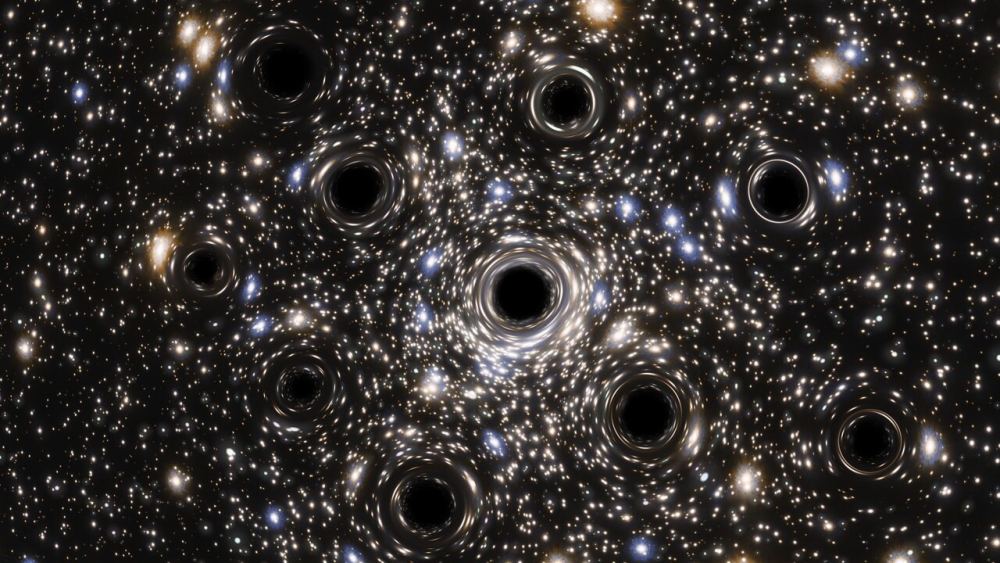
Who knows what lurks in the hearts of some globular clusters? Astronomers using a collection of gravitational wave observatories found evidence of collections of smaller black holes dancing together as binaries in the hearts of globulars. What’s more, they’ve detected an increased number of gravitational wave events when some of these stellar-mass black holes crashed together.
Continue reading “Black Holes Shouldn’t be Able to Merge, but Dozens of Mergers Have Been Detected. How Do They Do It?”Black Holes Shouldn’t be Able to Merge, but Dozens of Mergers Have Been Detected. How Do They Do It?