Image credit: Harvard
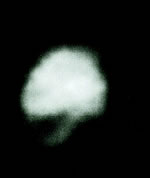
New images taken by the 100-inch Hooker telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory show Asteroid Juno with a huge chunk taken out of it. Harvard astronomer Sallie Baliunas used the adaptive optics system on the Hooker telescope, which compensates for distortions in the atmosphere, to take photos of the 241 km asteroid with incredible clarity. The photos show that Juno is misshapen and has a 100 km crater from an impact with another asteroid in the past.
Cambridge, MA -If someone sneaks a bite of your chocolate chip cookie, they leave behind evidence of their pilferage in the form of a crescent of missing cookie. The same is true in our solar system, where an impact can take a bite out of a planet or moon, leaving behind evidence in the form of a crater. By combining modern technology with a historical telescope, astronomers have discovered that the asteroide Juno has a bite out of it. The first direct images of the surface of Juno show that it is scarred by a fresh impact crater.
Juno, the third asteroid ever discovered, was first spotted by astronomers early in the 19th century. It orbits the Sun with thousands of other bits of space rock in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. One of the largest asteroids, at a size of 150 miles across, Juno essentially is a leftover building block of the solar system.
Astronomer Sallie Baliunas (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) and colleagues photographed Juno when it was located relatively nearby in astronomical terms, about 10 percent further from the Earth than the Earth is from the Sun. Even at that distance, Juno appeared very tiny in the sky, subtending only 330 milli-arcseconds – the equivalent of a dime seen at a distance of 7 miles. Imaging Juno at the high resolution needed to resolve surface details thus presented a challenge.
To solve the problem, the scientists used an adaptive optics system connected to the 100-inch Hooker telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory. Adaptive optics enables astronomers to compensate for the distortion created by air currents in our planet’s atmosphere, yielding images as sharp and clear as those taken in space.
Their surface maps showed that Juno, like other asteroids, is misshapen rather than round, and that it has “sharp” edges. Even better, as Juno tumbled through space during the night of observing, a “bite” came into view – an area that appeared dark as seen at near-infrared wavelengths. The astronomers concluded that the asteroid had recently (in astronomical terms) collided with another object, resulting in a 60-mile-wide crater, or possibly a smaller crater that is surrounded by a 60-mile blanket of ejecta debris.
“I look at an asteroid as a garden – a garden not of flowers and leaves, but one of rubble and dust churned up by constant impacts. This process of gardening pulverizes the asteroid’s surface into a fine-grained regolith,” said Baliunas. “The recent, large impact on Juno gives us an opportunity to see through the regolith and study excavated material from beneath the surface – a rare look into the material out of which the early Earth was formed.”
The blast that knocked a bite out of Juno may also have provided researchers with a convenient way of studying that asteroid up close without ever leaving our planet. Some meteorites found on the Earth are actually pieces of large asteroids like Juno. Those pieces were broken off and launched into space by an impact, and then fell on our planet. The newly-found impact crater on Juno may have sent samples of that asteroid to the Earth.
This remarkable result demonstrates how technology can be used to renew historical observatories, giving them a new lease on life. The Hooker telescope, now nearing the end of its first century of observing, can use adaptive optics systems to obtain views of the cosmos as clear as though the telescope were in space. Hence, the telescope that Edwin Hubble and his assistant used to discover evidence of the expanding universe continues to make groundbreaking discoveries today.
These results were published in the May 2003 issue of the astronomy journal Icarus.
Original Source: CfA News Release







