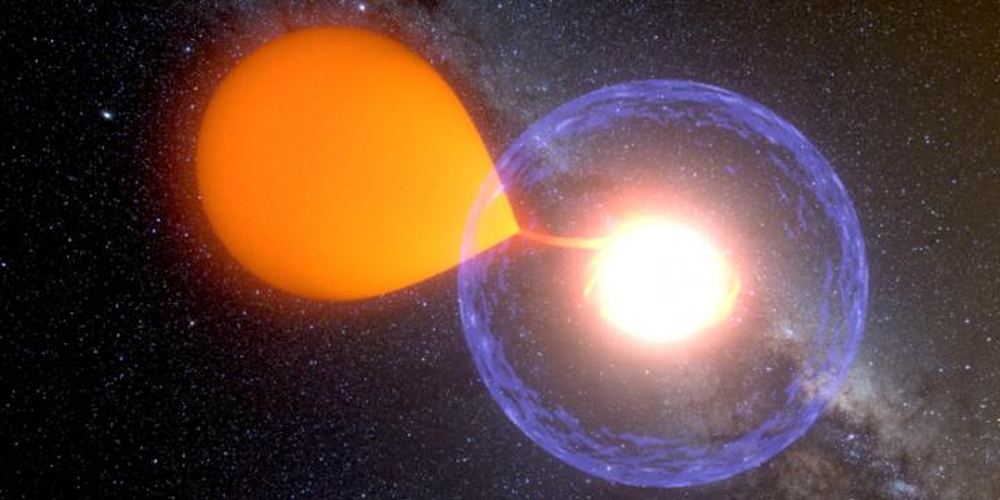
It’s easy to run out of superlatives and adjectives when your puny human language is trying to describe humongously-energetic events in the Universe. So now it’s down to this: a really powerful supernova is a “super-supernova.”
But whatever name we give it, it’s a monster. A monsternova.
Continue reading “Super-Supernova Released Ten Times More Energy than a Regular Supernova”