Titan is one of the solar system’s most fascinating worlds for several reasons. It has something akin to a hydrological cycle, though powered by methane. It is the solar system’s second-largest moonMooner our own. It is the only other body with liquid lakes on its surface. That’s part of the reason it has attracted so much attention, including an upcoming mission known as Dragonfly that hopes to use its thick atmosphere to power a small helicopter. But some of the most interesting features on Titan are its lakes, and Dragonfly, given its means of locomotion, can’t do much with those other than look at them from afar. So another mission, initially conceived by James McKevitt, then an undergraduate at Loughborough University but now a PhD student at University College London would take a look at both their surface and underneath.
Continue reading “A Mission to Dive Titan’s Lakes – and Soar Between Them”Need to Accurately Measure Time in Space? Use a COMPASSO
Telling time in space is difficult, but it is absolutely critical for applications ranging from testing relativity to navigating down the road. Atomic clocks, such as those used on the Global Navigation Satellite System network, are accurate, but only up to a point. Moving to even more precise navigation tools would require even more accurate clocks. There are several solutions at various stages of technical development, and one from Germany’s DLR, COMPASSO, plans to prove quantum optical clocks in space as a potential successor.
Continue reading “Need to Accurately Measure Time in Space? Use a COMPASSO”Antimatter Propulsion Is Still Far Away, But It Could Change Everything
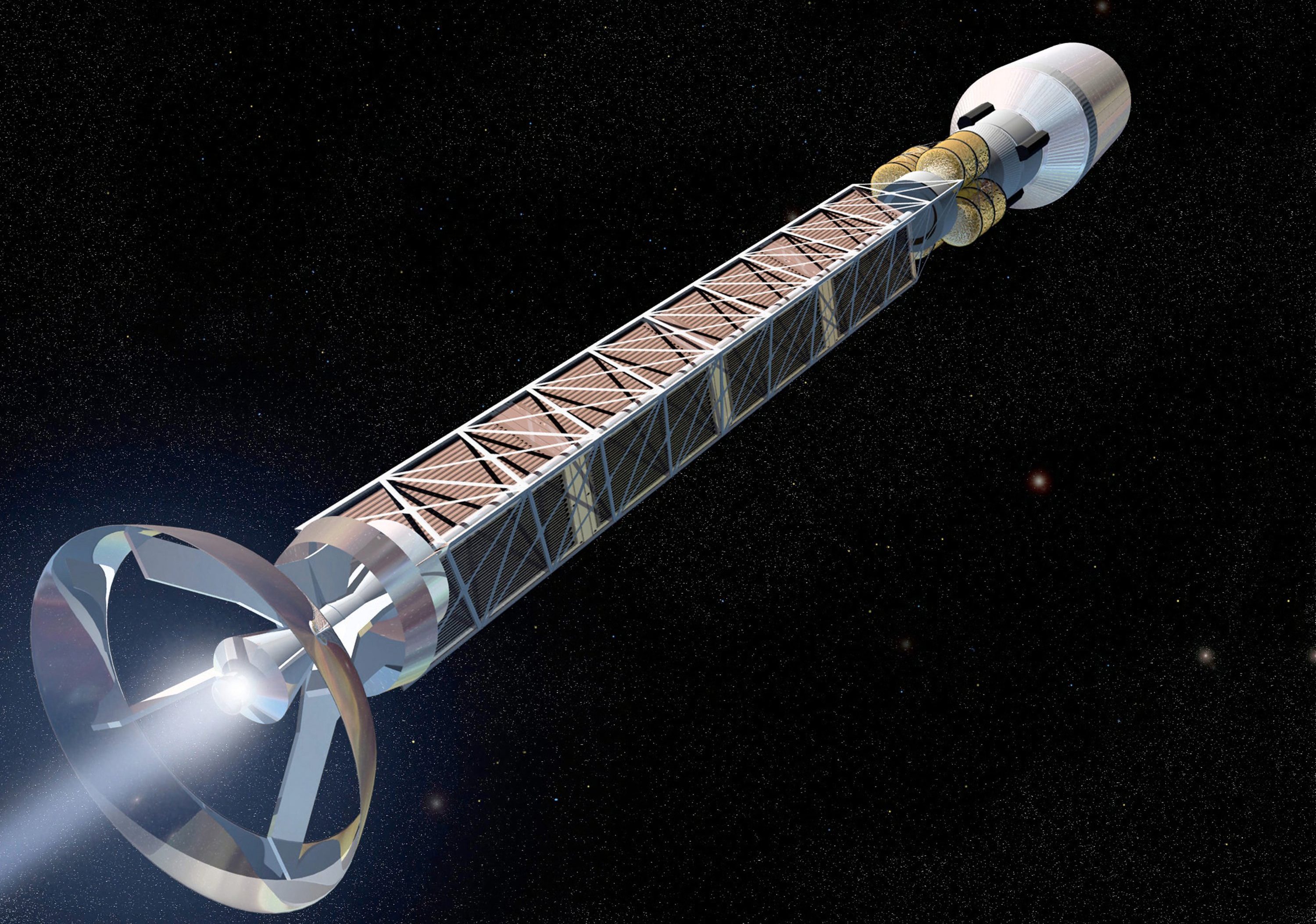
Getting places in space quickly has been the goal of propulsion research for a long time. Rockets, our most common means of doing so, are great for providing lots of force but extraordinarily inefficient. Other options like electric propulsion and solar sailing are efficient but offer measly amounts of force, albeit for a long time. So scientists have long dreamed of a third method of propulsion – one that could provide enough force over a long enough time to power a crewed mission to another star in a single human lifetime. And that could theoretically happen using one of the rarest substances in the universe – antimatter.
Continue reading “Antimatter Propulsion Is Still Far Away, But It Could Change Everything”A Commercial Tie-Up Bring High-Energy Nuclear Electric Propulsion Closer to Reality

Propulsion technologies are the key to exploring the outer solar system, and many organizations have been working on novel ones. One with a long track record is the Ad Astra Rocket Company, which has been developing its Variable Specific Impulse Magnetoplasma Rocket (VASIMR) system for decades. However, this type of electric propulsion system requires a lot of energy, so the company has opted for a unique tie-up for a power plant that could solve that problem – a nuclear reactor. Ad Astra has recently entered into a strategic alliance with the Space Nuclear Power Corporation, or SpaceNukes, responsible for developing the Kilopower reactor, a 1kW nuclear reactor for use in space missions.
Continue reading “A Commercial Tie-Up Bring High-Energy Nuclear Electric Propulsion Closer to Reality”A Cheap Satellite with Large Fuel Tank Could Scout For Interplanetary Missions
A spacecraft that can provide the propulsion necessary to reach other planets while also being reproducible, relatively light, and inexpensive would be a great boon to larger missions in the inner solar system. Micocosm, Inc., based in Hawthorne, California, proposed just such a system via a NASA Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grant. Its Hummingbird spacecraft would have provided a platform to visit nearby planets and asteroids and a payload to do some basic scouting of them.
Continue reading “A Cheap Satellite with Large Fuel Tank Could Scout For Interplanetary Missions”A 3U CubeSat Could Collect Data During an Asteroid Flyby

One of the great things about CubeSat designs is that they constrain the engineers who design them. Constraints are a great way to develop novel solutions to problems that might otherwise be ignored without them. As CubeSats become increasingly popular, more and more researchers are looking at how to get them to do more with less. A paper from 2020 contributes to that by designing a 3U CubeSat mission that weighs less than 4 kilograms to perform a fly-by of a Near Earth Asteroid (NEA) using entirely off-the-shelf parts.
Continue reading “A 3U CubeSat Could Collect Data During an Asteroid Flyby”Could We Use An Asteroid to Shield Astronauts On Their Way to Mars?
Radiation is a primary concern for long-duration human spaceflight, such as the planned trips to Mars, which are the stated goal of organizations such as NASA and SpaceX. Shielding is the standard way to protect astronauts from radiation during those flights. However, shielding is heavy and, therefore, expensive when it is launched off the Earth. What if, instead, astronauts could hitch a ride on a giant mass of shielding already in space that will take them directly to their destination? That is the basic thought behind a paper from Victor Reshetnyk and his student at Taras Shevchenko National University in Kyiv.
Continue reading “Could We Use An Asteroid to Shield Astronauts On Their Way to Mars?”NASA Wants Students’ Help Designing Missions to Other Moons
One of NASA’s primary missions is to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers to join the STEM field. It does so by producing inspirational and educational content on various platforms. But sometimes, it takes a more direct approach by rewarding students for their contributions to solving a particular problem NASA is facing. Recently, the organization announced such a challenge – the Power to Explore Challenge, which is open to submission from K-12 students until the end of January.
Continue reading “NASA Wants Students’ Help Designing Missions to Other Moons”A New Reconfigurable Structure Could Be Used to Make Space Habitats
Even some fields that seem fully settled will occasionally have breakthrough ideas that have reverberated impacts on the rest of the fields of science and technology. Mechanics is one of those relatively settled fields – it is primarily understood at the macroscopic level, and relatively few new breakthroughs have occurred in it recently. Until a few years ago, when a group of Harvard engineers developed what they called a totimorphic structure, and a recent paper by researchers at ESA’s Advanced Concepts Team dives into detail about how they can be utilized to create megastructures, such as telescope mirrors and human habitats in space.
Continue reading “A New Reconfigurable Structure Could Be Used to Make Space Habitats”NASA Is Seeking Ideas for Rescuing an Astronaut from the Moon
Space exploration is a dangerous business, especially when squishy living organisms, such as humans, are involved. NASA has always prided itself on how seriously it takes the safety of its astronauts, so as it gears up for the next big push in crewed space exploration, the Artemis program, it is looking for solutions to potentially catastrophic situations that might arise. One such catastrophe would be if one of the Artemis astronauts was incapacitated and couldn’t return to the lander. The only person who could potentially be able to save them would be their fellow astronaut, but carrying a fully suited human back to their base of operations would be a challenge for an astronaut similarly kitted out in their own bulky suit. So, NASA decided to address it as precisely that – a challenge – and ask for input from the general public, offering up to $20,000 for the best solution to the problem.
Continue reading “NASA Is Seeking Ideas for Rescuing an Astronaut from the Moon”