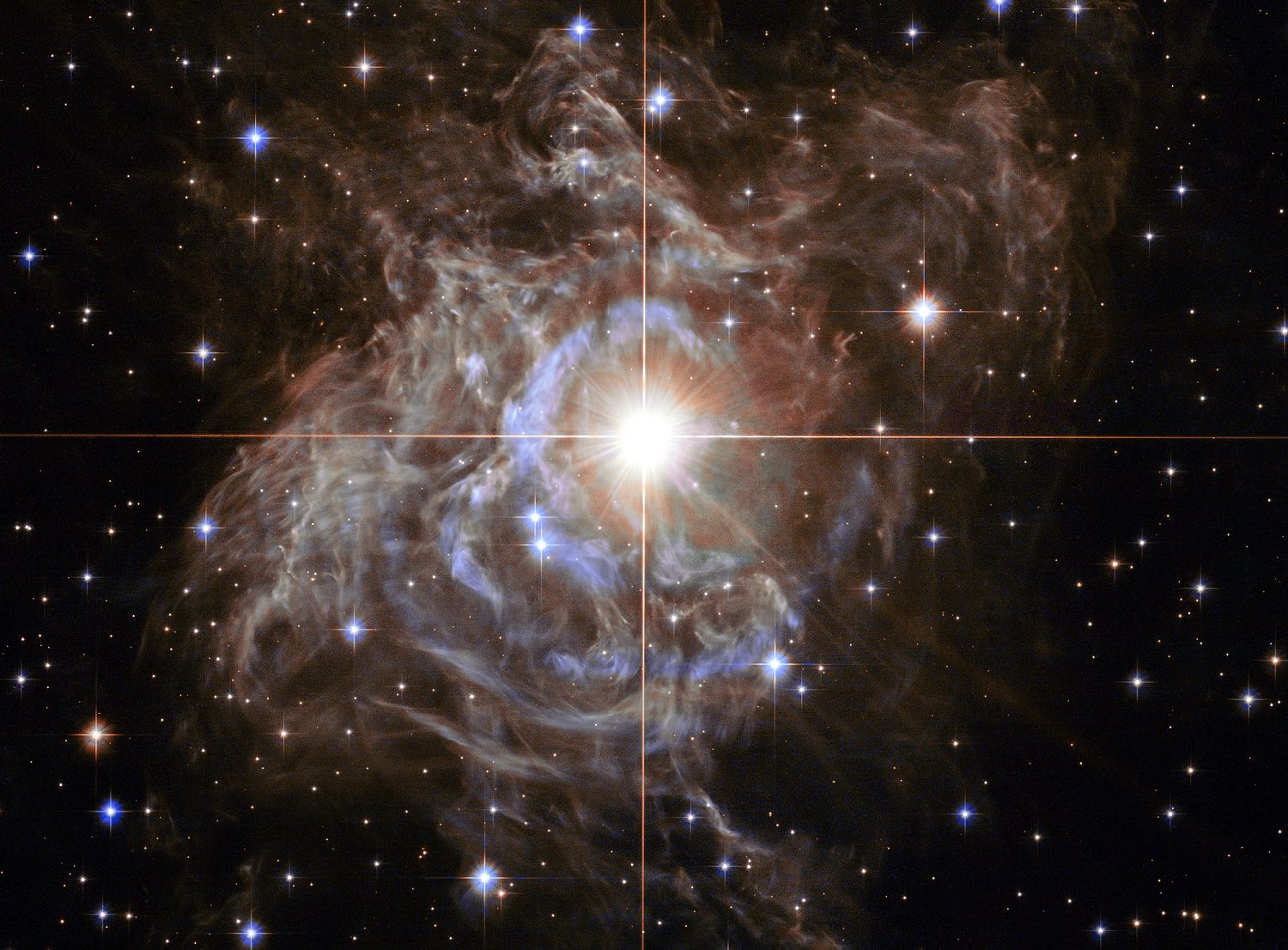
What do two guys from Ohio, the GAIA mission, a worldwide network of ground-based telescopes, machine learning, and citizen scientists all have to do with each other? Thanks to this interesting combo of people and computers, astronomers now have more than 116,000 new variable stars to study. Until now, they knew of about 46,000 of these stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. They had observed maybe 10,000 or so in other galaxies. The discovery gives astronomers even more chances to study variables and understand why they behave the way they do.
Continue reading “Astronomers Find 116,000 New Variable Stars”Astronomers Find 116,000 New Variable Stars