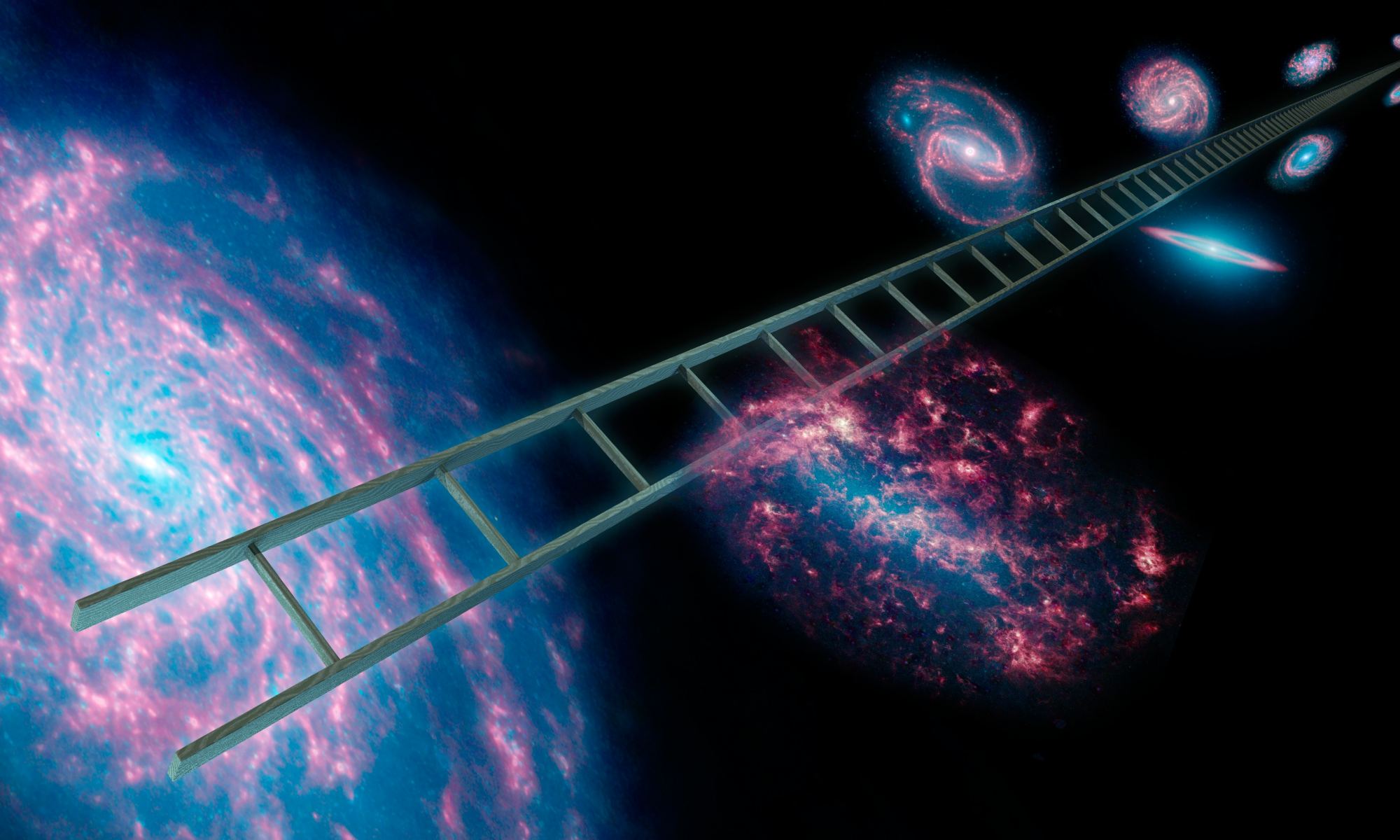
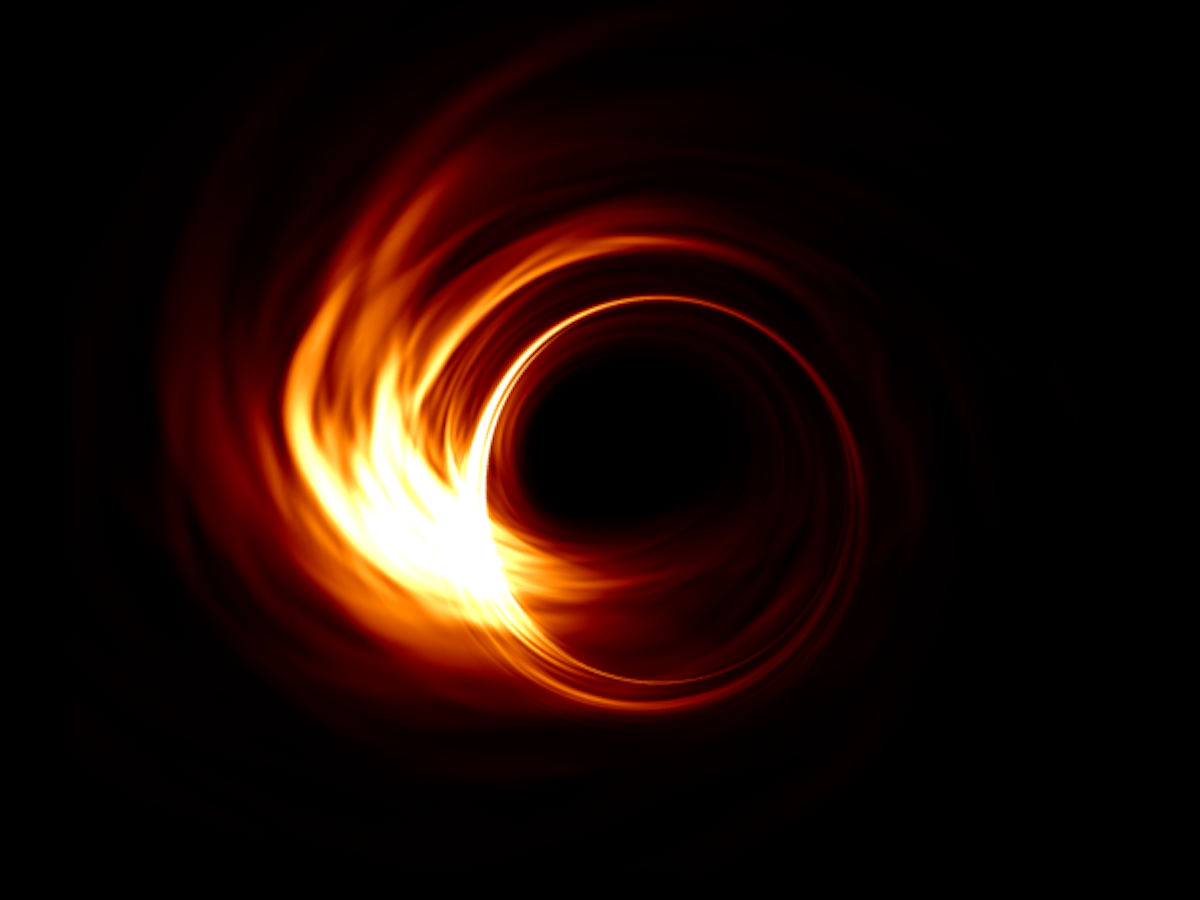
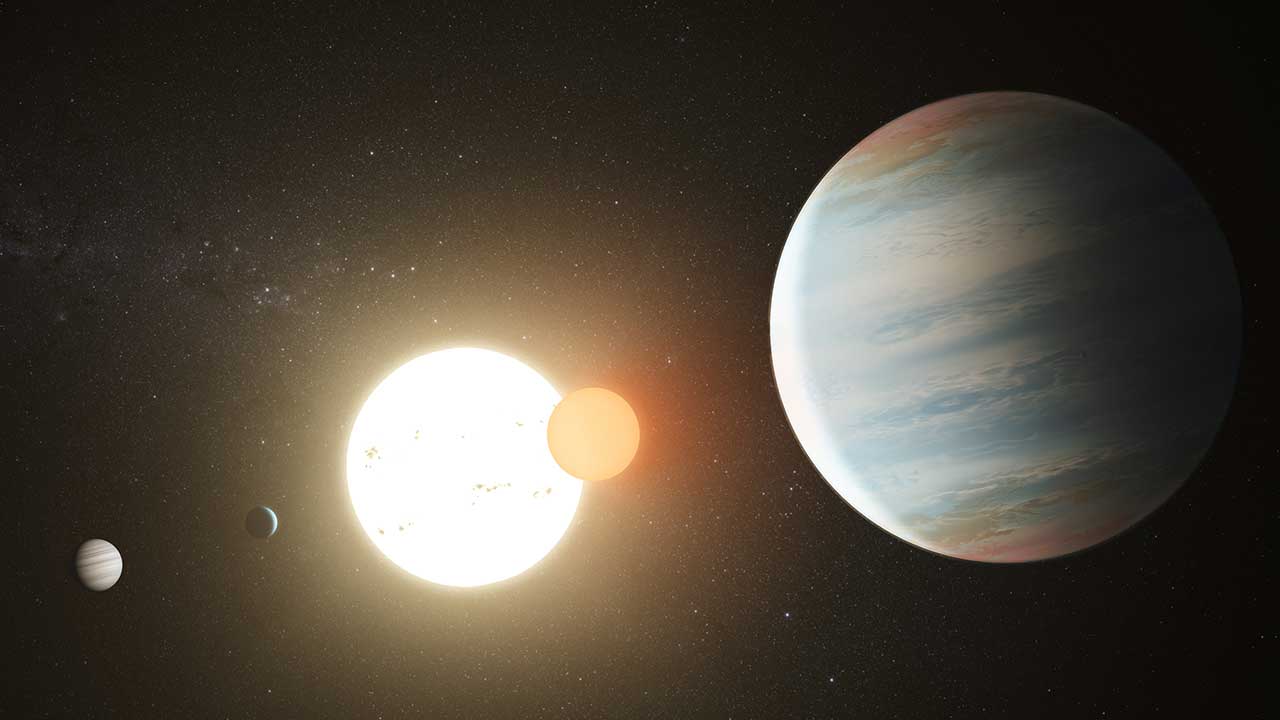
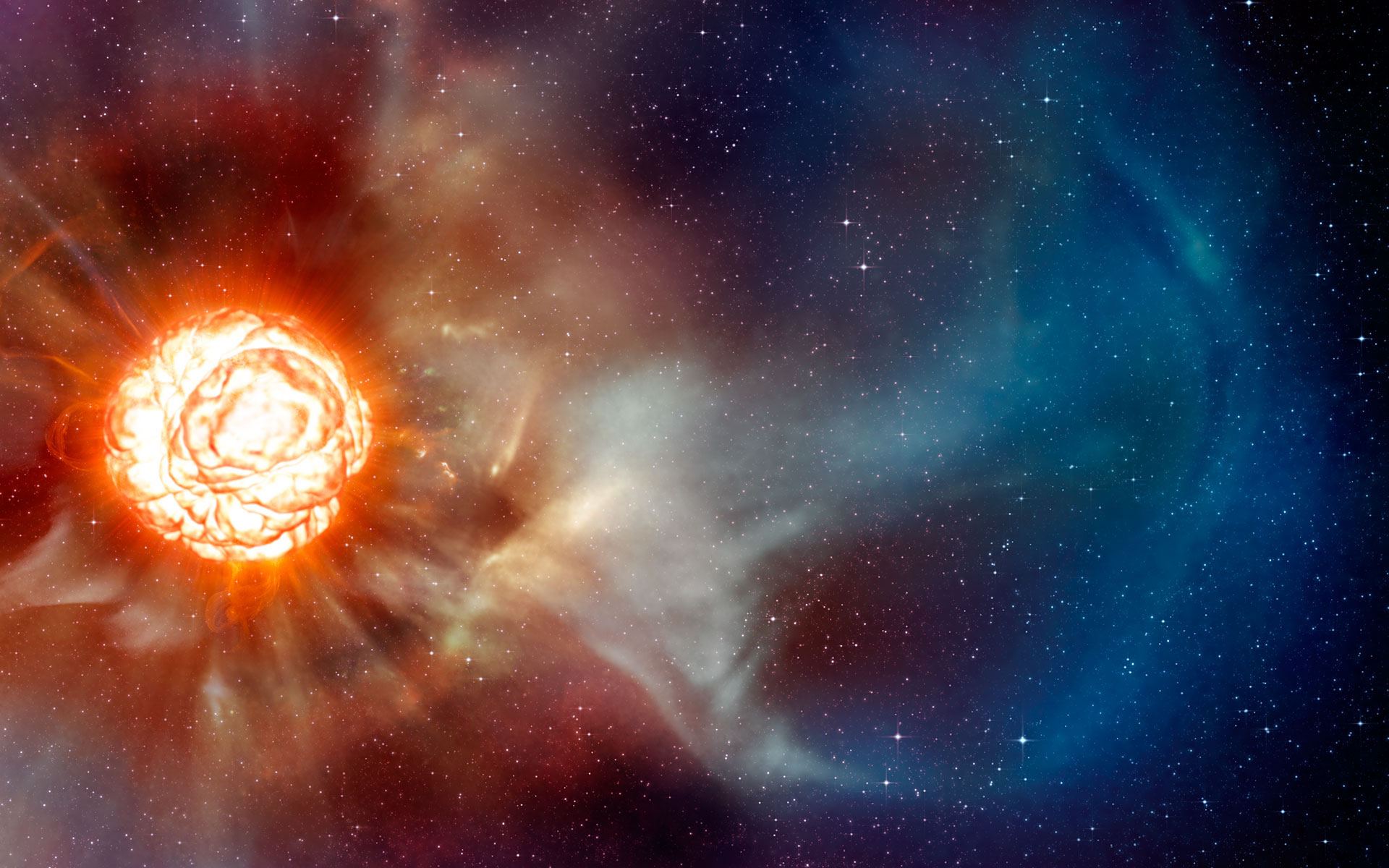
The standard model of cosmology is known as the LCDM model. Here, CDM stands for Cold Dark Matter, which makes up most of the matter in the universe, and L stands for Lambda, which is the symbol used in general relativity to represent dark energy or cosmic expansion. While the observational evidence we have largely supports the LCDM model, there are some issues with it. One of the most bothersome is known as cosmic tension.
Continue reading “The "Crisis in Cosmology" Might not be a Crisis After all”Hawking Made a Prediction About Black Holes, and Physicists Just Confirmed it
On its own, a black hole is remarkably easy to describe. The only observable properties a black hole has are its mass, its electric charge (usually zero), and its rotation, or spin. It doesn’t matter how a black hole forms. In the end, all black holes have the same general structure. Which is odd when you think about it. Throw enough iron and rock together and you get a planet. Throw together hydrogen and helium, and you can make a star. But you could throw together grass cuttings, bubble gum, and old Harry Potter books, and you would get the same kind of black hole that you’d get if you just used pure hydrogen.
Continue reading “Hawking Made a Prediction About Black Holes, and Physicists Just Confirmed it”Astronomers Detected a Black Hole-Neutron Star Merger, and Then Another Just 10 Days Later
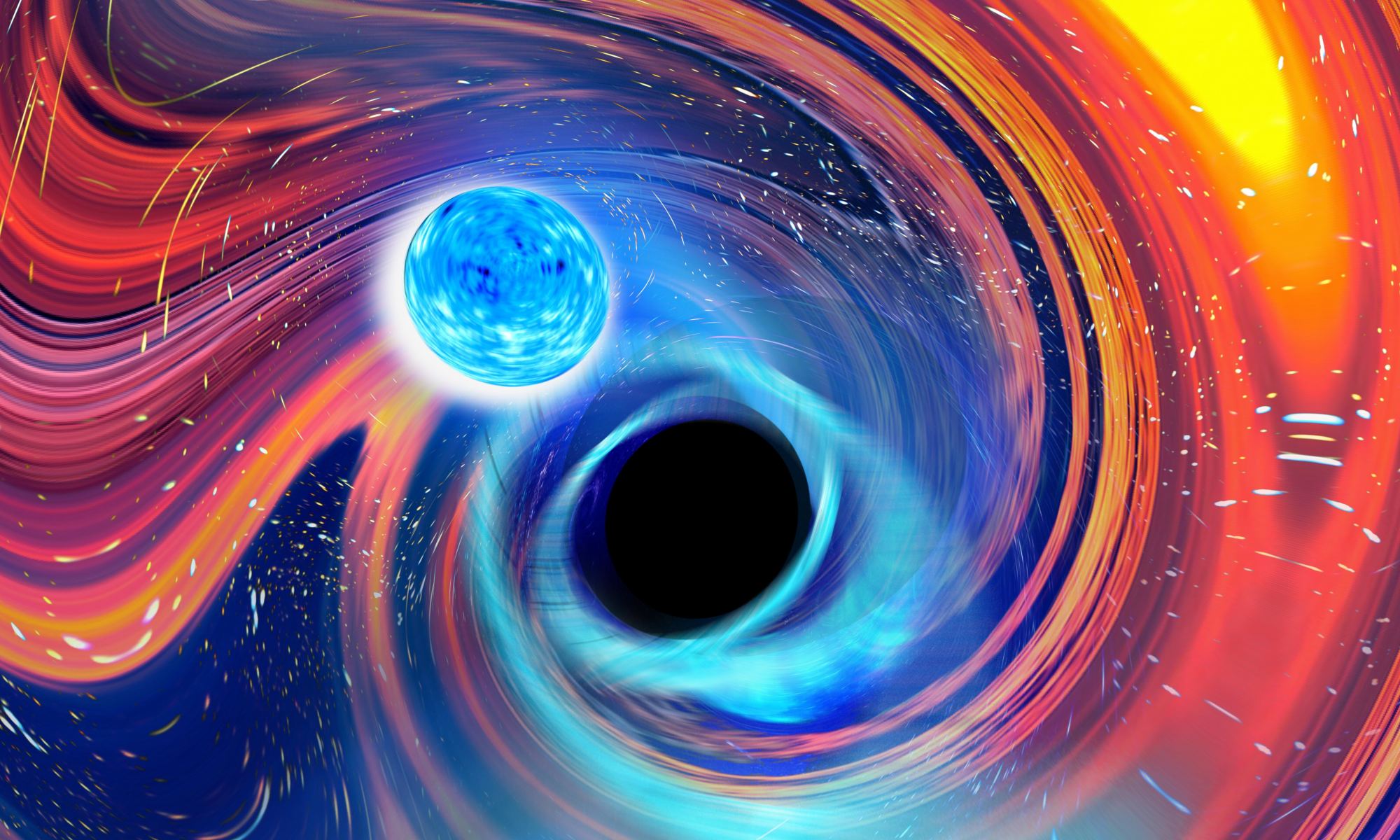

The interior of a neutron star is perhaps the strangest state of matter in the universe. The material is squeezed so tightly that atoms collapse into a sea of nuclear material. We still aren’t sure whether nucleons maintain their integrity in this state, or whether they dissolve into quark matter. To really understand neutron star matter we need to pull it apart to see how it works and to do that takes a black hole. This is why astronomers are excited about the recent discovery of not one, but two mergers between a neutron star and a black hole.
Continue reading “Astronomers Detected a Black Hole-Neutron Star Merger, and Then Another Just 10 Days Later”A Lunar Farside Telescope Could Detect Exoplanets Through Their Magnetospheres
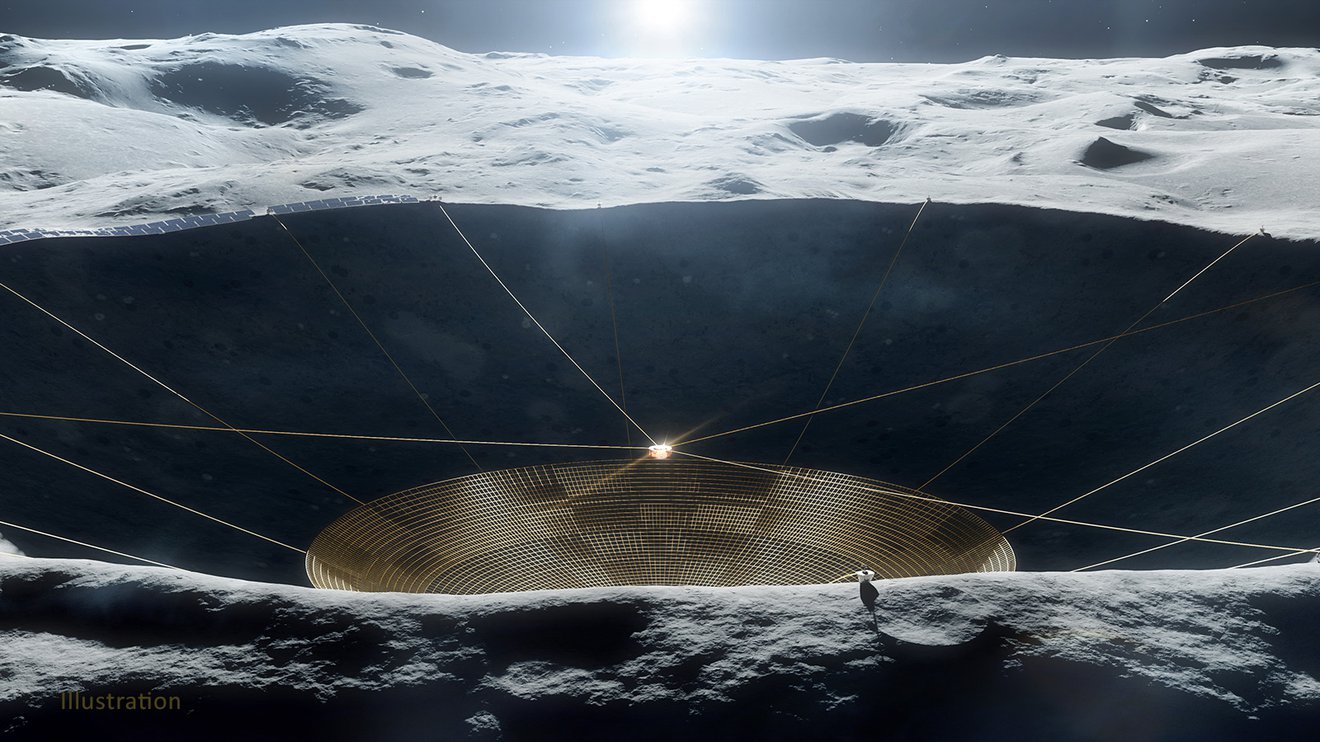
It’s difficult to do radio astronomy on Earth, and it’s getting harder every day. Our everyday reliance on radio technology means that radio interference is a constant challenge, even in remote areas. And for some wavelengths even the Earth’s atmosphere is a problem, absorbing or scattering radio light so that Earth-based telescopes can’t observe these wavelengths well. To overcome these challenges, astronomers have proposed putting a radio telescope on the far side of the Moon.
Continue reading “A Lunar Farside Telescope Could Detect Exoplanets Through Their Magnetospheres”Gravitational-Wave Detector Could Sense Merging Primordial Black Holes With the Mass of a Planet, Millions of Light-Years Away
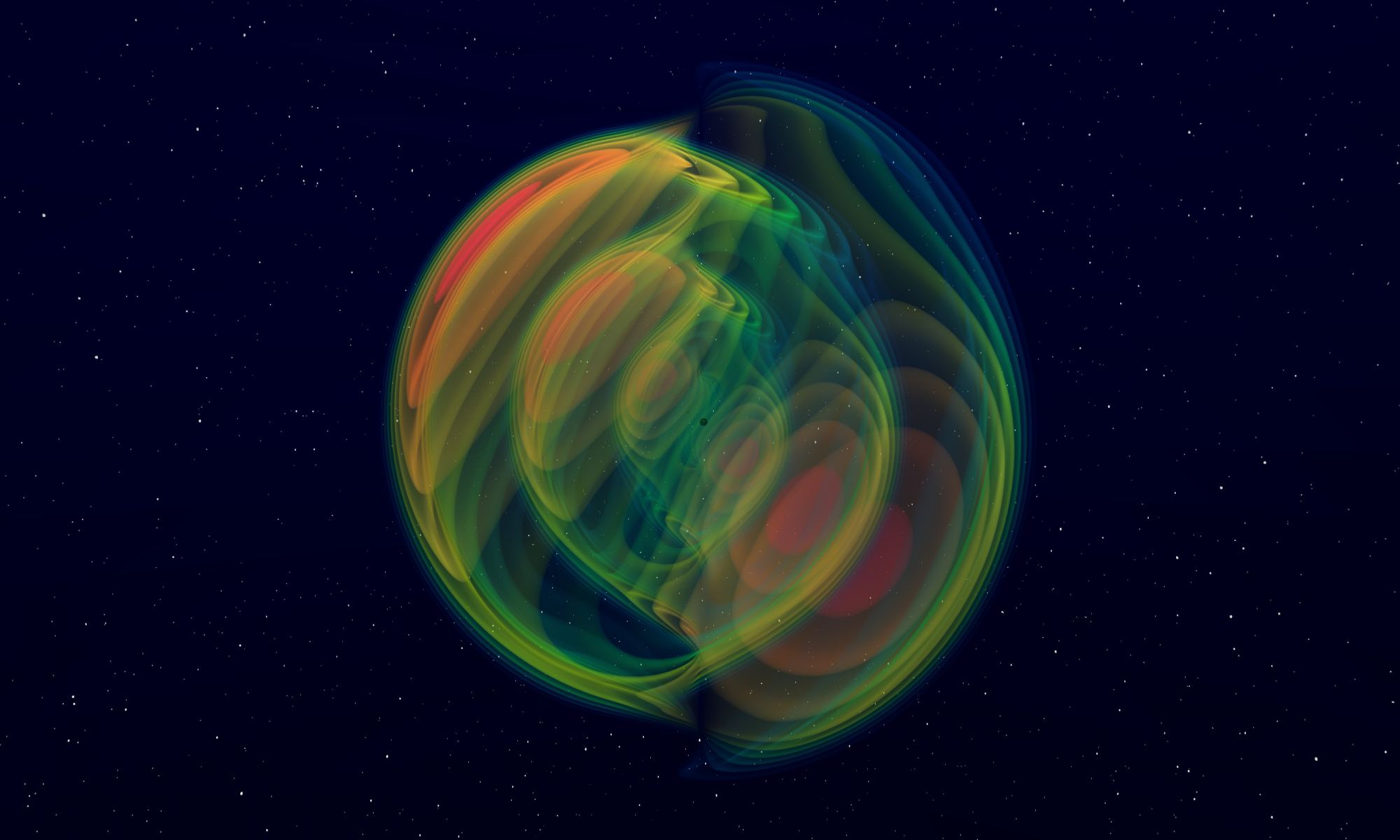
Gravitational-wave detectors have been a part of astronomy for several years now, and they’ve given us a wealth of information about black holes and what happens when they merge. Gravitational-wave astronomy is still in its infancy, and we are still very limited in the type of gravitational waves we can observe. But that could change soon.
Continue reading “Gravitational-Wave Detector Could Sense Merging Primordial Black Holes With the Mass of a Planet, Millions of Light-Years Away”Could Life Exist in the Atmosphere of a sub-Neptune Planet?
Earth is perfectly suited for organic life. It stands to reason then that similar worlds orbiting distant stars might also be rich with life. But proving it will be a challenge. One of the better ways to discover extraterrestrial life will be to study the atmospheres of inhabited exoplanets, but Earth is fairly small for a planet and has a thin atmosphere compared to larger worlds. It will be much easier to study the atmospheres of gas planets, but could such worlds harbor life? A new paper in Universe argues it could.
Continue reading “Could Life Exist in the Atmosphere of a sub-Neptune Planet?”Betelgeuse's Mysterious Dimming Solved. It was… Dust
At the beginning of 2020, the red giant star Betelgeuse started to dim significantly. Betelgeuse has been known to vary in brightness, but this one was unusual. It grew much dimmer than usual, and for a longer period. Since Betelgeuse is a star at the end of its life, it led some to speculate that perhaps it would go supernova. Astronomers didn’t think that was likely, and of course, Betelgeuse didn’t explode, and gradually its usual brightness returned. But astronomers were puzzled as to why Betelgeuse grew so dim.
Continue reading “Betelgeuse's Mysterious Dimming Solved. It was… Dust”Supermassive Black Hole Winds Were Already Blowing Less Than a Billion Years After the Big Bang
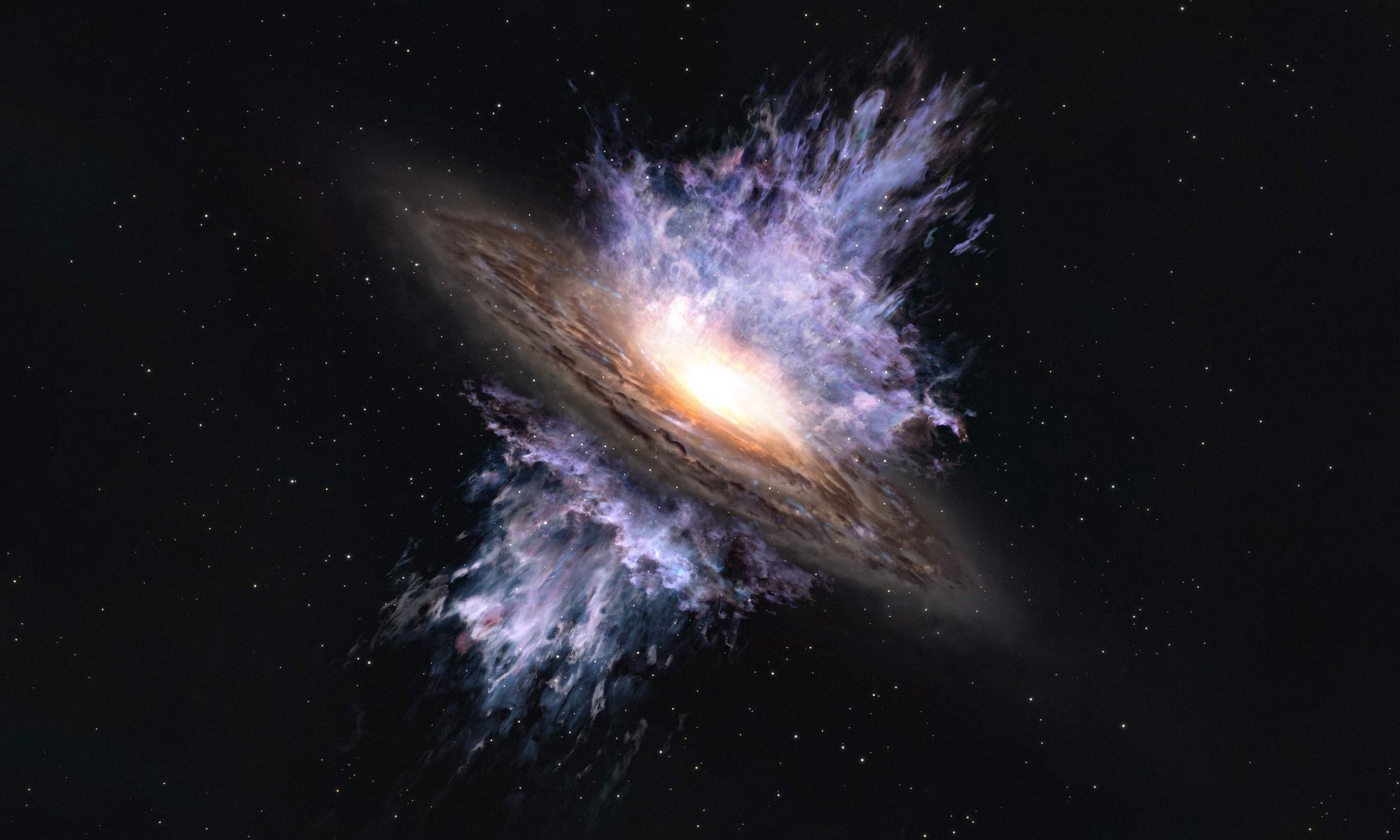

At the heart of most galaxies is a supermassive black hole. These beasts of gravity can play a crucial role in the formation and evolution of their galaxy. But astronomers still don’t fully understand when the influence of black holes becomes significant. Did large black holes form early in the universe, causing galaxies to form around them? Or did black holes grow after its primordial galaxy had begun to form? You might call this the chicken or egg problem. But a recent study suggests that galaxies and their supermassive black holes can have a mutual interaction that allows them to co-evolve.
Continue reading “Supermassive Black Hole Winds Were Already Blowing Less Than a Billion Years After the Big Bang”Black Holes don't Just Destroy, They Also Help With Star Formation
Black holes are the most powerful destructive forces in the universe. They can rip apart a star and scatter its ashes out of the galaxy at nearly the speed of light. But these engines of destruction can also pave the way for new stars to form, as a new study in Nature shows.
Continue reading “Black Holes don't Just Destroy, They Also Help With Star Formation”White Dwarf Measured Before it Exploded as a Supernova
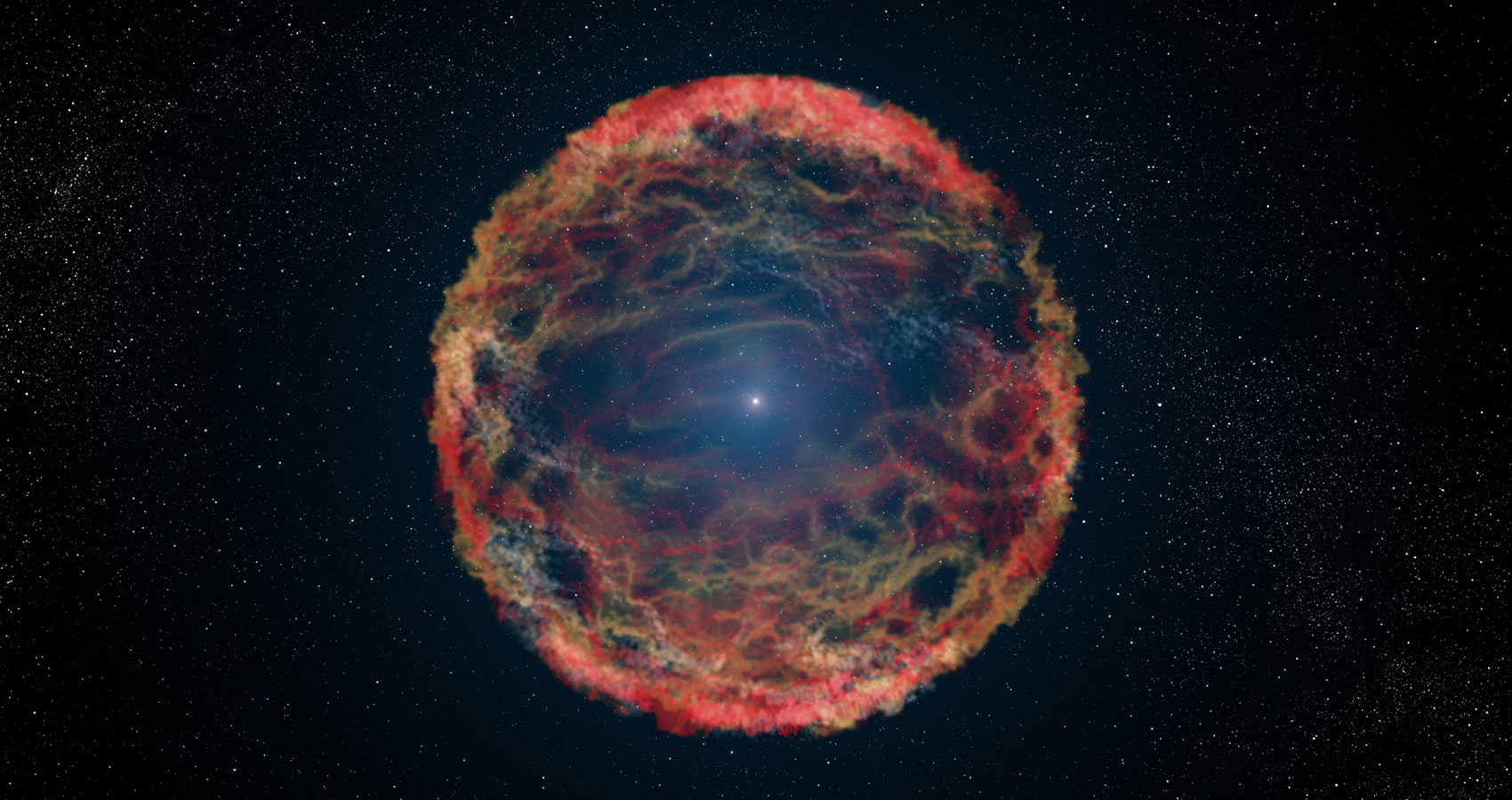
Type Ia supernovae are an important tool for modern astronomy. They are thought to occur when a white dwarf star captures mass beyond the Chandrasekhar limit, triggering a cataclysmic explosion. Because that limit is the same for all white dwarfs, Type Ia supernovae all have about the same maximum brightness. Thus, they can be used as standard candles to determine galactic distances. Observations of Type Ia supernova led to the discovery of dark energy and that cosmic expansion is accelerating.
Continue reading “White Dwarf Measured Before it Exploded as a Supernova”