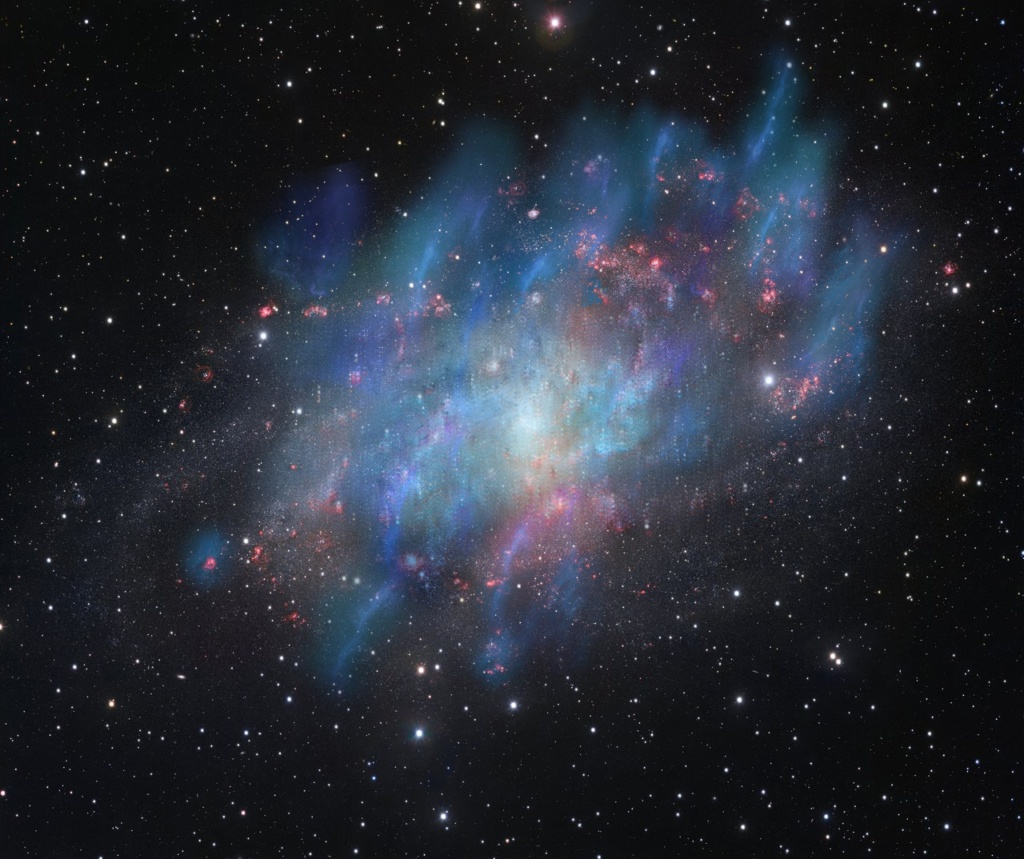
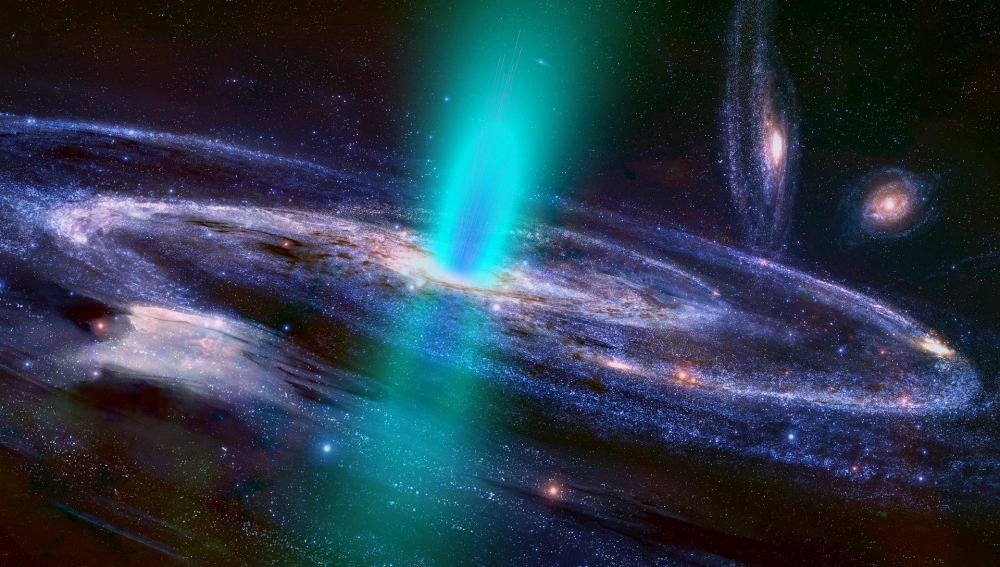
Interstellar winds are powerful agents of change. For one thing, they can interrupt or shut down the process of star birth completely. That’s what a team of astronomers using the Karl Jansky Very Large Array in New Mexico found when they studied the galaxy M33. They also learned that speedy cosmic rays play a huge role in pushing those winds across interstellar space.
Continue reading “Too Many Supernovae Can Slow Star Formation in a Galaxy”Too Many Supernovae Can Slow Star Formation in a Galaxy