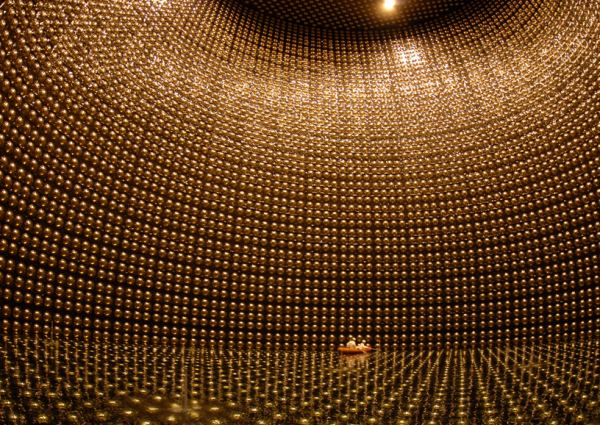
Readers of Universe Today are probably already familiar with the concept of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Its serendipitous discovery by a pair of radio astronomers at Bell Labs is the stuff of astronomical legend. Over the past decades, it has offered plenty of insights into the Big Bang and the origins of our universe. But there is another, less well-known background signal that could be just as revolutionary – or at least we think there is. The Cosmic Neutrino Background (CvB) has been posited for years but has yet to be found, primarily because neutrinos are notoriously difficult to detect. Now, a paper from Professor Douglas Scott of the University of British Columbia, developed as part of a summer school on neutrinos held by the International School of AstroParticle Physics in the Italian town of Varenna, discusses what we could potentially learn if we do manage to detect the CvB eventually.
Continue reading “The Cosmic Neutrino Background Would Tell Us Plenty About the Universe”How Long Will Advanced Civilizations Try to Communicate With Us?
Technosignature research is heating up, with plenty of papers speculating on the nature, and sometimes the longevity, of signals created by technically advanced extraterrestrial civilizations. While we haven’t found any so far, that isn’t to say that we won’t, and a better understanding of what to look for would undoubtedly help. Enter a new paper by Amedeo Balbi and Claudio Grimaldi, two professors at the Universita di Roma Tor Vergata and the Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, respectively. They have taken a statistical model to the problem of understanding how old a technosignature might be before we are likely to find it – and their answer is, surprisingly young.
Continue reading “How Long Will Advanced Civilizations Try to Communicate With Us?”Drones Could Help Map the Lunar Surface with Extreme Precision
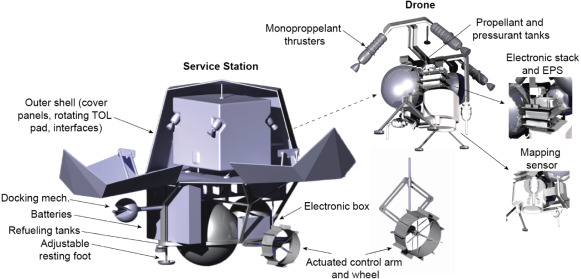
Exploring the Moon has become increasingly more of a focal point lately, especially with a series of landers recently launched with various degrees of success. One of the difficulties those landers and any future human missions face is understanding the terrain they are landing on and potentially traversing in the case of a rover or human. To help fight this problem, a team of researchers from Switzerland has developed a drone concept that could help map out some of the more interesting, potentially hazardous areas to explore on the Moon.
Continue reading “Drones Could Help Map the Lunar Surface with Extreme Precision”Mars Had its Own Version of Plate Tectonics
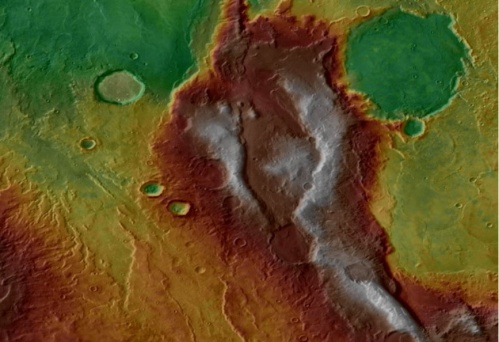
Plate tectonics is not something most people would associate with Mars. In fact, the planet’s dead core is one of the primary reasons for its famous lack of a magnetic field. And since active planetary cores are one of the primary driving factors of plate tectonics, it seems obvious why that general conception holds. However, Mars has some features that we think of as corresponding with plate tectonics – volcanoes. A new paper from researchers at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) looks at how different types of plate tectonics could have formed different types of volcanoes on the surface of Mars.
Continue reading “Mars Had its Own Version of Plate Tectonics”New NASA Report Suggests We Could See Space-Based Power After 2050
Space-based solar power (SBSP) has been in the news recently, with the successful test of a solar power demonstrator in space taking place last summer. While the concept is fundamentally sound, there are plenty of hurdles to overcome if the technology is to be widely adopted – not the least of which is cost. NASA is no stranger to costly projects, though, and they recently commissioned a study from their internal Office of Technology, Policy, and Strategy that suggests how NASA could continue to support this budding idea. Most interestingly, if the technological cards are played right, SBSP could be the most carbon-efficient, lowest-cost power source for humanity by 2050.
Continue reading “New NASA Report Suggests We Could See Space-Based Power After 2050”One of NASA’s Radio Dishes Can Now Track Space Lasers Too
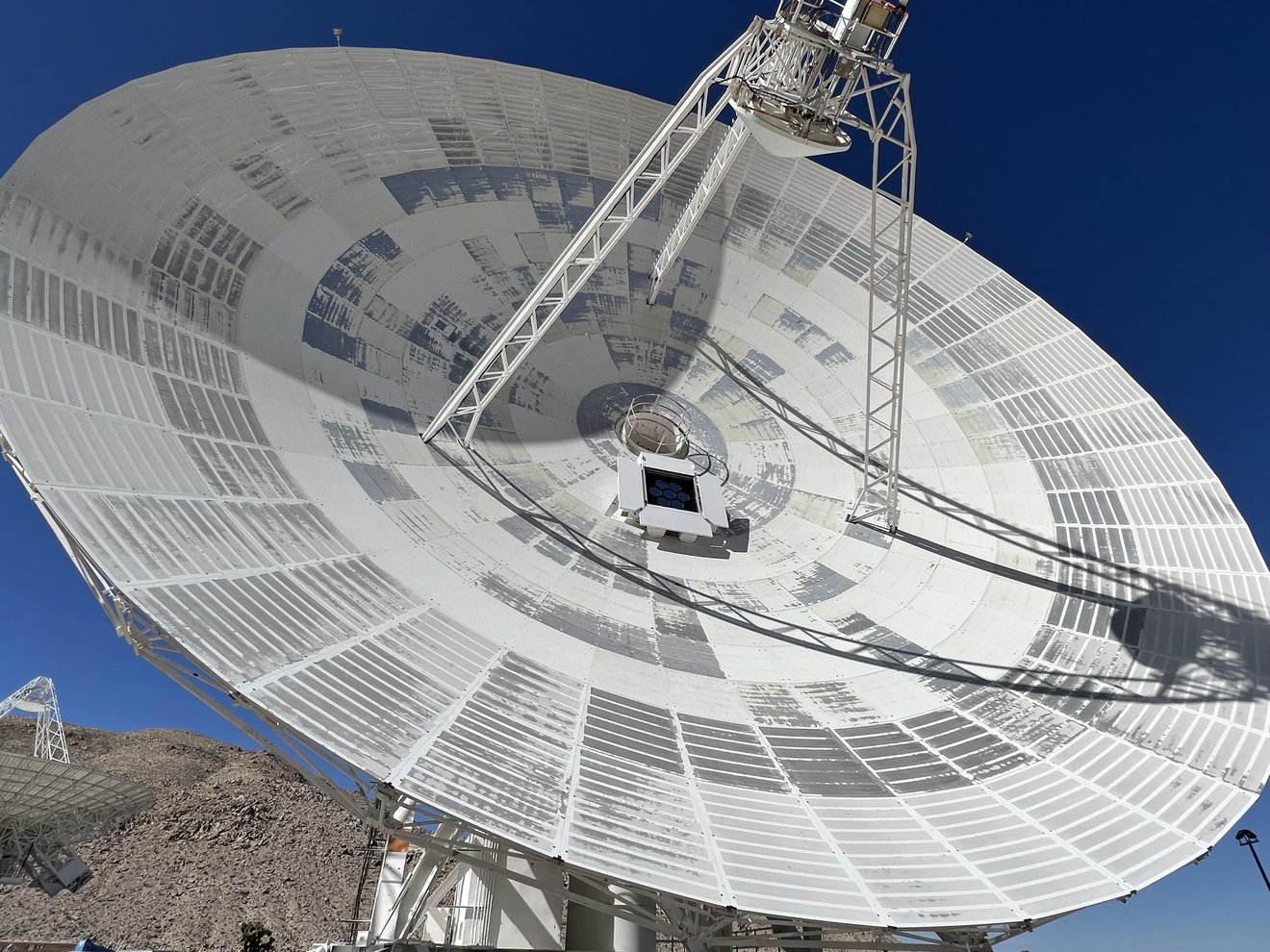
Beamed communication in space is almost exclusively tracked by one network – NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN) is used to communicate with nearly every spacecraft that has made its way past the Moon. Until recently, that has meant exclusively using radio communication, which can be extremely slow compared to other forms. But a recent test shows that, with some modification, DSN’s telescopes can communicate using a much more modern type of technology – space lasers.
Continue reading “One of NASA’s Radio Dishes Can Now Track Space Lasers Too”The Early Universe Had Small Galaxies with Oversized Black Holes
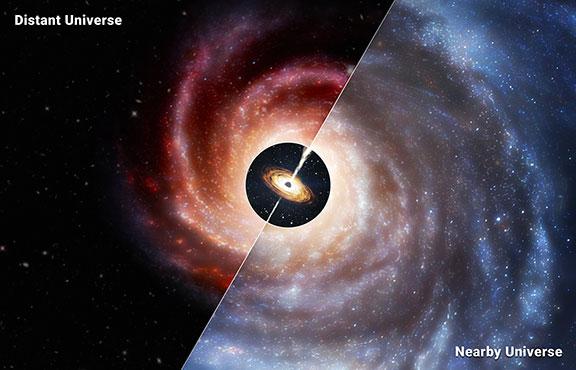
When doing the marketing for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), NASA and the other telescope contributors liked to point out how it would open up the early universe to scrutiny. They weren’t exaggerating, and now scientific studies are starting to proliferate that show why. A new study published by authors from Harvard, the University of Arizona, and the University of Cambridge used three surveys produced by the JWST to analyze the supermassive black holes at the center of early galaxies. And they found they were much different than the one at the center of our own, at least in terms of relative size.
Continue reading “The Early Universe Had Small Galaxies with Oversized Black Holes”What Future Propulsion Technologies Should NASA Invest In?
Researchers consistently complain about how difficult it is to fund breakthrough research. Most funding agencies, especially governmental ones, think funding incremental, evolutionary technological steps is the way to go, as it has the most significant immediate payback. But longer-term, higher-risk research is necessary to provide those incremental steps 20-30 years in the future. And in some cases, they are required to underpin completely new things that other researchers want to do.
Continue reading “What Future Propulsion Technologies Should NASA Invest In?”Astronomers Identify 164 Promising Targets for the Habitable Worlds Observatory
Planning large astronomical missions is a long process. In some cases, such as the now functional James Webb Space Telescope, it can literally take decades. Part of that learning process is understanding what the mission will be designed to look for. Coming up with a list of what it should look for is a process, and on larger missions, teams of scientists work together to determine what they think will be best for the mission. In that vein, a team of researchers from UC Berkeley and UC Riverside have released a paper describing a database of exoplanets that could be worth the time of NASA’s new planned habitable planet survey, the Habitable Worlds Observatory HWO.
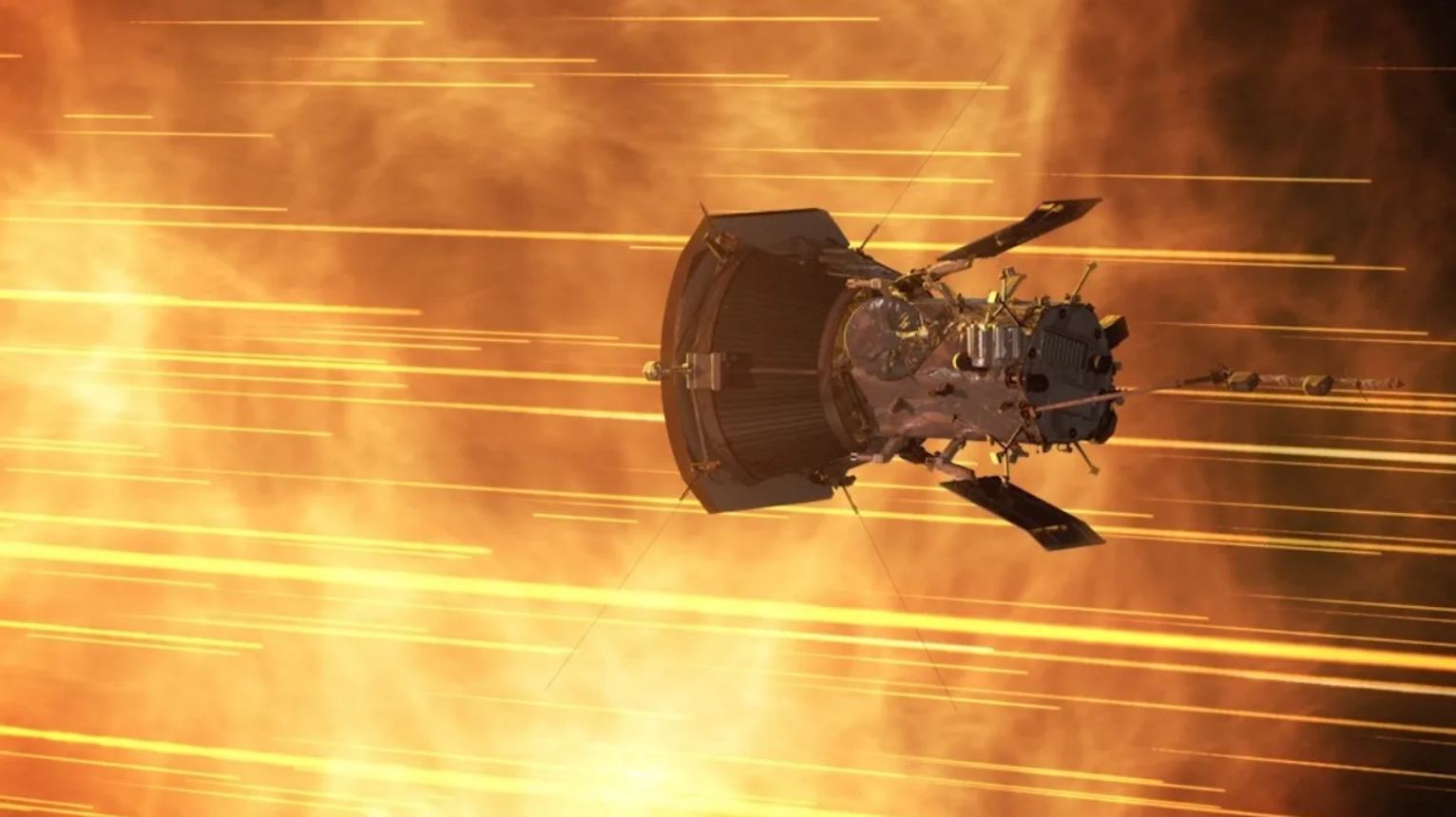
Continue reading “Astronomers Identify 164 Promising Targets for the Habitable Worlds Observatory”Parker Solar Probe Skims the Sun on its 18th Flyby
The fasted object ever made by humans has completed another milestone. The Parker Solar Probe recently celebrated the new year by completing its 18th flyby of the Sun.
Continue reading “Parker Solar Probe Skims the Sun on its 18th Flyby”