In a recent study, an international team of astronomers with the Searching for Giant Exoplanets around M-dwarf Stars (GEMS) survey detected a giant planet transiting in front of the primary star, designated TOI-6383Ab. This planet is similar in size and mass to the system’s companion star, which raises questions about the formation of giant planets in red dwarf star systems.
Continue reading “Exoplanet Discovered in a Binary System Could Explain Why Red Dwarfs Form Massive Planets”Most Mars Meteorites Came From Five Craters

Meteorites strike Earth every day. It’s estimated that about 100 – 300 metric tonnes of material strike our planet every year. Most of it consists of sand-grain sized dust that burns up in the atmosphere, but each year a few thousand will reach Earth’s surface.
Continue reading “Most Mars Meteorites Came From Five Craters”NASA Reveals the Mind-Boggling Scale of Hurricane Milton seen from Space
We often talk about Jupiter’s Great Red Spot quite candidly but forget that hurricanes can be devastating, destructive forces here on Earth. Hurricane Milton is a reminder of the awful effects here on Earth. It came out of nowhere, appearing in the Gulf of Mexico as a tropical storm and two days later was a category 5 hurricane. It tracked a course and hit land near Siesta Key in Florida. NASA have been tracking the storm from space, recording high sea temperatures that fuelled the storm allowing it to grow. Images have been released from the ISS showing the sheer enormity of the hurricane.
Continue reading “NASA Reveals the Mind-Boggling Scale of Hurricane Milton seen from Space”A New Way to Detect Rocky Exoplanet Atmospheres

The total number of exoplanets discovered to date totals 5,288. Among them are a host of rocky, Earth-like exoplanets but none of them seem to have atmospheres. It’s a fairly challenging observation to make but a team of researchers think they’ve come up with a new, simpler technique. It involves measuring the combined temperature of a star and the exoplanet just before the planet passes behind. If it’s lower than expected, the planet is likely to have an atmosphere regulating its temperature!
Continue reading “A New Way to Detect Rocky Exoplanet Atmospheres”How Did Mars Become Uninhabitable?

Mars has captured our imagination for centuries. Ever since the invention of the telescope our imagination has often drifted toward the possibility of life on Mars. Exploration of the red planet has often revealed that Mars once had plenty of water on its surface but it’s no longer there. Now NASA’s Curiosity rover has found deposits of carbon-rich minerals that could give us a much needed clue.
Continue reading “How Did Mars Become Uninhabitable?”Good News. Comet Encke Only Threw a Handful of Giant Space Rocks in our Direction

As comets travel along their orbit they dump material along the way. A stream of debris known as the Taurid swarm has been keeping astronomers attention. It’s thought the debris is the remains of comet Encke which has also been fuelling the Taurid meteor shower. The swarm is believed to be composed of mostly harmless, tiny objects but there has been concern that there may be some larger, kilometre size chunks. Thankfully, new observations reveal there are of the order of 9-14 of these 1km rocks.
Continue reading “Good News. Comet Encke Only Threw a Handful of Giant Space Rocks in our Direction”NASA Announces a New Class of Space Missions: Probe Explorers
NASA has sent a whole host of spacecraft across the Solar System and even beyond. They range from crewed ships to orbit and to the Moon to robotic explorers. Among them are a range of mission classes from Flagships to Discovery Class programs. Now a new category has been announced: Probe Explorers. This new category will fill the gap between Flagship and smaller missions. Among them are two proposed missions; the Advanced X-ray Imaging Satellite and the Probe Far-Infrared Mission for Astrophysics.
Continue reading “NASA Announces a New Class of Space Missions: Probe Explorers”The Open Star Cluster Westerlund 1, Seen by Webb

A long time ago, the Milky Way Galaxy was busy being a prodigious star-formation engine. In those times, it turned out dozens or hundreds of stars per year. These days, it’s rather more quiescent, cranking out only a few per year. Astronomers want to understand the Milky Way’s star-birth history, so they focus on some of the more recent star litters to study. One of them is Westerlund 1, a young so-called “super star cluster” that looks compact and contains a diverse array of older stars. It was part of a burst of star creation around 4 to 5 million years ago.
Continue reading “The Open Star Cluster Westerlund 1, Seen by Webb”


