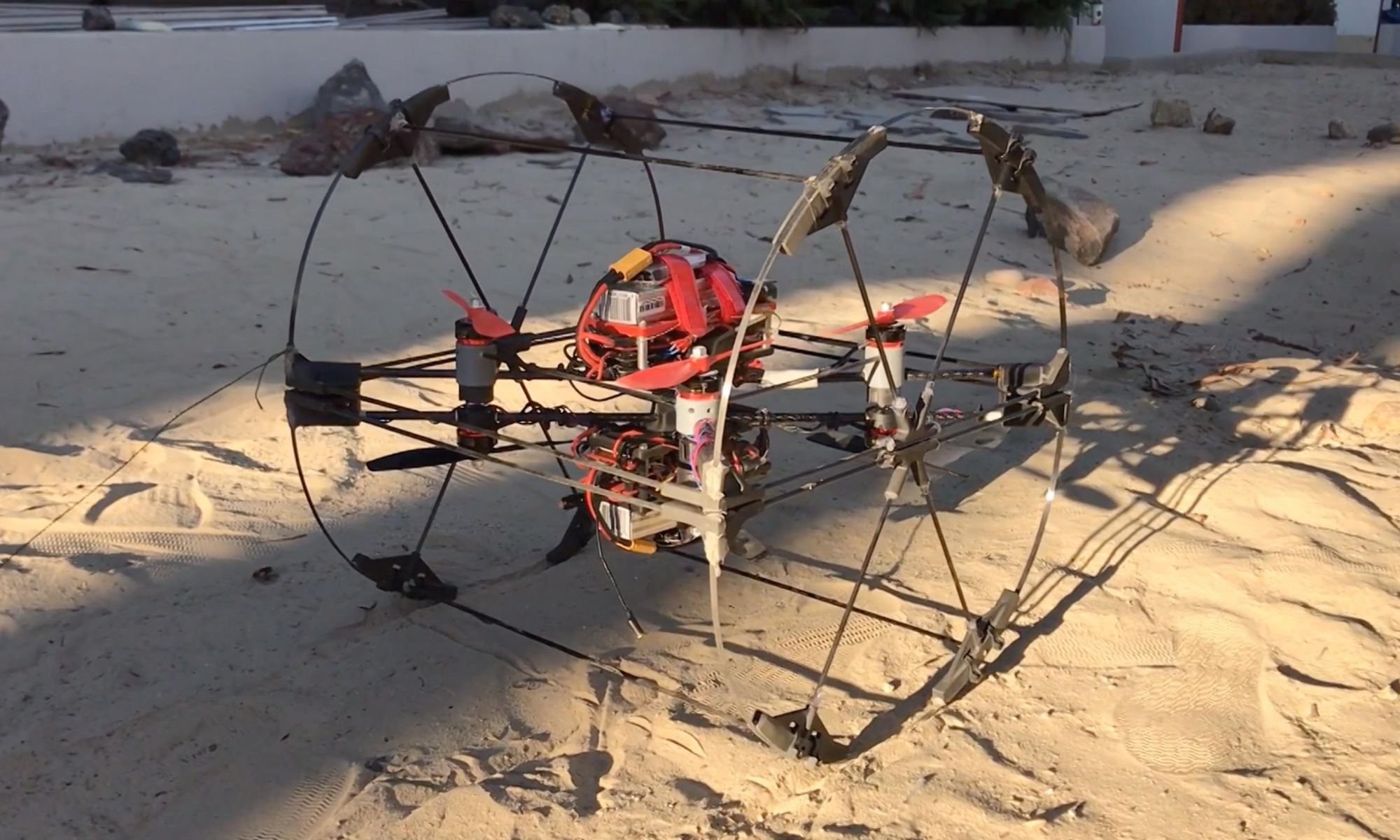
When it comes to space exploration, it’s robots that do most of the work. That trend will continue as we send missions onto the surfaces of worlds further and further into the Solar System. But for robots to be effective in the challenging environments we need to explore—like Saturn’s moon Titan—we need more capable robots.
A new robot NASA is developing could be the next step in robotic exploration.
Continue reading “Shape-shifting Robots Like These Could Be Just What We Need to Explore Titan”