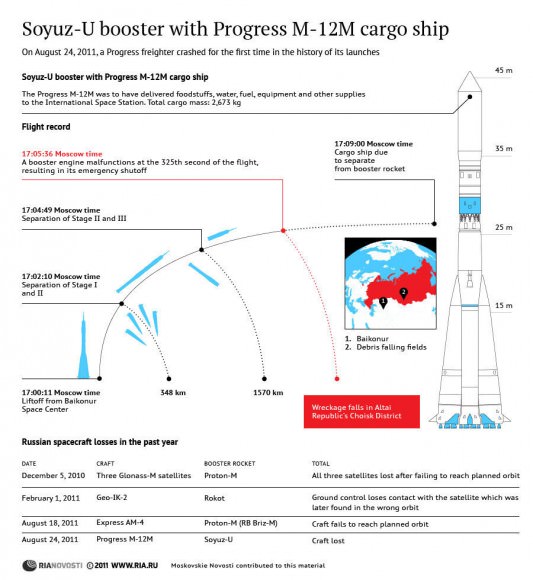
[/caption]
In the fall of 2006, observers at the Catalina Sky Survey in Arizona found an object orbiting the Earth. At first, it looked like a spent rocket stage — it had a spectrum similar to the titanium white paint NASA uses on rocket stages that end up in heliocentric orbits. But closer inspection revealed that the object was a natural body. Called 2006 RH120, it was a tiny asteroid measuring just a few metres across but it still qualified as a natural satellite just like the Moon. By June 2007, it was gone. Less than a year after it arrived, it left Earth’s orbit in search of a new cosmic companion.
Now, astrophysicists at Cornell are suggesting that 2006 RH120 wasn’t an anomaly; a second temporary moon is actually the norm for our planet.
Temporary satellites are a result of the gravitational pull of Earth and the Moon. Both bodies pull on one another and also pull on anything else in nearby space. The most common objects that get pulled in by the Earth-Moon system’s gravity are near Earth objects (NEOs) — comets and asteroids are nudged by the outer planets and end up in orbits that bring them into Earth’s neighbourhood.
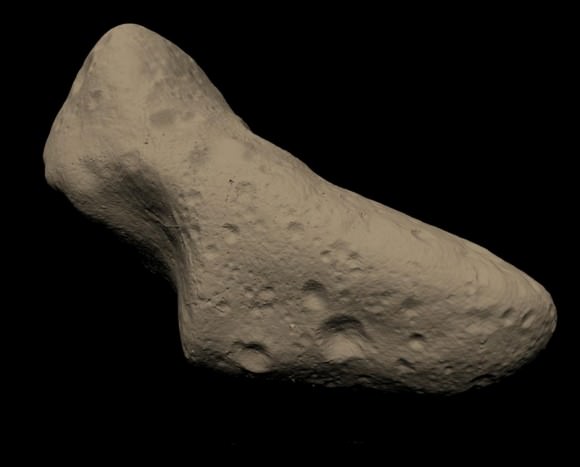
The team from Cornell, astrophysicists Mikael Granvik, Jeremie Vaubaillon, Robert Jedicke, has modeled the way our Earth-Moon system captures these NEOs to understand how often we have additional moons and how long they stick around.
They found that the Earth-Moon system captures NEOs quite frequently. “At any given time, there should be at least one natural Earth satellite of 1-meter diameter orbiting the Earth,” the team said. These NEOs orbit the Earth for about ten months, enough time to make about three orbits, before leaving.
Luckily, and very interestingly, this discovery has implication well beyond academic applications.
Knowing that these small satellites come and go but that one is always present around the Earth, astronomers can work on detecting them. With more complete information on these bodies, specifically their position around the Earth at a given time, NASA could send a crew out to investigate. A crew wouldn’t be able to land on something a few metres across, but they could certainly study it up close and gather samples.
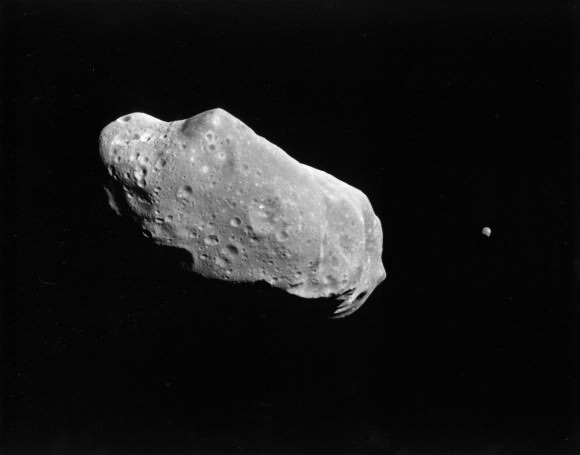

Proposals for a manned mission to an asteroid have been floating around NASA for years. Now, astronauts won’t have to go all the way out to an asteroid to learn about the Solar System’s early history. NASA can wait for an asteroid to come to us.
If the Cornell team is right and there is no shortage of second satellites around the Earth, the gains from such missions increases. The possible information about the solar system’s formation that we could obtain would be amazing, and amazingly cost-efficient.