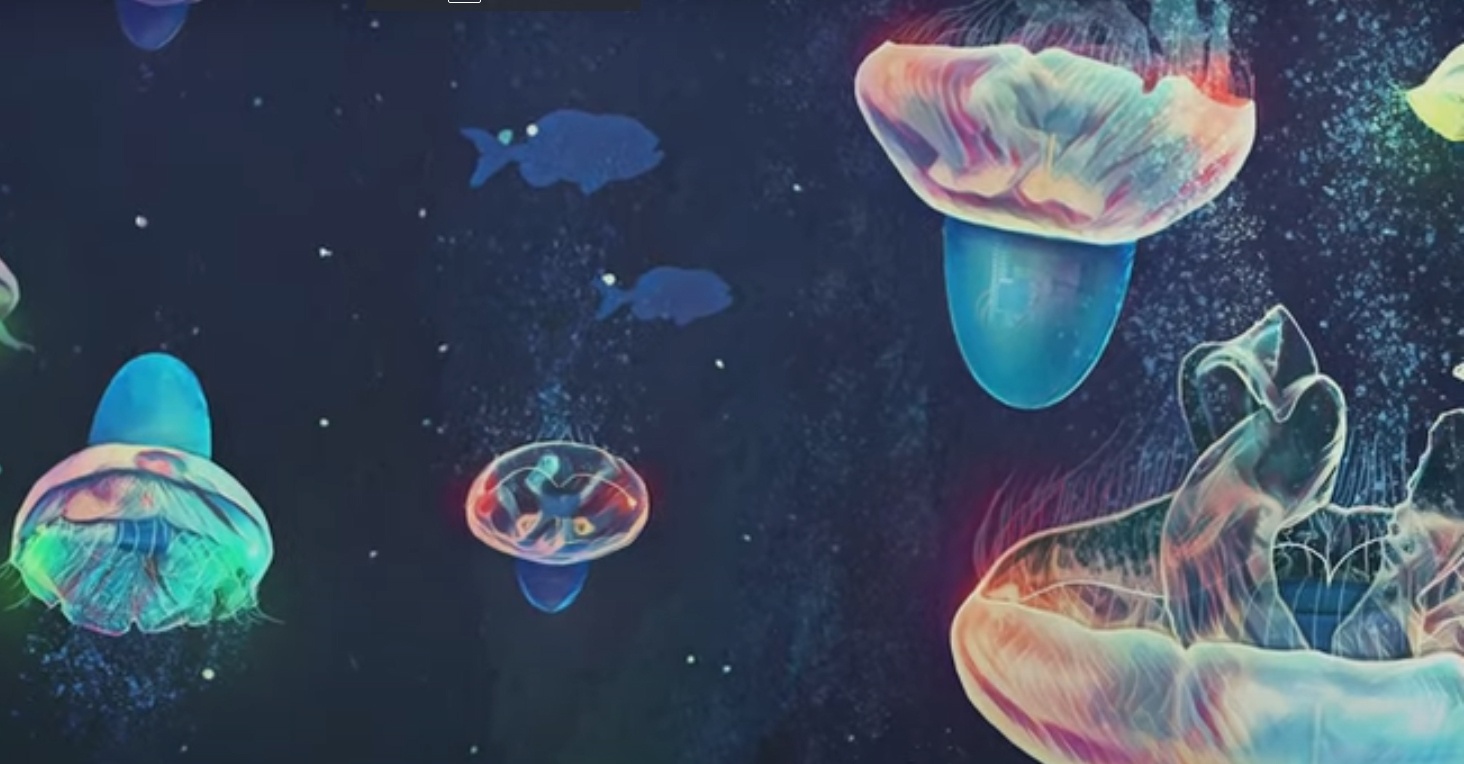
Earth’s oceans are—like space—a largely unexplored frontier. Relatively few humans have explored either place, using specialized life-support equipment. Unlike space, however, the oceans also have other beings that can explore them: jellyfish. They can head to places underwater that humans can never go. That makes them interesting candidates for autonomous ocean exploration.
Continue reading “Cyborg Jellyfish Could Help Explore Oceans Autonomously”This Galaxy Was Already Dead When the Universe Was Only 700 Million Years Old

When a galaxy runs out of gas and dust, the process of star birth stops. That takes billions of years. But, there’s a galaxy out there that was already dead when the Universe was only 700 million years old. What happened to it?
Continue reading “This Galaxy Was Already Dead When the Universe Was Only 700 Million Years Old”What’s the Best Way to Pack for Space?
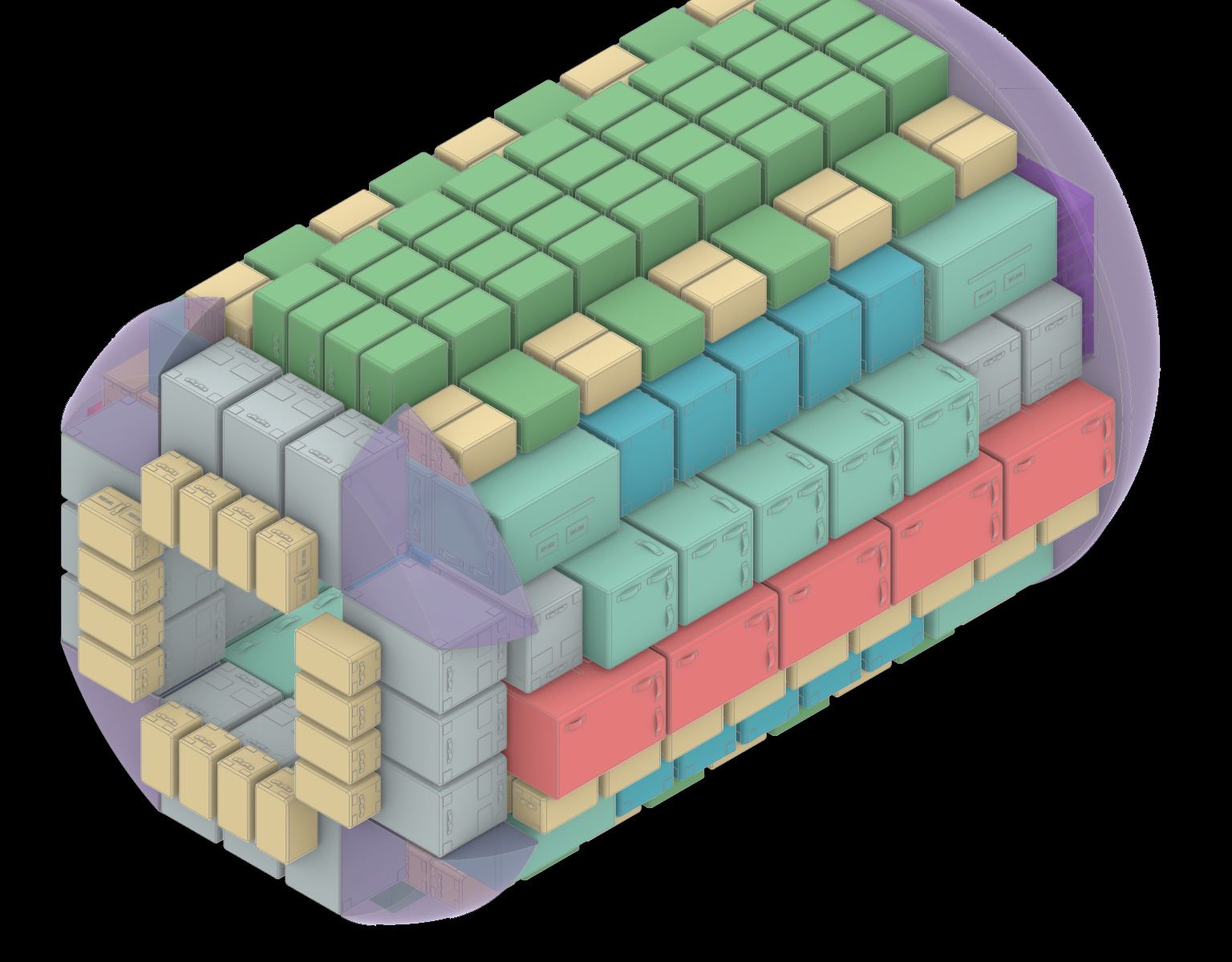
Packing to go to space is a lot like getting ready for a plane ride with only a carry-on bag. You have to maximize the use of the space in your bag at the same time you want to make sure you have what you need. That’s the challenge astronauts face in the upcoming Artemis moon missions. So, NASA held a competition to figure out the best and most innovative ways to store cargo for the missions.
Continue reading “What’s the Best Way to Pack for Space?”Curiosity Rover is Climbing Through Dramatic Striped Terrain on Mars
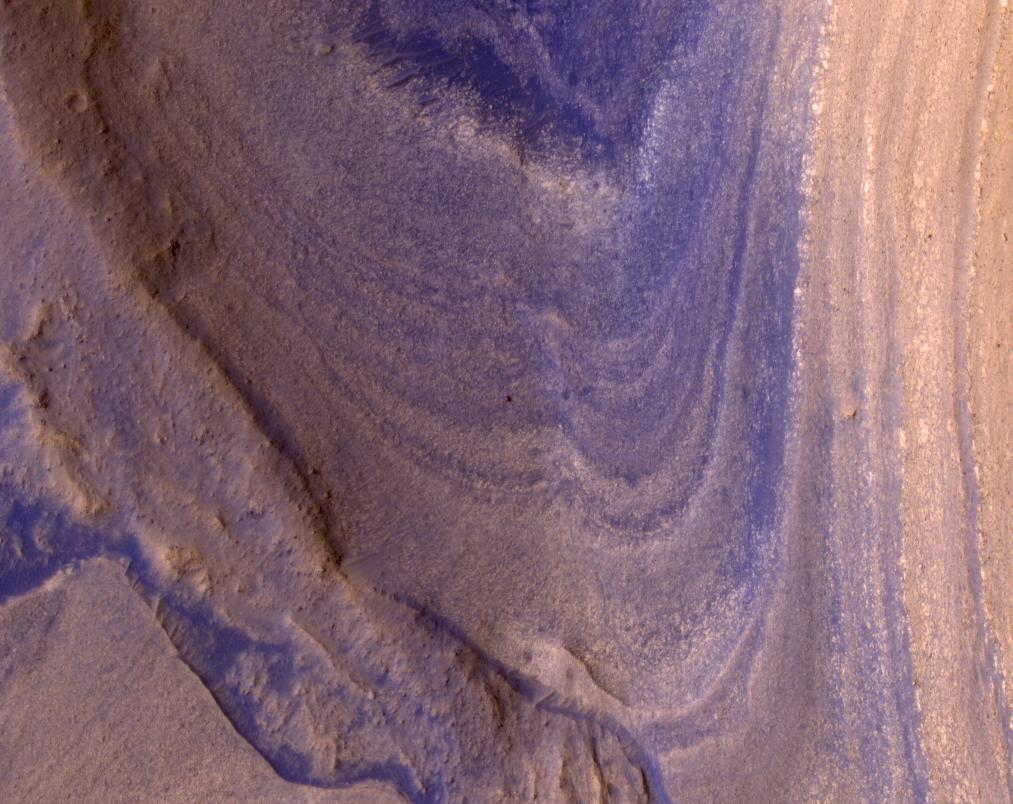

Just about every day we here on Earth get a breathtaking picture of Mars’s terrain sent back by a rover. But, the view from space can be pretty amazing, too. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) just sent back a thought-provoking picture of Curiosity as it makes its way up a steep ridge on Mount Sharp.
Continue reading “Curiosity Rover is Climbing Through Dramatic Striped Terrain on Mars”Planets in Binary Star Systems Could be Nice and Habitable

The Star Wars world Tatooine is one of the most recognizable planets in the realm of science fiction. It’s a harsh place, and its conditions shaped the hero Luke Skywalker in many ways. In the reality-based Universe, there may not be many worlds like it. That’s because, according to a new study out from Yale researchers, the Universe likes to be more orderly, and that affects planets and their environments.
Continue reading “Planets in Binary Star Systems Could be Nice and Habitable”A Planetary Disk in the Orion Nebula is Destroying and Replenishing Oceans of Water Every Month

Planet-forming disks are places of chaotic activity. Not only do planetesimals slam together to form larger worlds, but it now appears that the process involves the destructive recycling of water within a disk. That’s the conclusion from scientists studying JWST data from a planetary birth crèche called d203-506 in the Orion Nebula.
Continue reading “A Planetary Disk in the Orion Nebula is Destroying and Replenishing Oceans of Water Every Month”A Star Passed Through the Oort Cloud Less Than 500,000 Years Ago. It Wasn’t the Only One.
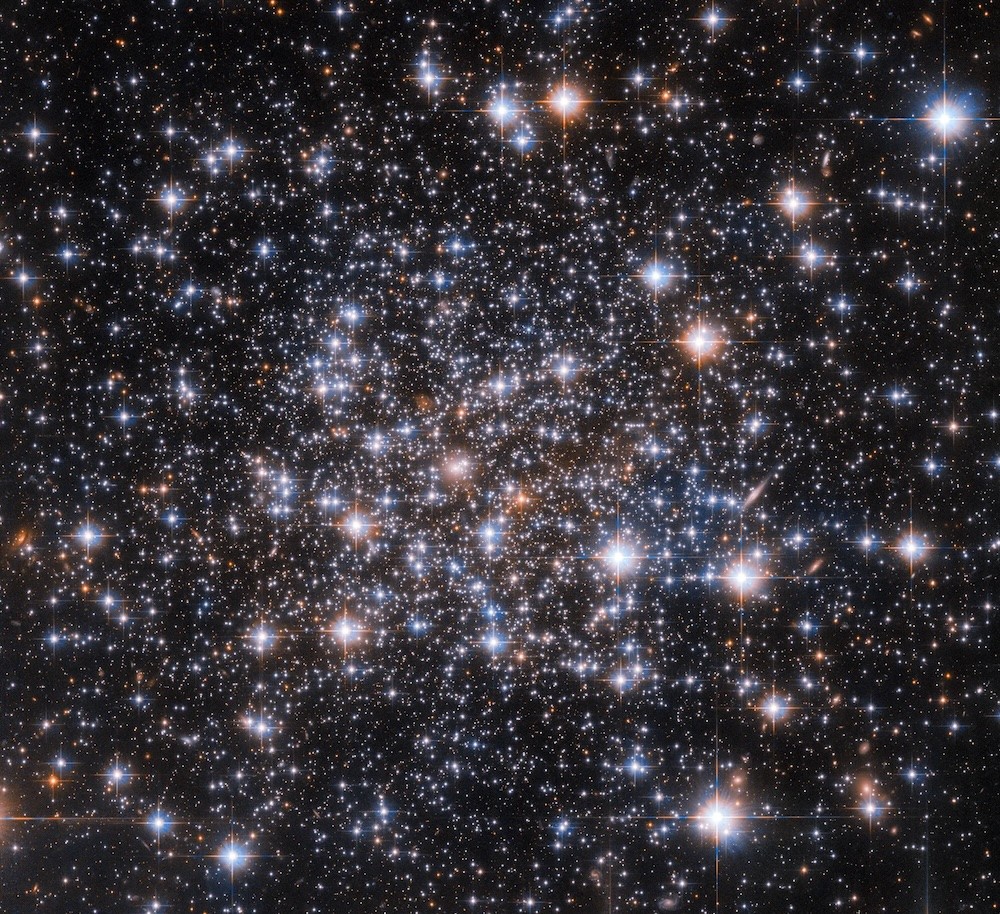

As stars in the Milky Way move through space, some of them have an unexpected effect on the Solar System. Over time, one comes closer to the Sun during its orbit in the galaxy. Some of them actually get within a light-year of our star and pass through the Oort Cloud. Such close flybys can affect the orbits of the outer planets and send cometary nuclei on a long inward rush to the Sun.
Continue reading “A Star Passed Through the Oort Cloud Less Than 500,000 Years Ago. It Wasn’t the Only One.”A New, More Accurate Measurement for the Clumpiness of the Universe
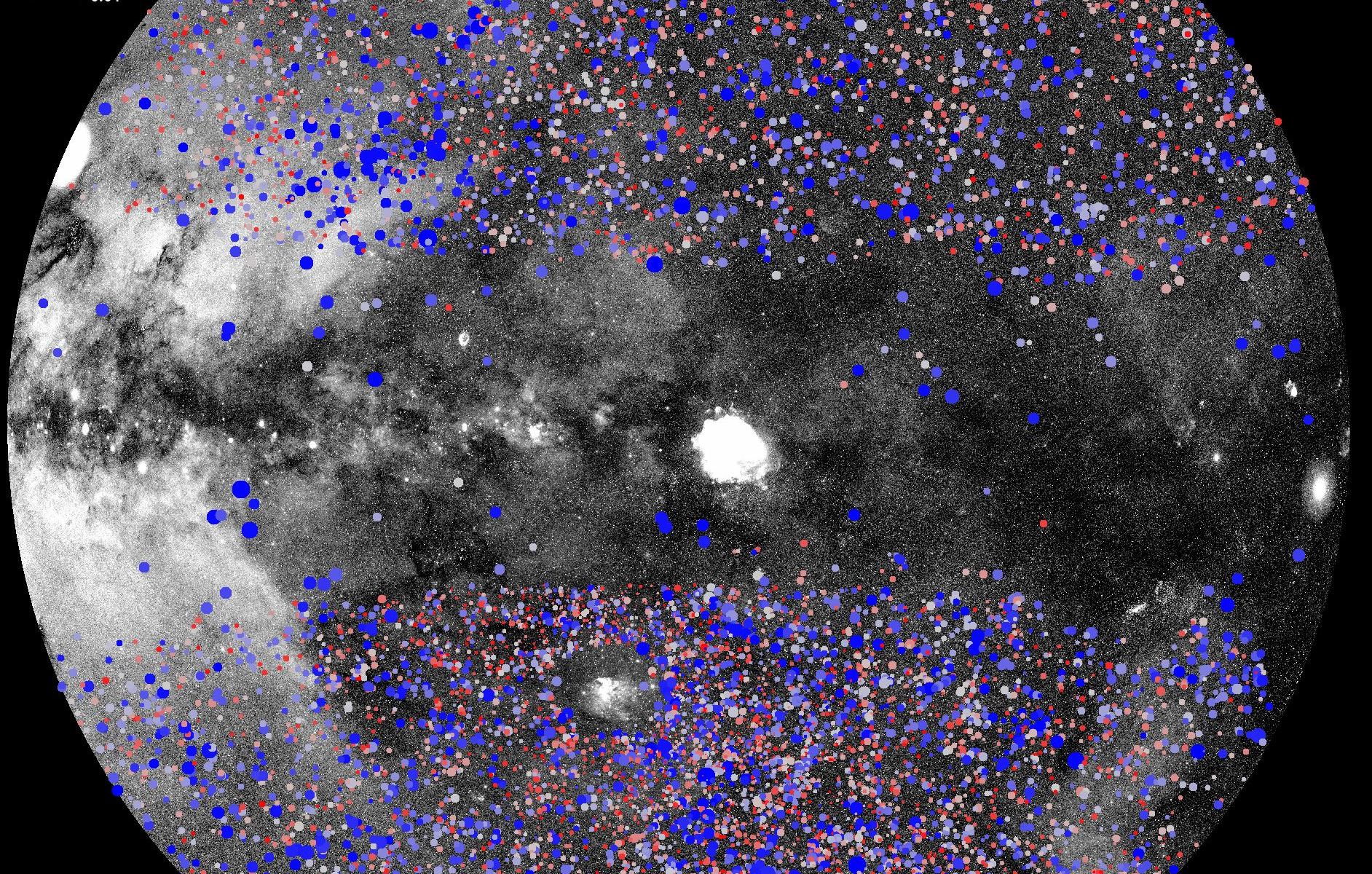

Cosmologists are wrestling with an interesting question: how much clumpiness does the Universe have? There are competing but not compatible measurements of cosmic clumpiness and that introduces a “tension” between the differing measurements. It involves the amount and distribution of matter in the Universe. However, dark energy and neutrinos are also in the mix. Now, results from a recent large X-ray survey of galaxy clusters may help “ease the tension”.
Continue reading “A New, More Accurate Measurement for the Clumpiness of the Universe”Even Stars Like the Sun Can Unleash Savage Flares in Their Youth
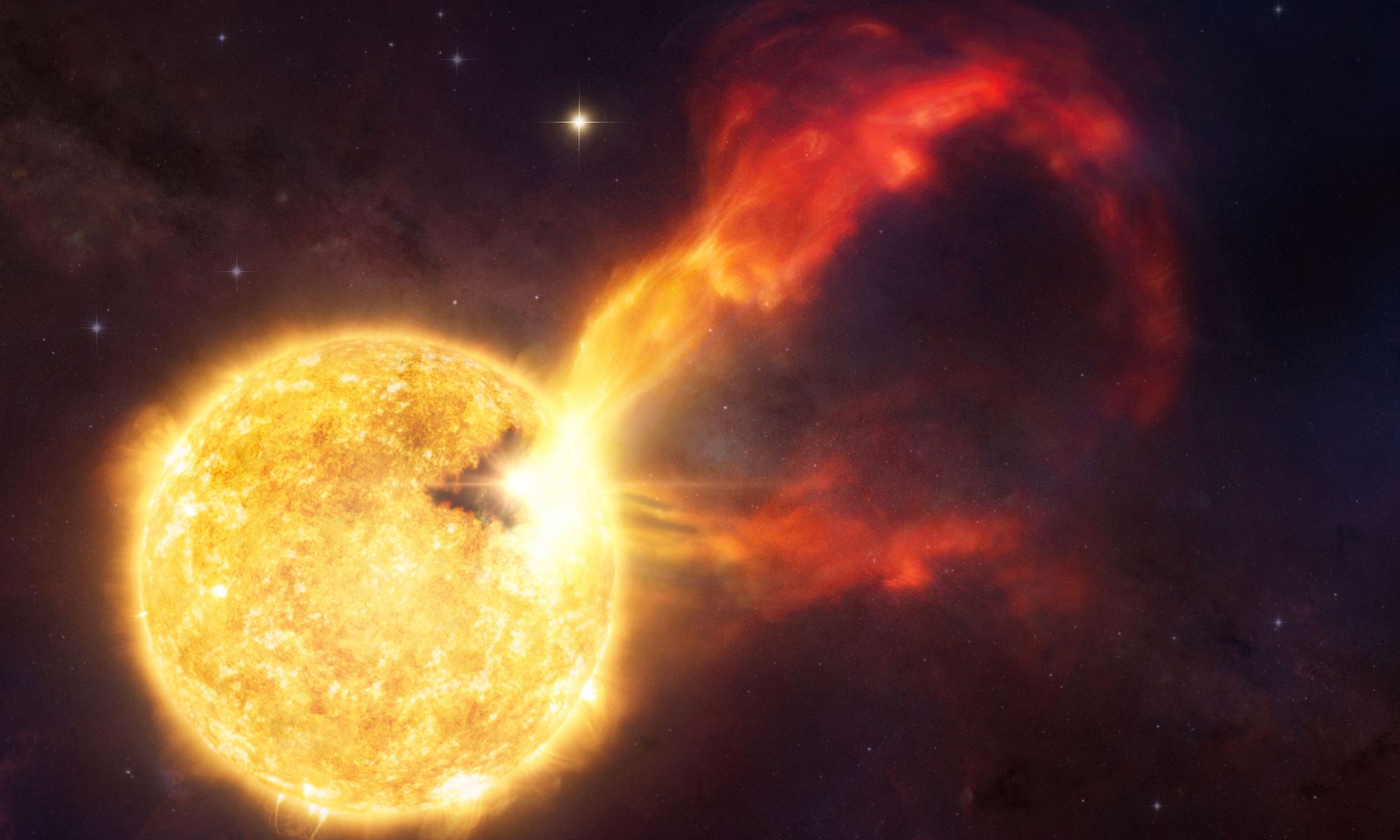

Why would a young Sun-like star suddenly belch out a hugely bright flare? That’s what astronomers at Harvard Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory want to know after they spotted such an outburst using a sensitive submillimeter-wave telescope. According to Joshua Bennett Lovell, leader of a team that observed the star’s activity, these kinds of flare events are rare in such young stars, particularly at millimeter wavelengths. So, what’s happening there?
Continue reading “Even Stars Like the Sun Can Unleash Savage Flares in Their Youth”Black Holes Existed at the Dawn of Time, Birthing Stars and Encouraging Galaxy Formation
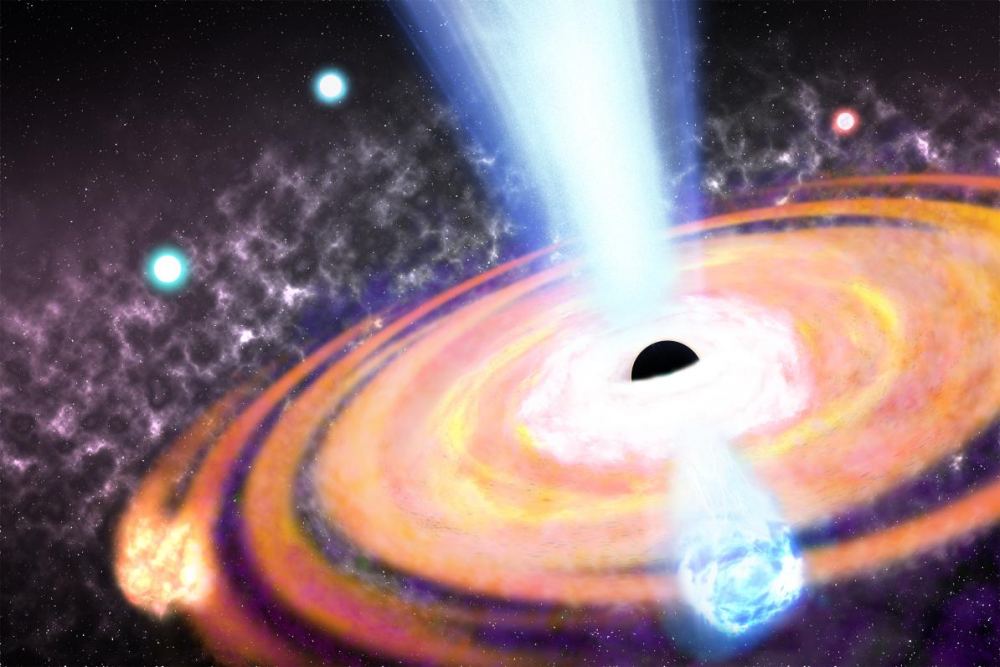

The Universe is full of galaxies, many containing supermassive black holes. That sparked a question: which came first—the galaxies or their black holes? The answer is becoming very clear, thanks to the first year of observations made by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Black holes were in the Universe from the earliest times, along with the very first galaxies. And, they helped shape the cosmos we observe today.
Continue reading “Black Holes Existed at the Dawn of Time, Birthing Stars and Encouraging Galaxy Formation”
