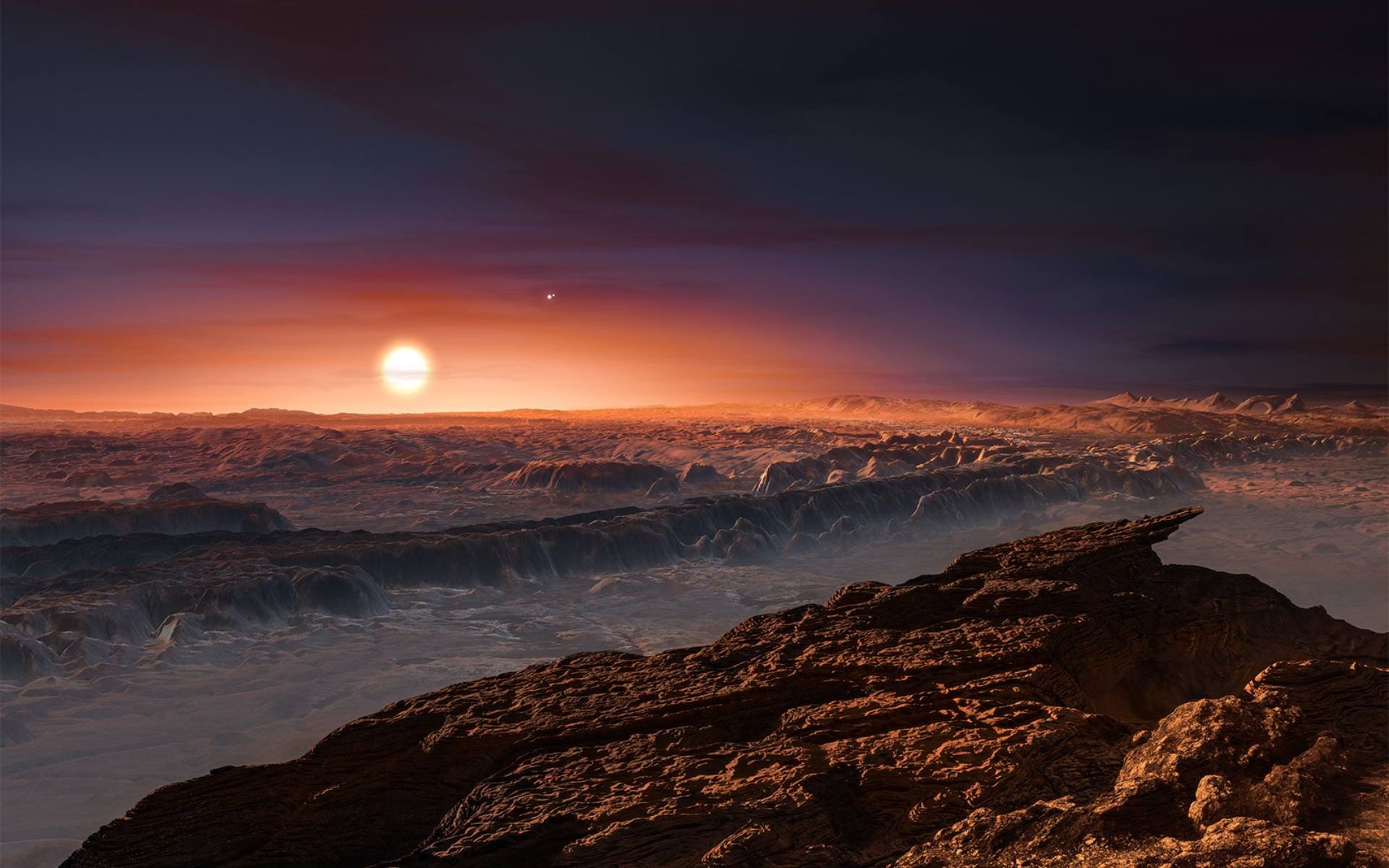
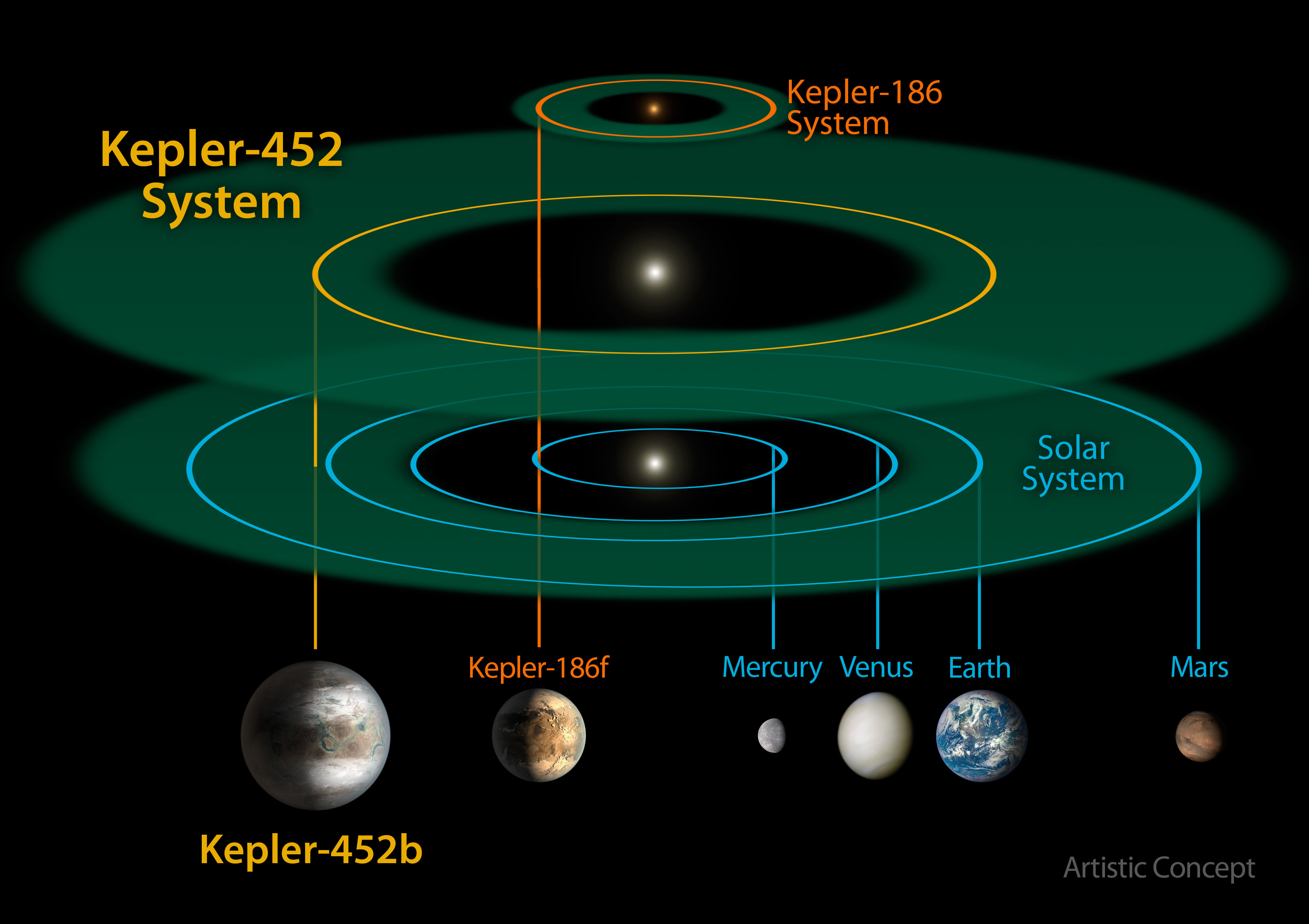
In our search for exoplanets, we have found more than three dozen potentially habitable worlds. It’s estimated that there are 8 to 20 billion potentially habitable, Earth-like worlds in our galaxy alone. But there is a big difference between potentially habitable and actually habitable, and scientists are starting to narrow their definitions.
Continue reading “Is the Concept of a Habitable Zone Too Wide?”Is the Concept of a Habitable Zone Too Wide?