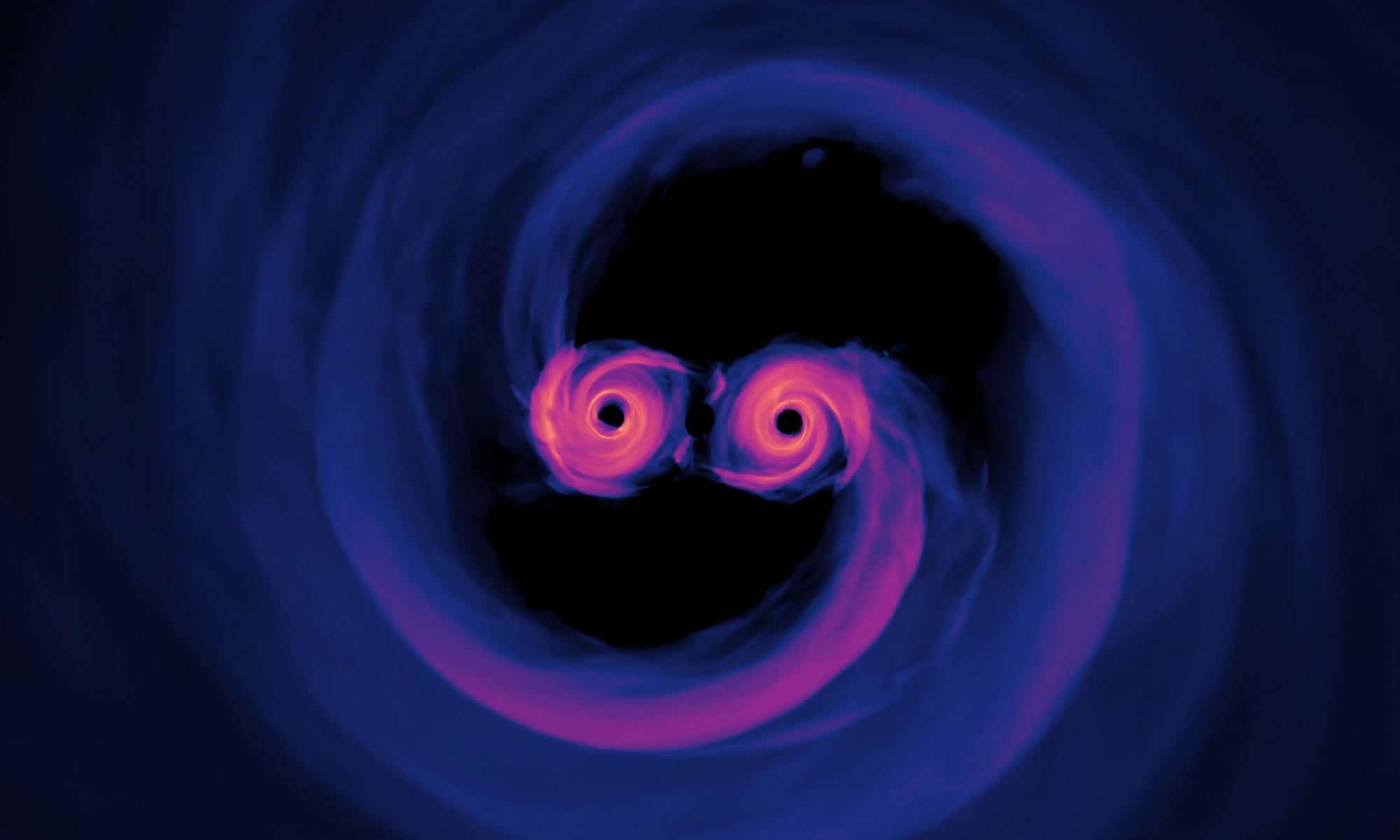
Gravitational waves don’t travel through space and time. They are ripples in the fabric of spacetime itself. This is why they are so difficult to detect. We can only observe them by closely watching how objects bent and stretched within spacetime. But despite their oddness, gravitational waves behave in many of the same ways as light, and astronomers can use that fact to study cosmic expansion.
Continue reading “Gravitational Waves Can Be Gravitationally Lensed, and This Could Provide Another Way to Measure the Expansion of the Universe”A Planet Was Swallowed by a Red Giant, But it Survived

The Sun is going to kill us. Not anytime soon, but it will kill us. At the moment the Sun keeps itself going by fusing hydrogen into helium and other heavier elements, but in five or so billion years it is going to run out of hydrogen. When that happens, the Sun will make a desperate attempt to keep going by fusing helium. During this period it will swell to a red giant, likely so large that it engulfs the Earth, baking it to a crisp in its diffuse hot atmosphere.
Continue reading “A Planet Was Swallowed by a Red Giant, But it Survived”Astronomers Find the Fastest Spider Pulsar, Filling in the Missing Link in Their Evolution
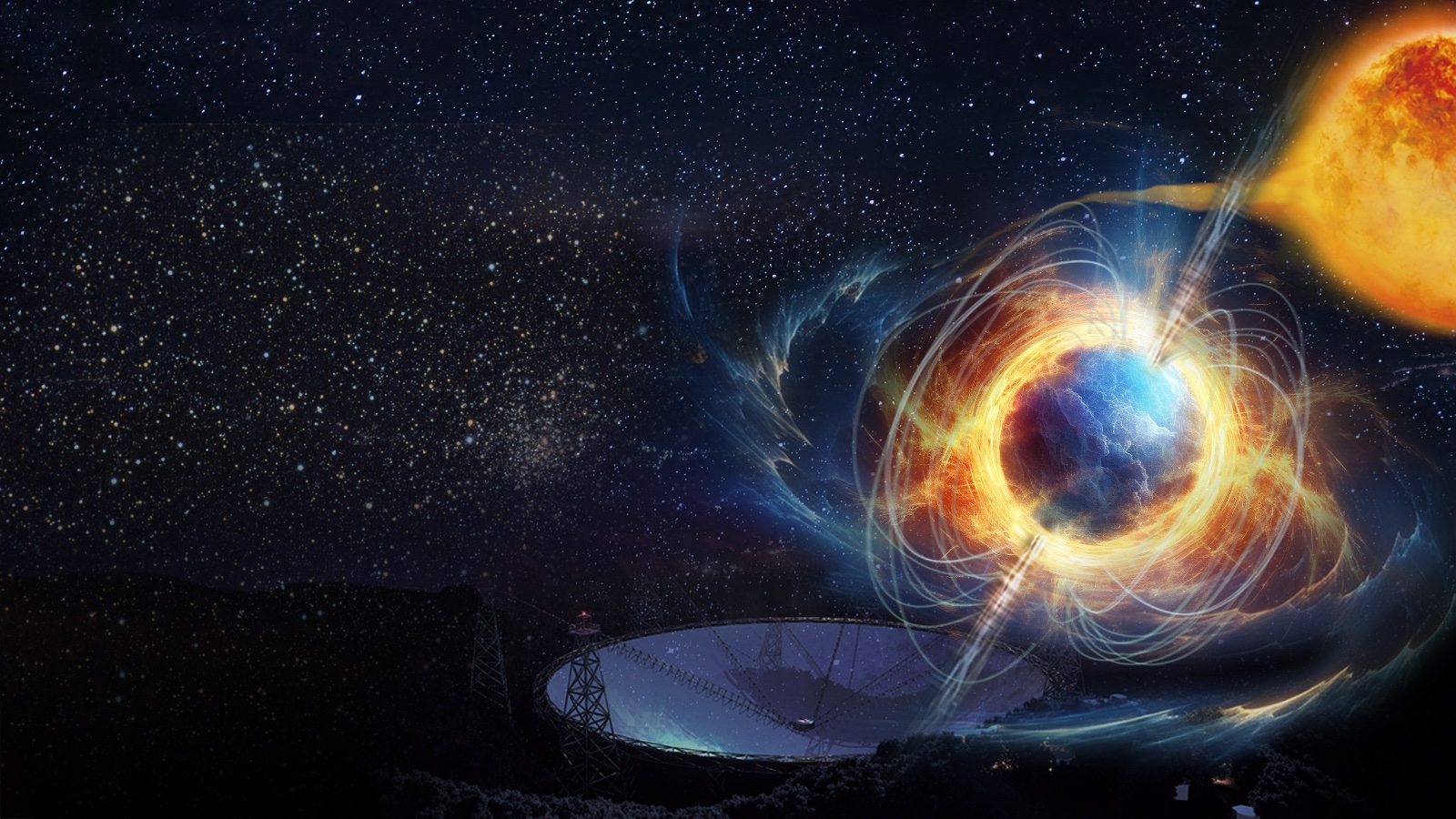
Pulsars are rotating neutron stars aligned with Earth in just such a way that the energy radiated from their magnetic poles sweeps across us with each rotation. From this, we see a regular pulse of radio light, like a cosmic lighthouse. The fastest pulsars can rotate very quickly, pulsing hundreds of times per second. These are known as millisecond pulsars.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find the Fastest Spider Pulsar, Filling in the Missing Link in Their Evolution”Nancy Grace Roman and Vera Rubin Will be the Perfect Astronomical Partnership

Two of the most important telescopes being constructed at the moment are Vera C. Rubin and Nancy Grace Roman. Each has the capability of transforming our understanding of the universe, but as a recent paper on the arxiv shows, they will be even more transformative when they work together.
Continue reading “Nancy Grace Roman and Vera Rubin Will be the Perfect Astronomical Partnership”What Would the Milky Way Look Like From Afar?
Our understanding of galaxies is rooted in the fact that we can see so many of them. Some, such as the Andromeda and Pinwheel galaxies are fairly close, and others are more distant, but all of them give a unique view. Because of this, we can see how the various types of galaxies appear from different points of view, from face-on to edge-on and all angles in between. But there is one galaxy that’s a bit harder to map out, and that’s our own. Because we are in the galactic plane of the Milky Way, it can be difficult to create an accurate bird’s-eye view of our home galaxy. That’s where a recent study in Nature Astronomy comes in.
Continue reading “What Would the Milky Way Look Like From Afar?”Touch Galaxies and Listen to Black Holes. Now You Can Explore the Universe With Multiple Senses
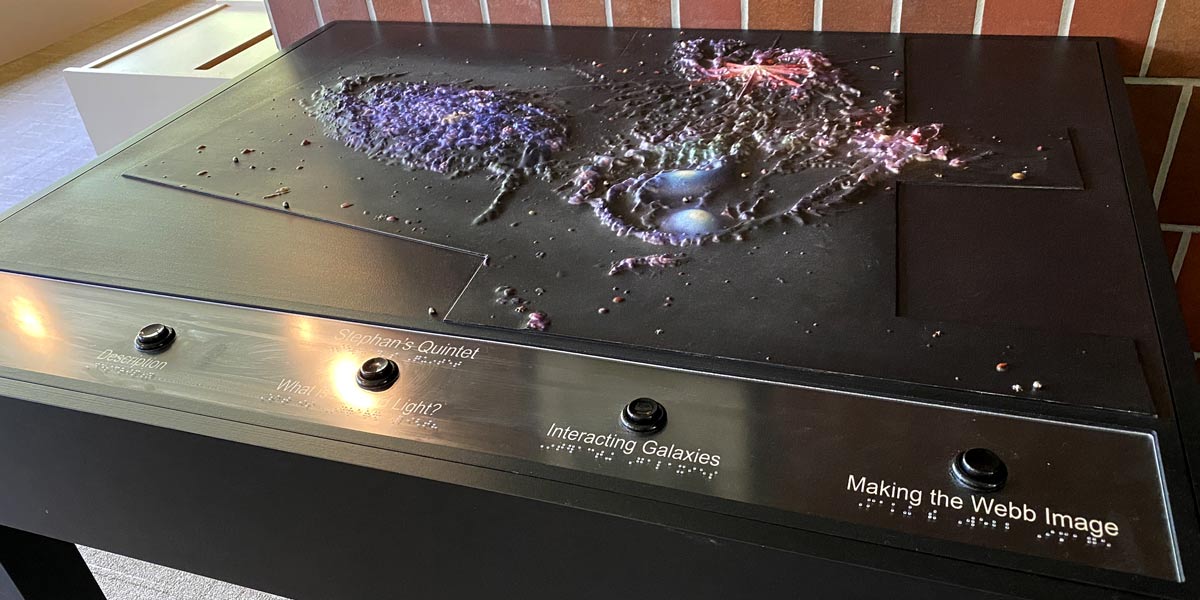
One of the amazing benefits of modern astronomy is the wealth of astronomical images it gives us. From Hubble to Webb, new images appear online almost every day. They are powerful and beautiful, and so bountiful they are easy to take for granted. But those images aren’t for everyone. Whether you are visually impaired, color blind, or best process information auditorily or kinesthetically, astronomical images can be extremely limiting. Because of this, NASA’s Universe of Learning project is exploring how astronomy can be conveyed in multi-sensory ways.
Continue reading “Touch Galaxies and Listen to Black Holes. Now You Can Explore the Universe With Multiple Senses”Watching the Watchers With Nancy Grace Roman
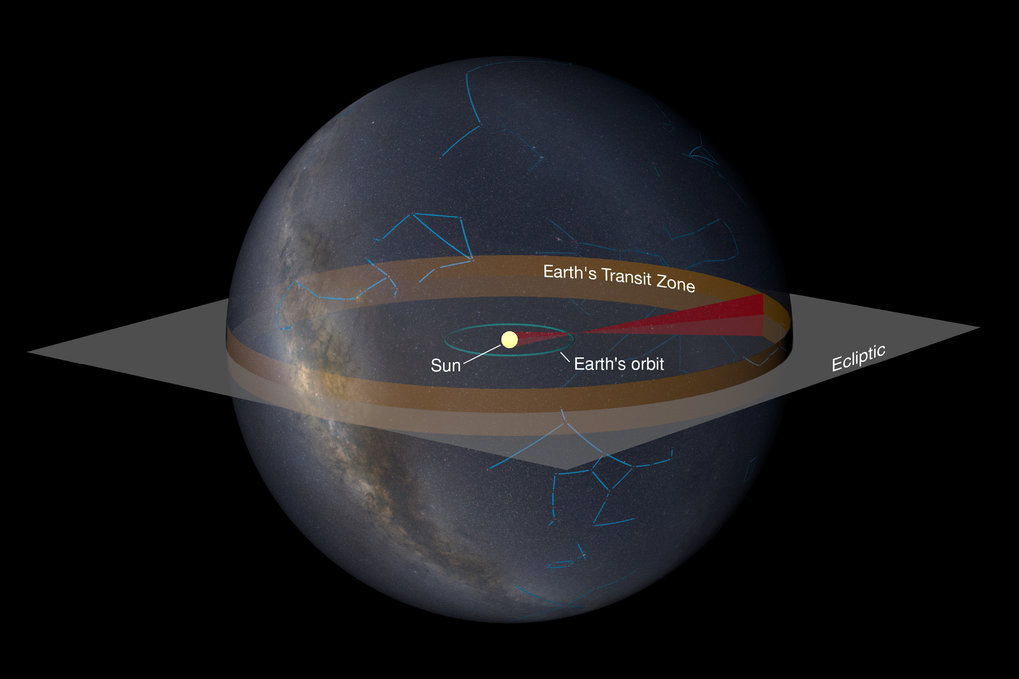
Astronomers are getting better at gathering data about exoplanets. We have discovered thousands of them, measuring their mass, size, and orbital parameters, and we are starting to measure other aspects such as their temperature and atmospheric composition. Of course, the big hope is that in time we will discover the presence of life on some of these distant worlds, and perhaps even find evidence of an alien civilization. And if there are aliens out there, it’s reasonable to assume they might be looking for us as well. A new study proposes one way we might find each other.
Continue reading “Watching the Watchers With Nancy Grace Roman”Another Key Amino Acid Found in Space: Tryptophan
Astrochemistry is the study of how molecules can form and react in space. Its roots trace back to the 1800s when astronomers such as William Wollaston and Joseph von Fraunhofer began identifying atomic elements from the spectral lines of the Sun. But it wasn’t until recent decades that the field began to mature.
Continue reading “Another Key Amino Acid Found in Space: Tryptophan”Extending Earth's Internet to Mars With Orbital Data Servers
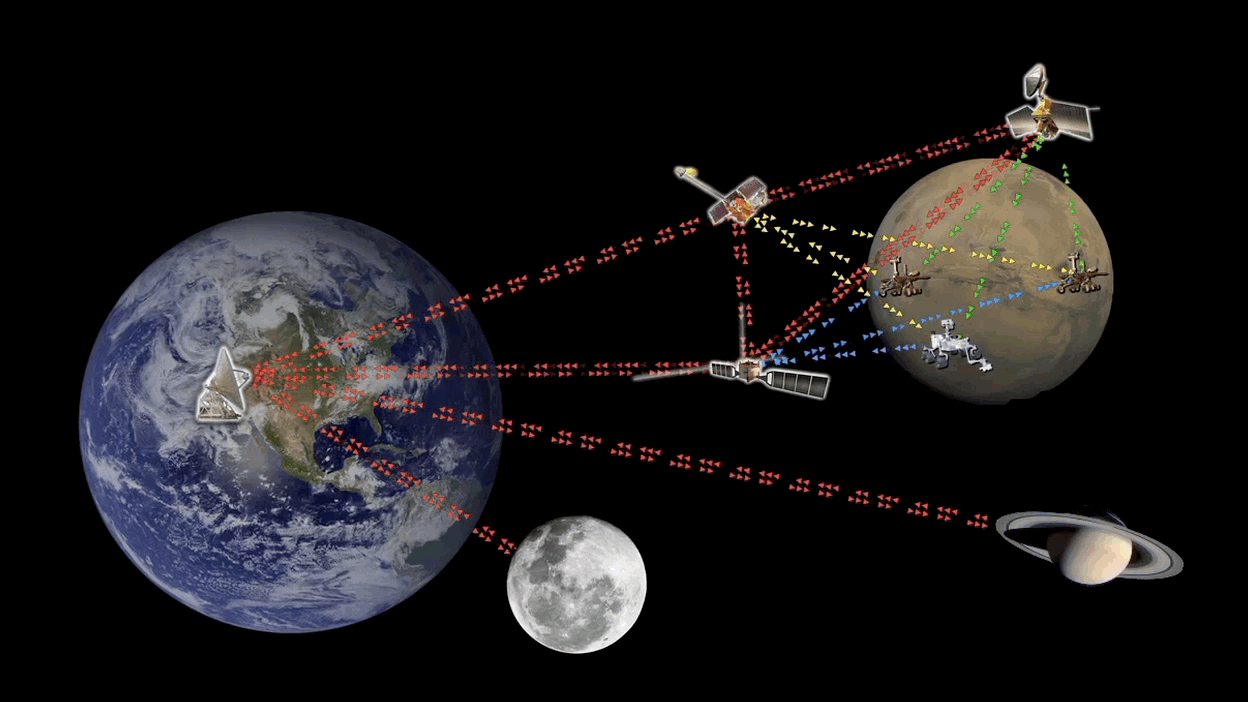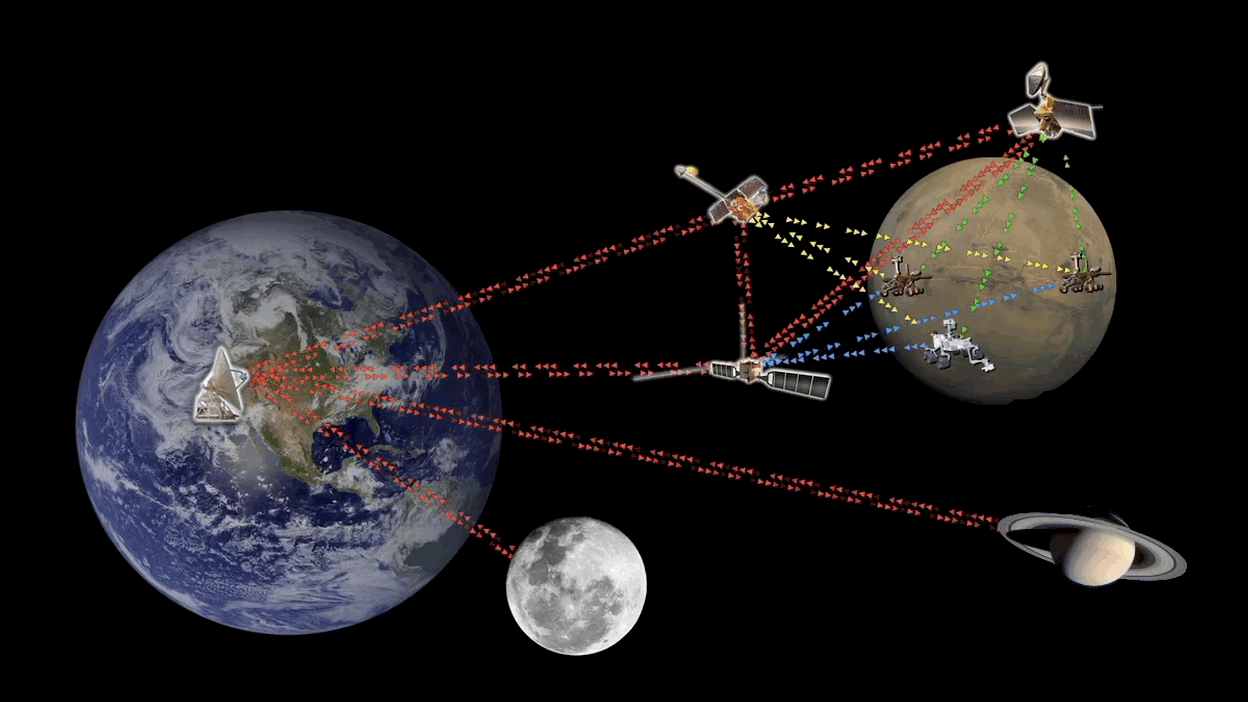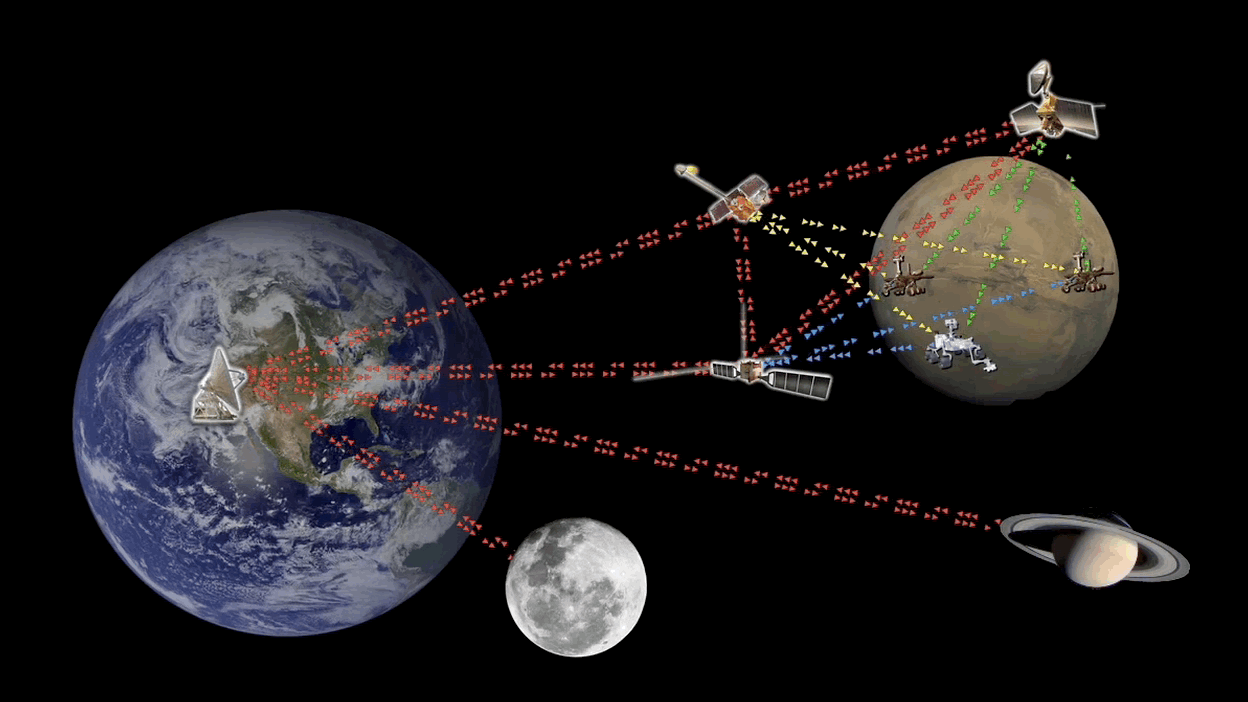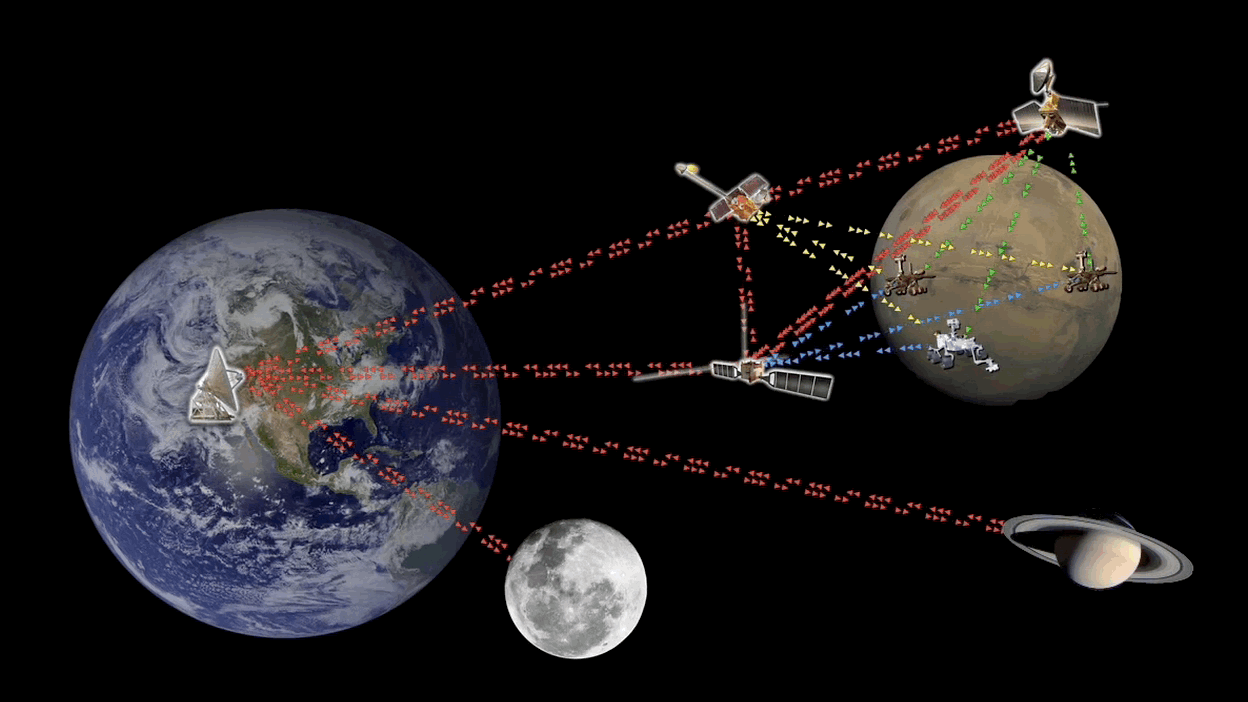
You’ve done it. After years of effort and training, sacrifice, and pain, you become an astronaut and have finally set foot on Mars. Time to post your triumph on TikTok for that sweet social media cred. If only you can get a signal.
Continue reading “Extending Earth's Internet to Mars With Orbital Data Servers”There Could Be Captured Planets in the Oort Cloud
Our solar system has had a chaotic past. Earth and the other planets are now in stable orbits, but while they were forming they experienced drastic location shifts. Jupiter was likely much closer to the Sun than it is now, and its shift not only shifted other planets but also cleared the solar system of debris, tossing much of it to the Oort Cloud.
Continue reading “There Could Be Captured Planets in the Oort Cloud”