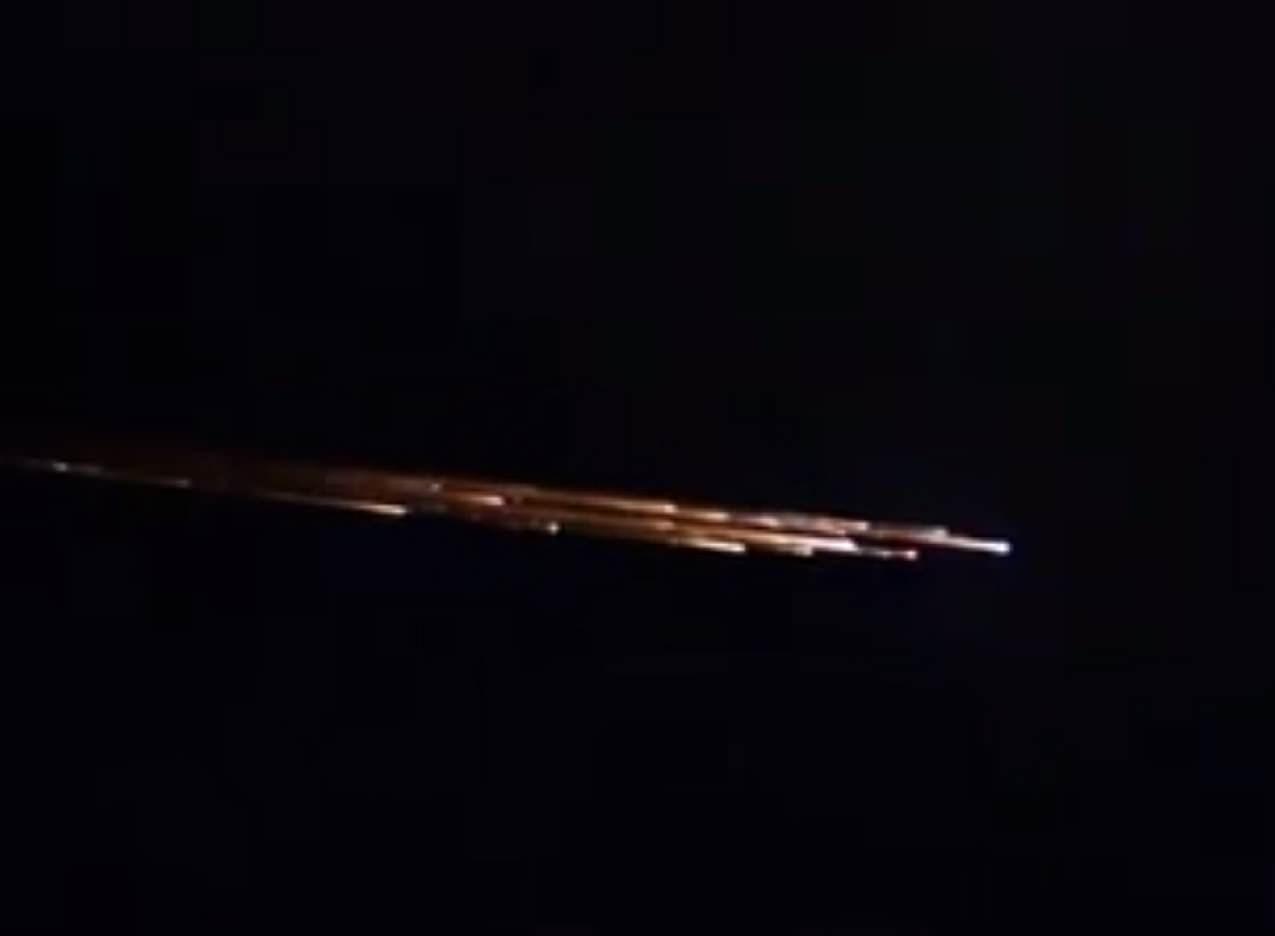
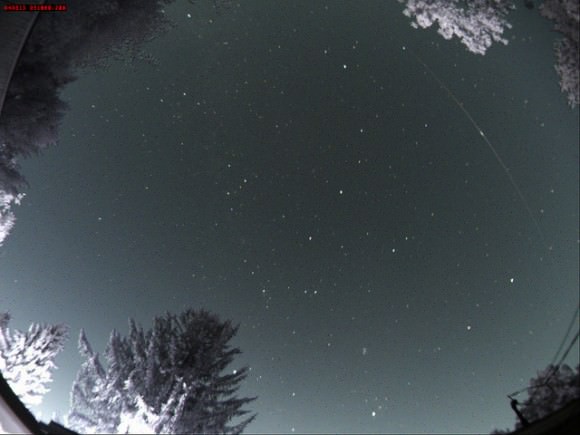
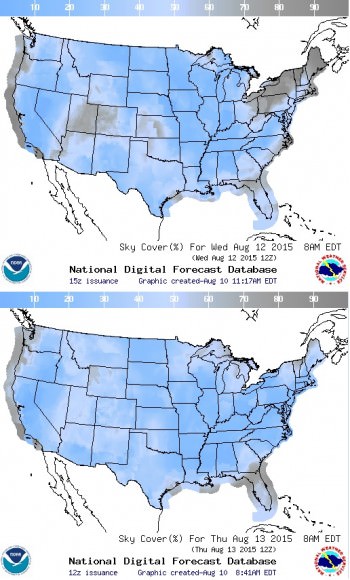
A relic of the Cold War surprised beach-goers and Hawaiian islands residents Sunday night, as Kosmos-1315 reentered the Earth’s atmosphere in a dramatic display.
The reentry occurred right around 11:00 PM Sunday night on August 30th local time (Hawaii is 10 hours behind Universal Time). Folks in the satellite tracking community had been following the predicted reentry for some time, which was projected for August 31st at 10:56 UT +/- an hour. That puts the Hawaii sighting right at the beginning of the window.


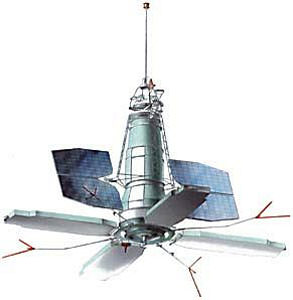
Kosmos 1315 (Sometimes listed as Cosmos 1315) was an electronic signal intelligence (ELINT) satellite launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in the then Soviet Union on October 13th, 1981. First developed in the late 1960s, Kosmos 1315 was a typical Tselina-D type component of the two-satellite Tselina ELINT system. Kosmos 1315 was launched atop a Vostok-2M rocket, the booster for which still remains in orbit today as NORAD ID 1981-103B. Kosmos 1315 was in a 533 x 574 km low Earth orbit.
Long-time satellite tracker Ted Molczan has been compiling a list of reentries that goes back to the dawn of the Space Age, and notes that this was the 256th reentry sighting he’s confirmed in his cataloging effort.
“Objects launched by Russia account for 205 sightings or 80 percent, followed by the U.S., which accounts for 40 sightings or 16 percent. China, Europe and Japan account for the remaining 4 percent,” Molczan told Universe Today. “Considering the vast areas of the Earth that have been under-reported, the total number of reentries seen during the Space Age probably is between 500 and 1000, the large majority lost to history.”
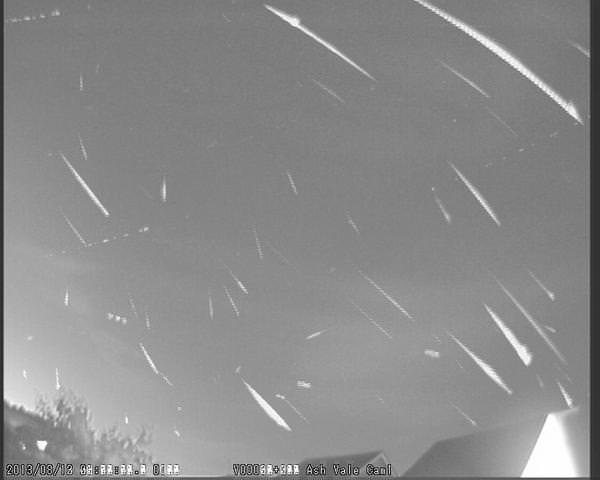
This was a fine example of a classic reentry versus a typical fireball or meteor train. Satellites typically have a slower reentry velocity, and you can see this in several of the videos captured of the event. Most fireball captures come from security and dashboard cams (remember Chelyabinsk?) or cameras that are already up and running recording another event, such as a concert or a football game. The famous Peekskill meteor in 1992 was captured in the background during a high school football game. Remember, during Chelyabinsk, the very first images of the event were from dashcams; minutes later, after everyone rushed to aim their hastily deployed mobile phone cameras at the contrail, we got the recordings of the blast wave. The very fact that several folks grabbed their phones and managed to capture the reentry in progress on Sunday night (how fast can YOU have your phone out, camera running?) speaks to the slow, stately traverse typical of a satellite reentry.
…and folks on social media often try to get in on the hype during a breaking story involving a meteor train or fireball event. Feel free to try to be creative, but trust us, we’ve seen ‘em all. Some ‘meteor wrongs’ (to paraphrase Meteorite Man Geoff Notkin) that typically get recycled and advertised as new videos are: the reentries of Mir, Hayabasa, the aforementioned Peekskill event, Chelyabinsk, and screen grabs from the film Armageddon.
“As is common with reentries, a few people reported the phenomenon as a UFO. A couple of witnesses perceived the glowing fragments as individual craft of some kind,” Molczan told Universe Today. “Satellite orbits closely follow the curvature of the Earth’s surface, and they continue to do so as they begin their final descent during reentry. As reentry proceeds, velocity is lost due to drag, causing the descent to gradually become steeper, but to an observer, the motion appears to be nearly horizontal. By the time an object descends below about 30 kilometers, it will have lost nearly all of its forward velocity, and from there, any surviving fragments will descend almost vertically to the Earth.”
This final descent is similar to what’s known as ‘dark flight’ prior to a meteorite impact.
And though we usually get a few high interest reentries such as Phobos-Grunt or UARS every year, space junk is reentering worldwide weekly. The Aerospace Corp. keeps a running list of upcoming reentries, and the See-Sat-L message board is a great source of fast-breaking news.
It’s definitely a space junk shooting gallery out there. Keep those smartphones charged up and handy, and keep watching the skies!