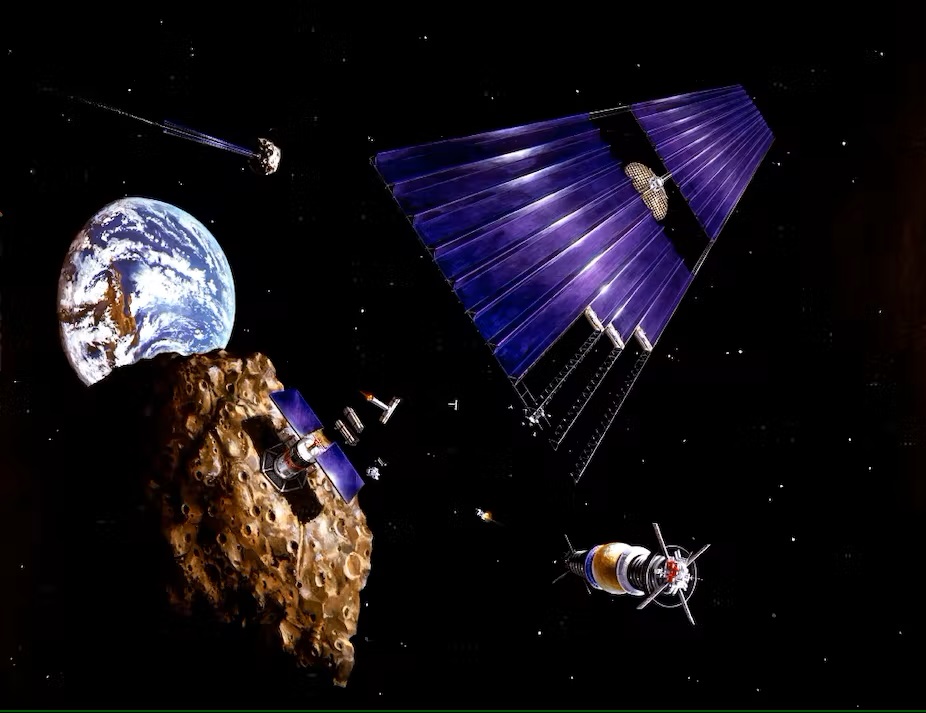
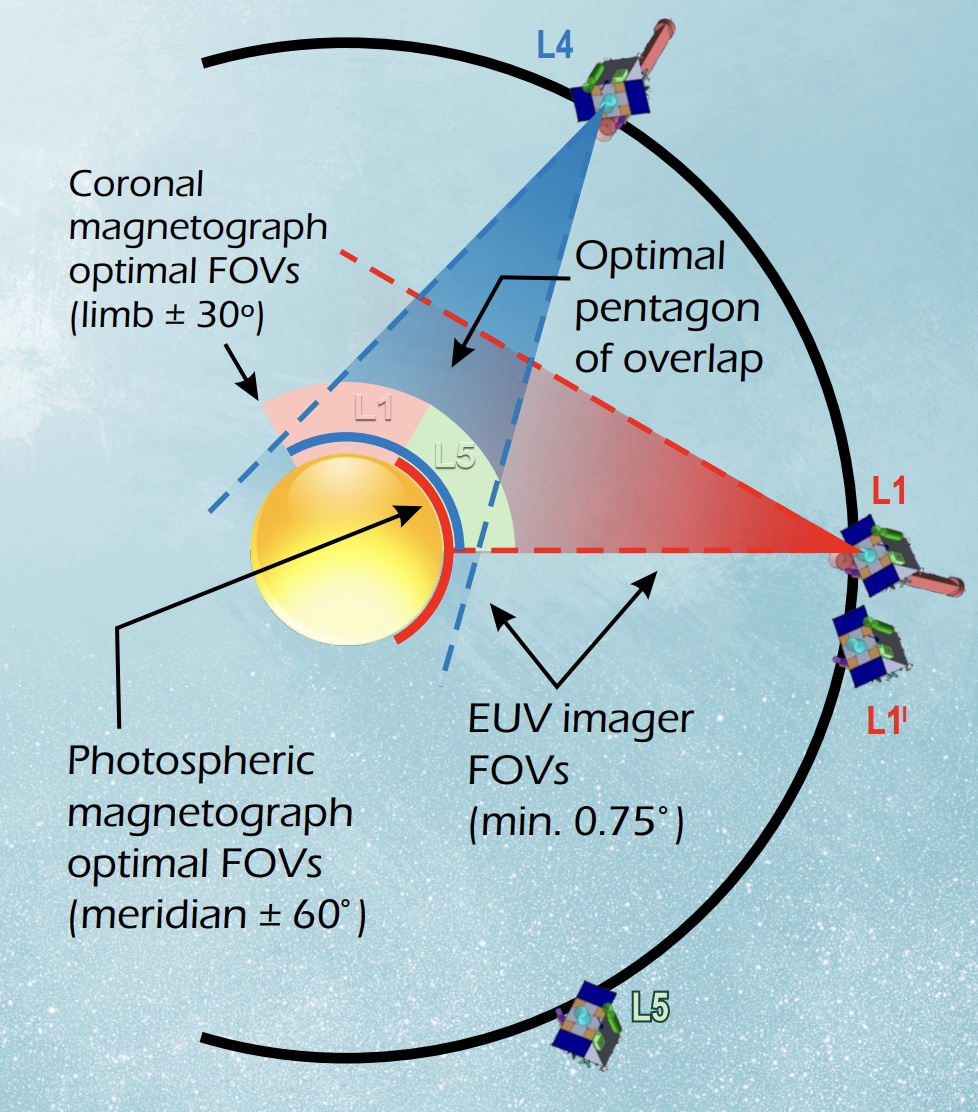
There are always more space missions than there is money to support them. Ultimately, some make the funding cut, and some do not. Various factors go into that decision, though those factors can change over the years and decades that some of these missions are designed to take. But the more ideas, the better, and now a new idea has sprung up from a group of scientists at SWRI, NASA, and the University of Minnesota, among others. It involves four different probes sent to various points in the solar system to observe the Sun as it has never been seen before – and just in time to see its most spectacular display in 2032.
Continue reading “The Sun Reaches Solar Maximum in 2032. A new NASA Flagship Mission Could Give Us a Perfect View”What Role Will NASA Play In Developing ISRU On The Moon?

Space agencies will play a vital role in the developing space economy, especially in the beginning. But what will the part of the biggest of all space agencies be when considering how space resources, especially those on the Moon, are accessed? NASA has a plan for that as it does for so many other things – and this article will dig into a slideshow that describes that plan in detail.
Continue reading “What Role Will NASA Play In Developing ISRU On The Moon?”SLS Could Launch a Sample Return Mission to Phobos and Deimos

NASA’s next colossal rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS), recently had its first successful flight back in November after years of development. Much of that development was done by aerospace contractors like Northrop Grumman and Boeing, so it is a good bet that engineers at those companies want the SLS to be seen as a success. One measure of its success will be how many missions it manages to help launch successfully – the more missions, the better. To help plan out some of those missions, a pair of Boeing engineers wrote a paper describing an outline of a sample return mission to Phobos and Deimos. And, of course, it would be launched by the SLS.
Continue reading “SLS Could Launch a Sample Return Mission to Phobos and Deimos”Airbus Developed a System To Extract Oxygen and Metal From Lunar Regolith

New technologies utilizing material found in space are constantly popping up, sometimes from smaller companies and sometimes from larger ones. Back in 2020, one of the largest companies of them all announced a technology that could have significant implications for the future lunar exploration missions planned over the next ten years. The European aerospace giant Airbus developed the Regolith to OXYgen and Metals Conversion (ROXY) system.
Continue reading “Airbus Developed a System To Extract Oxygen and Metal From Lunar Regolith”It Might Take Space Telescopes to Finally Resolve the Crisis in Cosmology
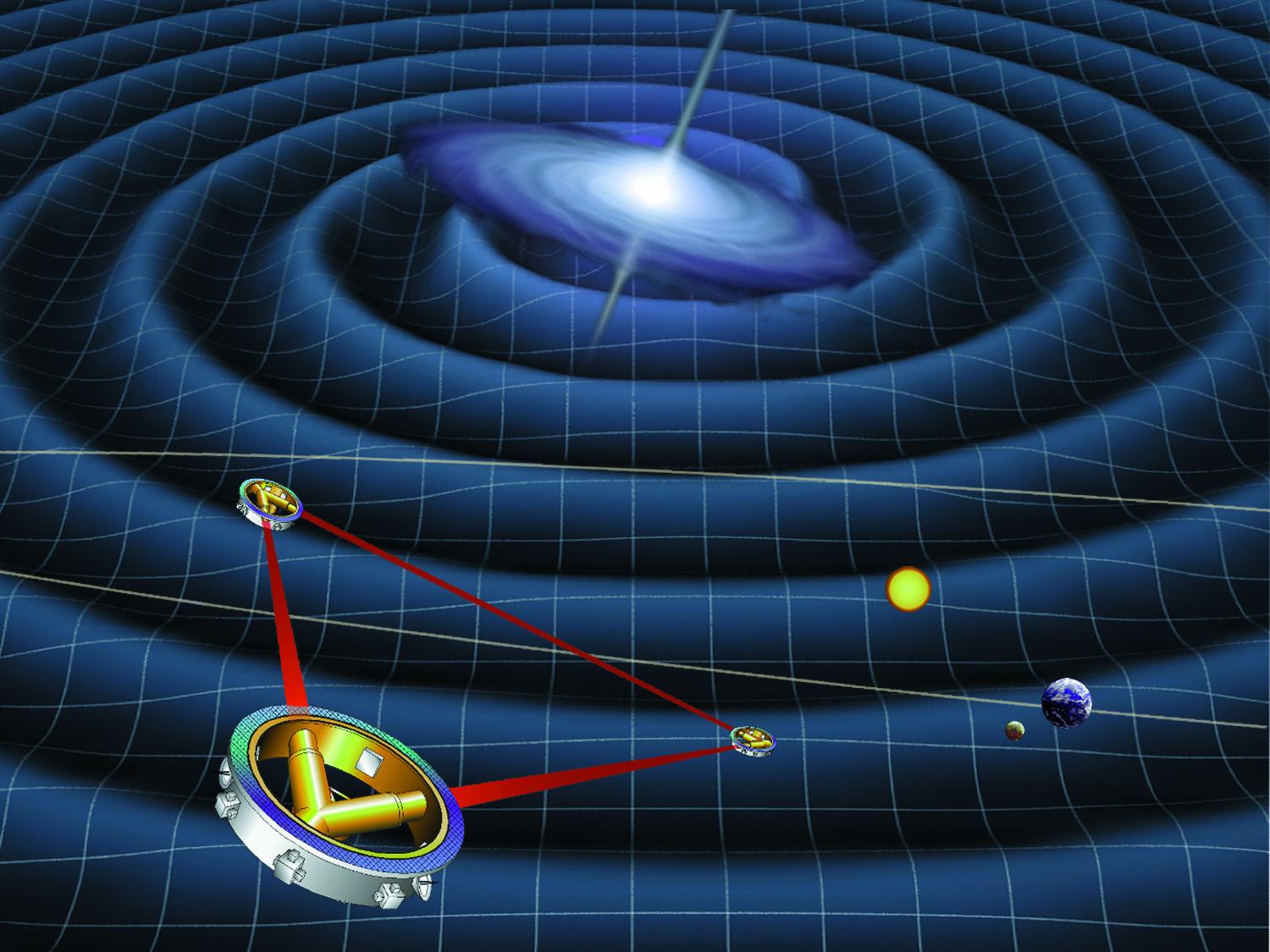
Gravitational wave (GW) observatories have been a great addition to cosmologists’ arsenal in the lack decade. With their first effective detection at the Laser Interferometric Gravitational Observatory completed in 2015, they opened up a whole new world of data collection for scientists. However, so far, they haven’t solved one of the fundamental problems at the heart of their discipline – the “Hubble tension.” Now a new paper discusses the possibility of utilizing a network of new, space-based gravitational wave observatories to get closer than ever to the real value of one of the most important numbers in the Universe.
Continue reading “It Might Take Space Telescopes to Finally Resolve the Crisis in Cosmology”NASA Has a Plan to Power the Moon

Despite all the hype surrounding the coming of the commercial space age, NASA and other governmental agencies will still play a vital role in the early stages of getting much of the infrastructure up and running before commercial actors can come in. That role will primarily be filled by being the first (and sometimes only) customer for a wide variety of companies that hope to profit from exploiting space resources.
Continue reading “NASA Has a Plan to Power the Moon”Robots in orbit are becoming even more popular. There are still many technical challenges ahead.
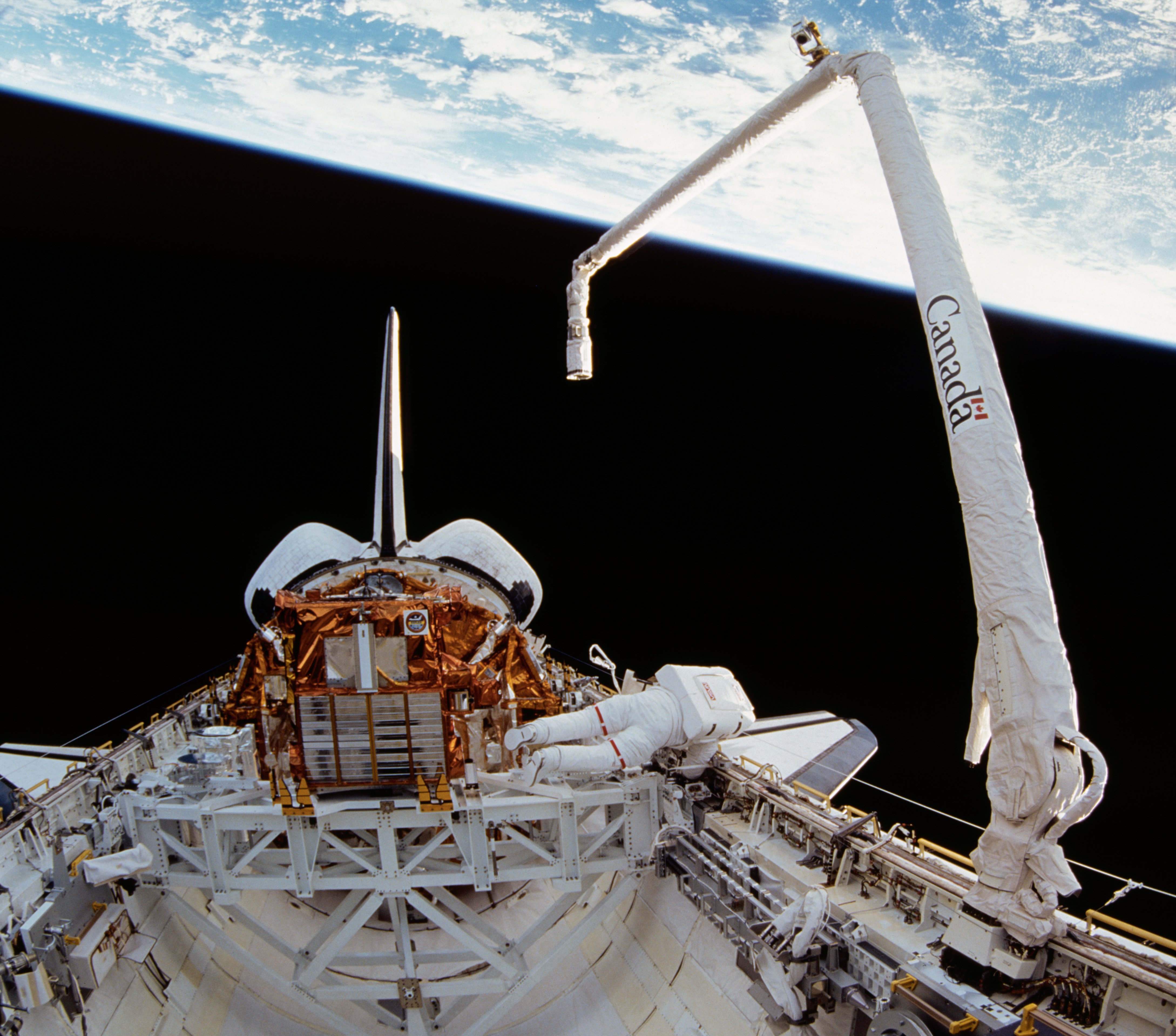

Robots will be one of the keys to the expanding in-space economy. As launch costs decrease, hopefully significantly when Starship and other massive lift systems come online, the most significant barrier to entry for the space economy will finally come down. So what happens then? Two acronyms have been popping up in the literature with increasing frequency – in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing (ISAM) and On-orbit servicing (OOS). Over a series of articles, we’ll look at some papers detailing what those acronyms mean and where they might be going shortly. First, we’ll examine how robots fit into the equation.
Continue reading “Robots in orbit are becoming even more popular. There are still many technical challenges ahead.”Want to be an asteroid miner? There’s a database for that.
Asteroid mining is slowly but surely coming closer to reality. Many start-ups and governmental agencies alike are getting in on the action. But plenty of tools that would help get this burgeoning industry off the ground are still unavailable. One that would be particularly useful is a list of potential candidate asteroids to visit. While the information has been available in various places, no one has yet combined it into a single, searchable database until now.
Continue reading “Want to be an asteroid miner? There’s a database for that.”An Astronaut Will Be Controlling Several Robots on Earth… from Space
Germany’s DLR has been hosting a series of robotic teleoperation experiments where an astronaut abroad the ISS controls a robot back on the ground. We’ve previously reported on some of their successes. Now it’s time for the next round of experiments, with one individual astronaut on the ISS controlling four separate robots to perform a task back on Earth.
Continue reading “An Astronaut Will Be Controlling Several Robots on Earth… from Space”The Heaviest Neutron Stars Could Have Strange Matter Cores
Physics gets weird at the extremes. Astrophysics usually deals with the extremely large – large energies, large gravities, and lots and lots of stuff. Quantum mechanics, on the other hand, typically deals with the extremely small – quarks and other particles that are completely unseen by the human eye. So far, despite decades of trying, no Grand Unified Theory (or any other theory) combines these two opposed theories. This makes it all the more interesting that a team from the Purple Mountain Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed an idea that the interior cores of neutron stars, one of the most extreme examples of large extremes in the universe, might be made up of a type of tiny particle that makes up part of the “soup” of quantum mechanics called a strange quark.
Continue reading “The Heaviest Neutron Stars Could Have Strange Matter Cores”