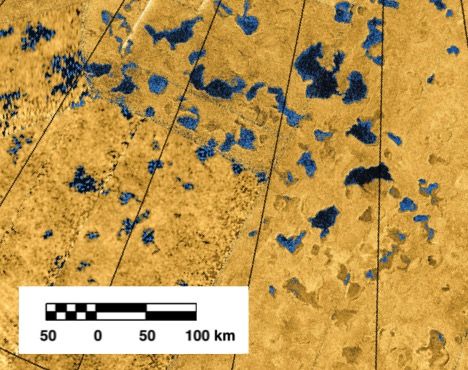
Lakes on Earth are a common sight in many locales. They’re central to the recreation and livelihood of millions of people. Few of those people think of the hydrodynamics that happen in a lake system. It is common for lakes to stratify into different layers. On Earth that stratification is the result of the sun heating the upper layer of water, which then becomes less dense and floats on top of the colder, more dense layer beneath it. Now, scientists from the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) have found similar dynamic cycles in a different kind of lake – the ethane and methane lakes on Titan.
Continue reading “Lakes On Titan Will Have Layers, Like Lakes On Earth, But for a Completely Different Reason”Testing the Rover That’ll Land on Phobos
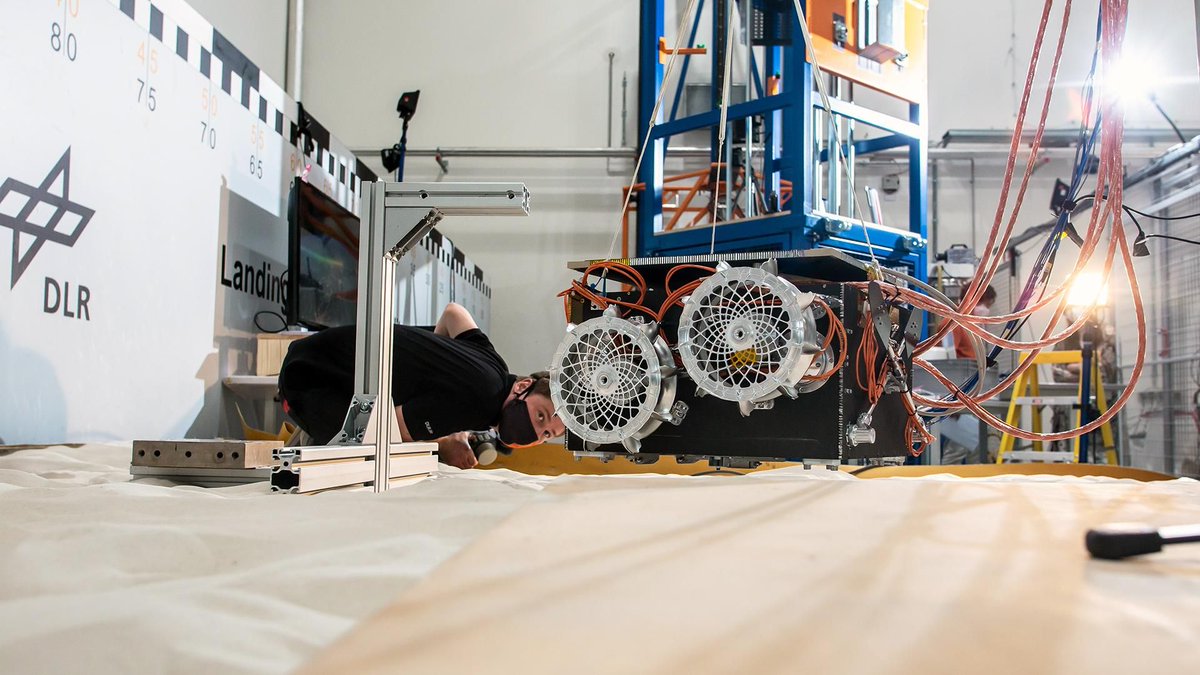
Rovers seem to be proliferating all over Mars. There are currently 4 on the surface, and another (Perseverance) will be arriving in a few months after a successful launch at the end of July. Mars itself isn’t the only interesting rocky body in the Martian system, however. Its two moons, Phobos and Deimos, pose a bit of a mystery. How were they formed? Were they captured asteroids or caused by an impact similar to Earth’s own Moon?
Scientists and engineers are now one step closer to answering those questions with the successful test of a rover that will visit Phobos with JAXA’s Martian Moon Exploration (MMX) mission that will launch in 2024. The rover, which has yet to be separately named from its parent mission, just underwent some testing that will help to prove it’s worthy to join the pantheon of rovers roaming around the Martian system.
Continue reading “Testing the Rover That’ll Land on Phobos”Is There Life Deep Underground on Mars?
It’s been a great month for planetary science. Scientists first discovered the chemical signature of phosphine on Venus, then found additional underground lakes on Mars. While no life has been conclusively found yet, science continues to take incremental steps toward proving what could be one of the most impactful discoveries in history: that we are not alone.
But in order to definitively prove that, science will have to conclusively find life first. The methods for doing so will differ dramatically based on whether the location is in the clouds of Venus or under the ice of Mars. Scientists have come up with a model to understand the conditions for any life to exist in the subsurface oceans of not only Mars, but any rocky body with underground liquid water.
Continue reading “Is There Life Deep Underground on Mars?”New Radio Telescope Is Going to Fly to the Far Side of the Moon to Listen to the Signals From the Early Universe
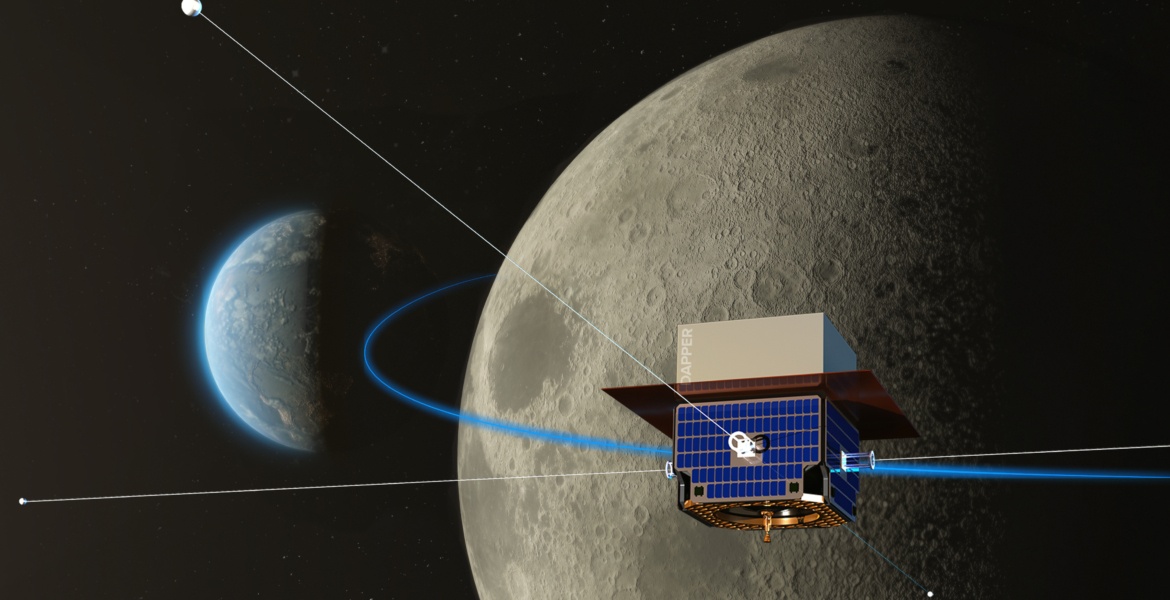
The phrase “silence is golden” is even more important for radio astronomers. The sheer amount of radio output created by humans can drown out any interesting signal from the heavens that they might wish to study. Those signals are also partially blocked by Earth’s atmosphere, adding more complexity to the challenge.
The obvious solution to the atmosphere problem is to launch space based observatories, and that has been done in the past. However, in near Earth orbit the radio waves emitted from radio stations all around the world can still blast any radio receiver with an unwanted deluge of signals. So scientists have come up with a novel idea to get the silence they so crave: park a probe on the far side of the moon.
Continue reading “New Radio Telescope Is Going to Fly to the Far Side of the Moon to Listen to the Signals From the Early Universe”Asteroid Bennu has little pieces of Vesta on it
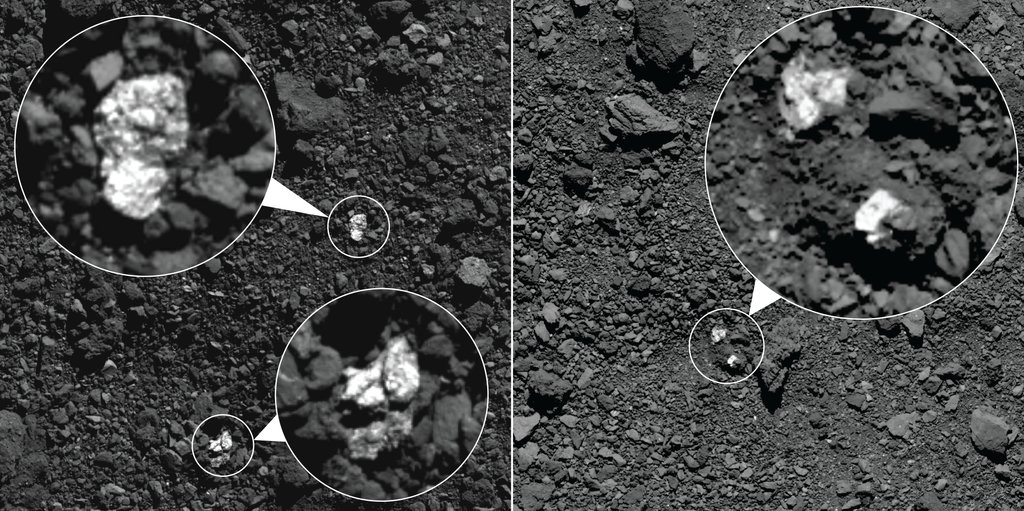
The asteroid belt is a chaotic place. Things smash into each other, get thrown into completely different orbital planes, and are occasionally visited by small electronic spacecraft launched by humans. All three things seem to have happened to the asteroid Bennu, which is currently being orbited by OSIRIS-REx, a mission launched by NASA in 2016.
The most recently released results from the mission show that Bennu might have small pieces of Vesta on it. Given that Vesta is one of the biggest asteroid belt objects and Bennu is a near Earth asteroid millions of kilometers away from the asteroid belt, this hints at a pretty exciting past history for the asteroid currently being visited by NASA’s first asteroid sample return mission.
Continue reading “Asteroid Bennu has little pieces of Vesta on it”NASA’s Janus Mission is Going to Visit Two Binary Asteroids
Gravity is good for a lot of things. It brings objects closer together. Occasionally they crash into each other. But sometimes two objects get locked in a unique gravitational dance that pairs them together. That dance can be short-lived, or it can last for billions of years. In some cases the objects are large (i.e. planets and moons), but they can also be quite small.
These small dancing objects are called binary asteroids, and we know very little about them, despite making up approximately 15% of all asteroids in the solar system. That is until a newly greenlighted NASA mission, called Janus, will arrive at two different binary asteroids around 2026.
Continue reading “NASA’s Janus Mission is Going to Visit Two Binary Asteroids”Design for a Space Habitat With Artificial Gravity That Could Be Grown Larger Over Time to Fit More People
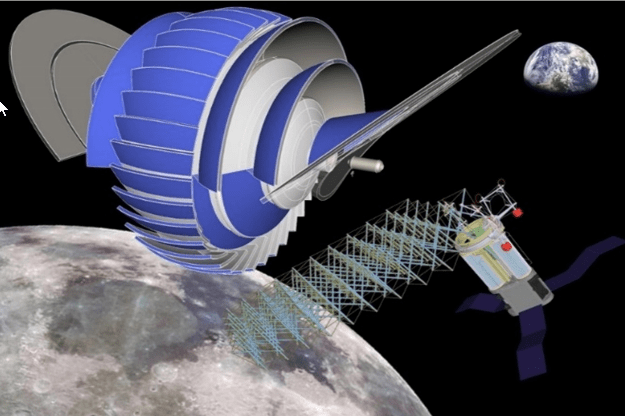
There are two main approaches that humanity can take to living in space. The one more commonly portrayed is of us colonizing other celestial bodies such as the Moon and Mars. That approach comes with some major disadvantages, including dealing with toxic soils, clingy dust, and gravity wells.
The alternative is to build our own habitats. These could be located anywhere in the solar system, could be of any size that material science allows, and have different characteristics, such as temperature, climate, gravity, and even lengths of day. Unfortunately, we are still a very long way from building anything like a fully sized habitat. However, we are now one step closer to doing so with the release of a paper from a team at Texas A&M that describes a way to build an expandable space habitat of concentric cylinders that can house up to 8000 people.
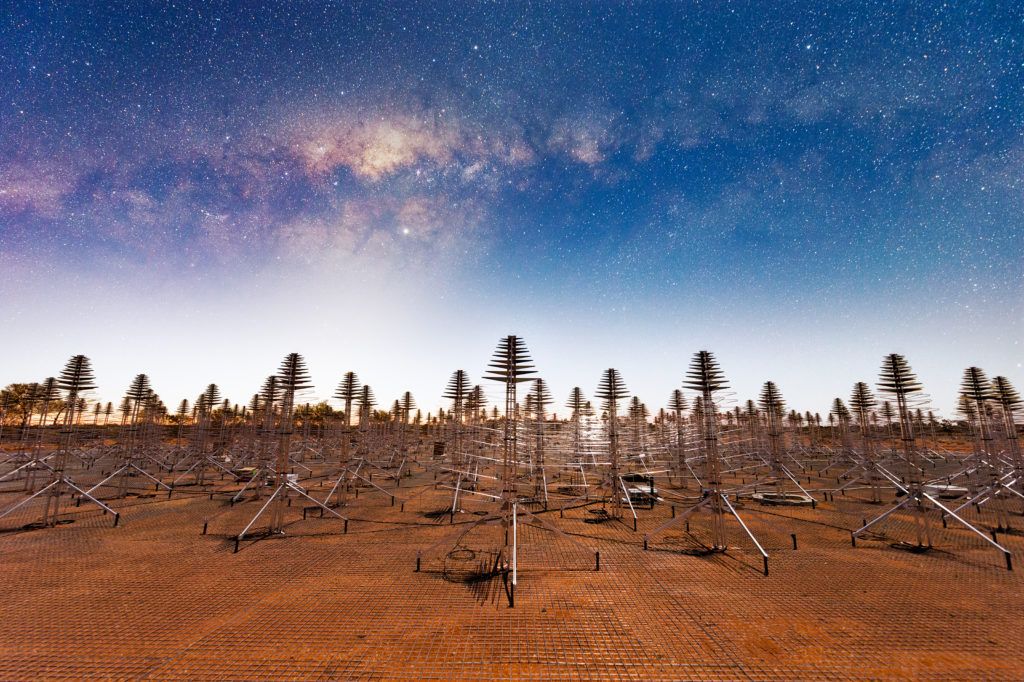
Continue reading “Design for a Space Habitat With Artificial Gravity That Could Be Grown Larger Over Time to Fit More People”Australian Telescope Just Scanned 10 million Stars For Any Sign of Extraterrestrial Signals. No sign.
One of the most important results of science is the negative result. If something doesn’t work or a hypothesis is disproven, often it’s not widely reported or disseminated. That is a shame. However, science is getting better at incorporating negative results into its reporting system, which has resulted in publications like the Journal of Negative Results, which covers biomedicine.
Unfortunately there isn’t a similar journal for Astronomy. At least not yet. But the field could really use one. There are plenty of disproven hypotheses that don’t see the light of day in academically peer reviewed publications. When it comes to topics like SETI, sometimes those negative results are extremely important, as it lends credence to one of the most important hypotheses out there – that we are alone in the universe. Papers that cover negative SETI results can be accepted into journals that otherwise might not accept a paper centered around not finding anything. That’s what happened recently when a team of astronomers from Australia and elsewhere used the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) to search a patch of sky that included 10 million stars. The negative results was that they did not see a single sign of intelligent life anywhere in those 10 million stars.
Continue reading “Australian Telescope Just Scanned 10 million Stars For Any Sign of Extraterrestrial Signals. No sign.”Finally! A Solution to Deal With Sticky Lunar Dust
As a wise man once said, “I don’t like sand. It’s coarse and rough and irritating – and it gets everywhere”. The same could be said for another material in our solar system – dust.
The kind of dust present on the moon is even more annoying than the grains that bothered Anakin Skywalker on Tatooine. It is constantly bathed in solar radiation, smells like spent gunpowder, and can cause allergic reactions, as it did in some of the Apollo astronauts. It’s also notoriously difficult to clean off of surfaces. Now a team of scientists at the University of Colorado at Boulder think they have a solution that would remove lunar dust without harming the material it’s attached to. And they would do this by using a tool that sounds like it’s straight out of Star Wars – an electron beam.
Continue reading “Finally! A Solution to Deal With Sticky Lunar Dust”Okay, New Idea. Oumuamua is an Interstellar “Dust Bunny”
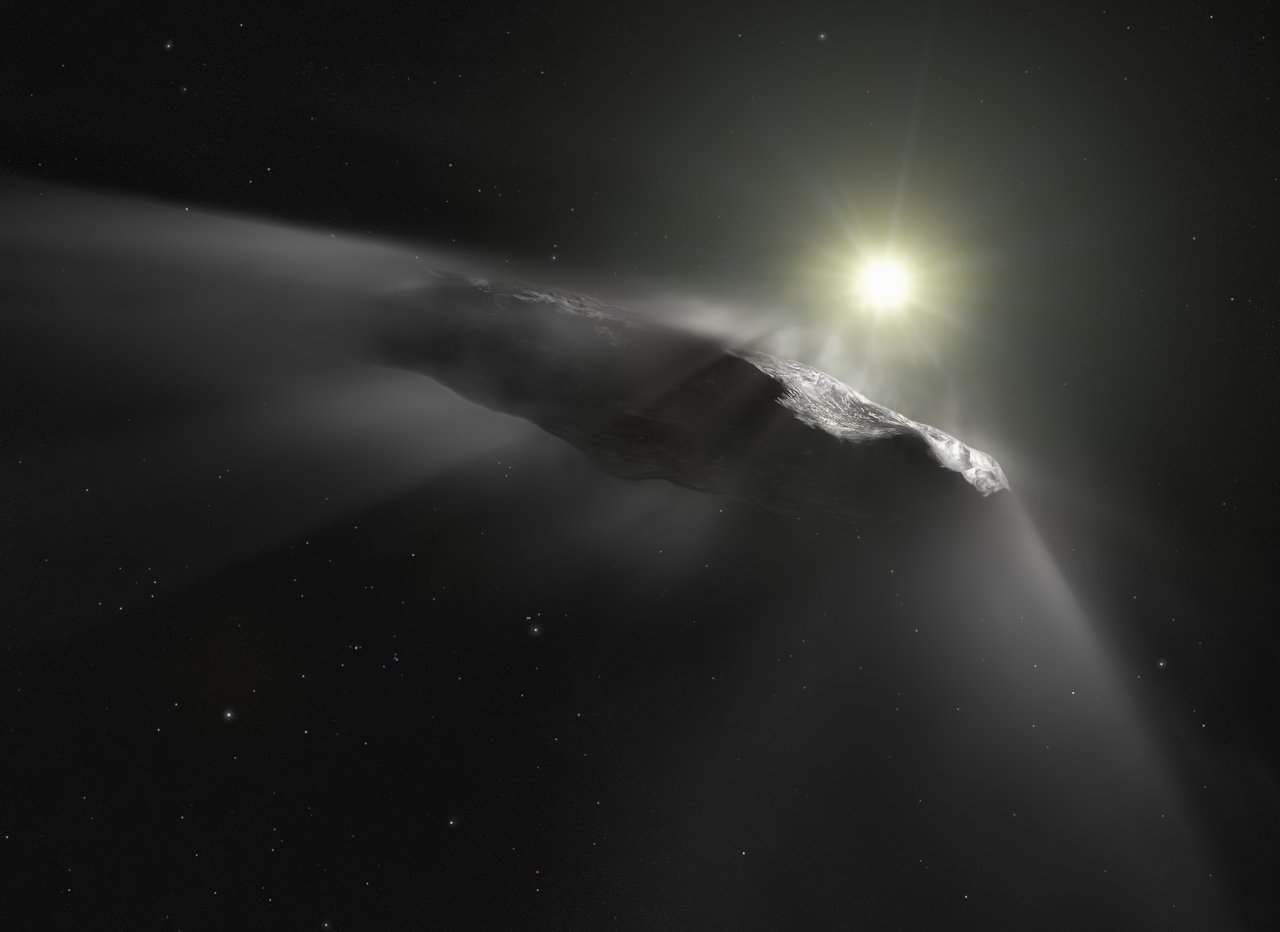

Explaining the concept of a dust bunny to small children can be quite amusing. No, it’s not actually alive. It’s moving around because of really small currents of wind that we can’t even see. It’s mainly formed out of dead skin and spider webs. No, the spiders don’t actually eat the dead skin. Most of the time.
Now take that same concept of a bunch of particles stuck together, scale it up a few orders of magnitude, and put it in space. Though it’s still not alive, it would be blown by solar radiation rather than the winds. And instead of being made out of skin and spider webs, it could be made up of cometary dust particles. That is what scientists think our first detected visitor from another star might be – an interstellar dust bunny.
Continue reading “Okay, New Idea. Oumuamua is an Interstellar “Dust Bunny””