Most of the Universe is a complete and total mystery. And one of these mysteries is dark matter. It’s out there, and astronomers are slowly teasing out its characteristics, but it’s not giving up its secrets easily. The problem is, dark matter only interacts with regular matter through gravity (and maybe through the weak nuclear force). It doesn’t shine, it doesn’t give off heat or radio waves, and it passes through regular matter like it isn’t there. But when dark matter is destroyed, it might give astronomers the clues they’re looking for.
Researchers have theorized that one productive way to search for dark matter might not be to search for it directly, but to look for the resulting particles and energy which are emitted when it’s destroyed. In the environment around the centre of our galaxy, dark matter might be dense enough that particles regularly collide, releasing a cascade of energy and additional particles; which could be detected.
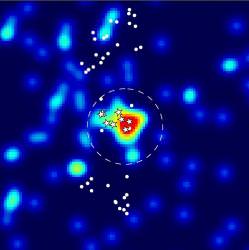
And this theory could help account for a strange result gathered by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), a NASA spacecraft which is mapping the temperature of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR). This background radiation was supposed to be roughly even across the entire sky. But for some reason, the satellite turned up an excess of microwave emission around the centre of our galaxy.
Perhaps this microwave radiation is the glow of all that dark matter getting annihilated.
This conclusion was reached by a team of US astronomers: Dan Hooper, Douglas P. Finkbeiner and Gregory Dobler. Their work is published in a new research paper called Evidence Of Dark Matter Annihilations In The WMAP Haze.
The excess microwave radiation around our galactic centre is known as the WMAP Haze, and was originally thought to be the emissions from hot gas. Astronomers set about trying to confirm this theory, but observations in other wavelengths failed to turn up any evidence.
According to the researchers, the microwave haze could be explained by annihilating particles of dark matter, like the interaction between matter and antimatter. As dark matter particles collide they could give off any number of detectable particles and radiation, including gamma-rays, electrons, positrons, protons, antiprotons and neutrinos.
The size, shape and distribution of the haze matches the central region of our galaxy which should also have a high concentration of dark matter. And if the dark matter particles are within a certain range of mass – 100 to 1000s of times the mass of a proton – they could release a torrent of electrons and positrons that nicely match the microwave haze.
In fact, their calculations precisely match one of the most attractive dark matter particle candidates: the hypothetical neutralino which is predicted in supersymmetry models. When annihilated, these would produce heavy quarks, gauge bosons or the Higgs boson, and would have the right mass and particle size to produce the microwave haze observed by WMAP.
One of the predictions made in this paper is for the upcoming Gamma Ray large Area Space Telescope (GLAST), due to launch in December, 2007. If they’re correct, GLAST will be able to detect a glow of gamma rays coming from the Galactic Centre, matching the microwave haze, and even put an upper limit of the mass of dark matter particles. The upcoming ESA Planck mission will give an even more precise look at the microwave haze, providing better data.
It might still be mysterious, but dark matter is revealing its secrets slowly but surely.
Original Source: Arxiv (PDF)