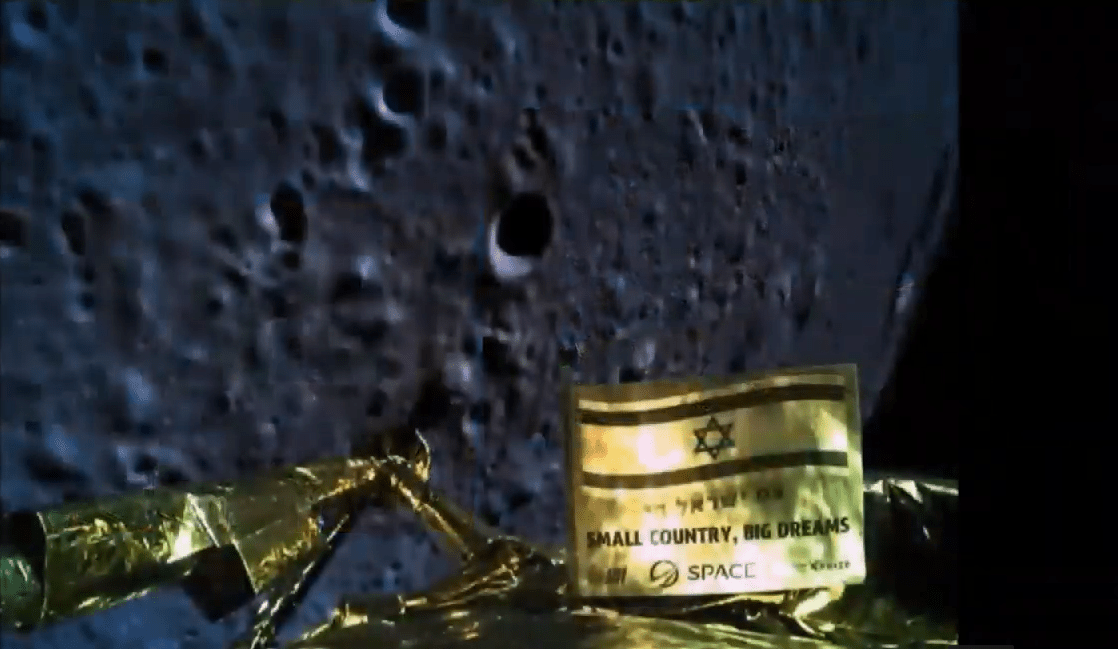
The Israeli Beresheet spacecraft has crashed into the Moon. The craft, whose name is Hebrew for “in the beginning” made its descent to the Moon but failed to stick its landing. If it had been successful, it would have put Israel in elite company, and made them only the fourth country to have a soft landing on the Moon, joining the USA, China, and the former Soviet Union.
Continue reading “Beresheet Crashed.”Space Weather Forecasts can now give Satellites One Whole Day of Warning when a Killer Solar Storm is Inbound

Earth’s fleet of satellites is in a vulnerable position. When solar activity increases, high-energy particles are directed toward Earth. Our large fleet is in the direct path of all that energy, which can damage them or render them inoperable. But now we have another tool to help us protect our satellites.
Continue reading “Space Weather Forecasts can now give Satellites One Whole Day of Warning when a Killer Solar Storm is Inbound”It’s Finally here. The First Ever Image of a Black Hole

“We have taken the first picture of a black hole.”
EHT project director Sheperd S. Doeleman of the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian.
What was once un-seeable can now be seen. Black holes, those difficult-to-understand singularities that may reside at the center of every galaxy, are becoming seeable. The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) has revealed the first-ever image of a black hole, and with this image, and all the science behind it, they may help crack open one of the biggest mysteries in the Universe.
Continue reading “It’s Finally here. The First Ever Image of a Black Hole”The World’s Glaciers are Down by 9 Trillion Tonnes of Ice in the Last Half Century
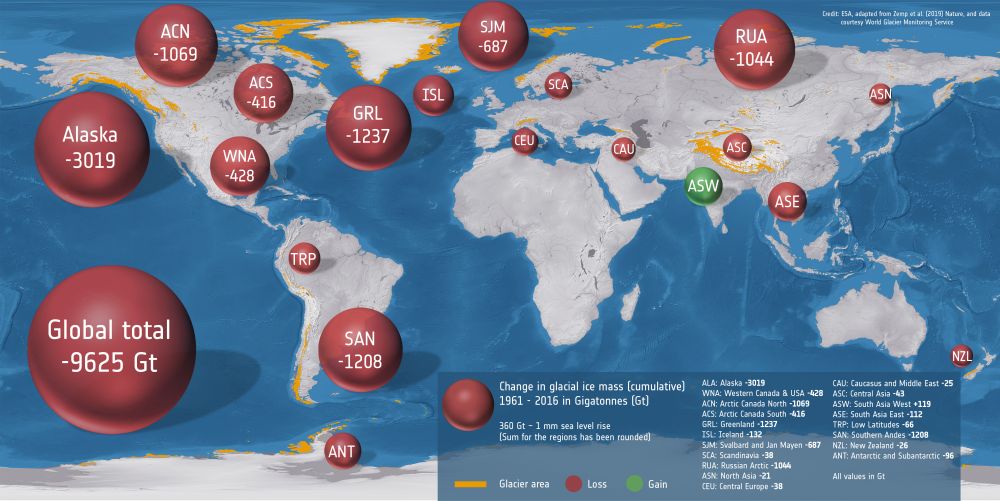
Things are not looking good for Earth’s glaciers. Usually, when it comes to climate change and melting ice, we think of the Earth’s polar regions. But they’re not the only important ice formations, and they’re not the only ice that’s melting due to climate change.
Continue reading “The World’s Glaciers are Down by 9 Trillion Tonnes of Ice in the Last Half Century”Metal Asteroid Psyche Might Have Had Volcanoes of Molten Iron
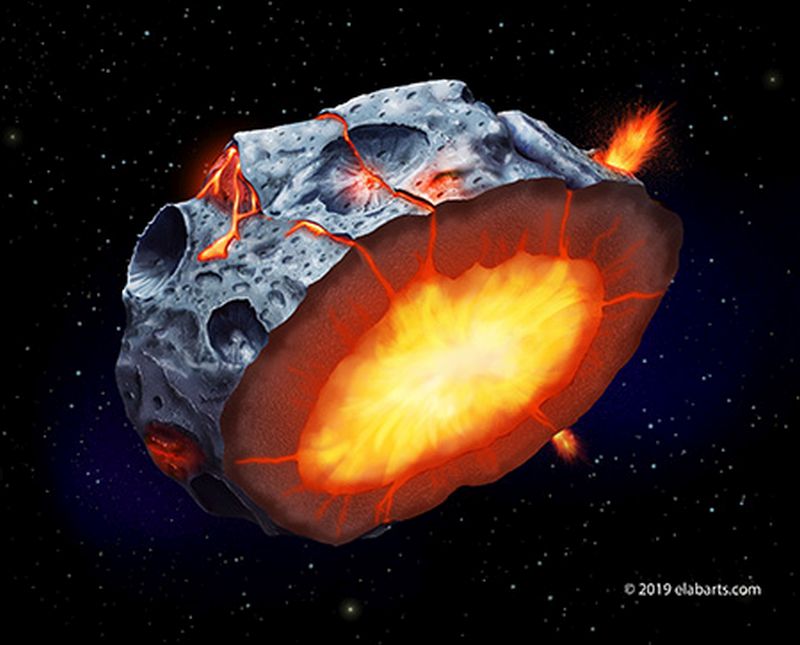
Imagine a time in the Solar System’s past, when the asteroids were not solid rock, but blobs of molten iron. It sounds strange, but that may have been the case. And in the right conditions, some of those asteroids would have sprouted volcanoes. One of those asteroids, Psyche, is the destination for a NASA mission.
Continue reading “Metal Asteroid Psyche Might Have Had Volcanoes of Molten Iron”Mars Express Saw the Same Methane Spike that Curiosity Detected from the Surface of Mars
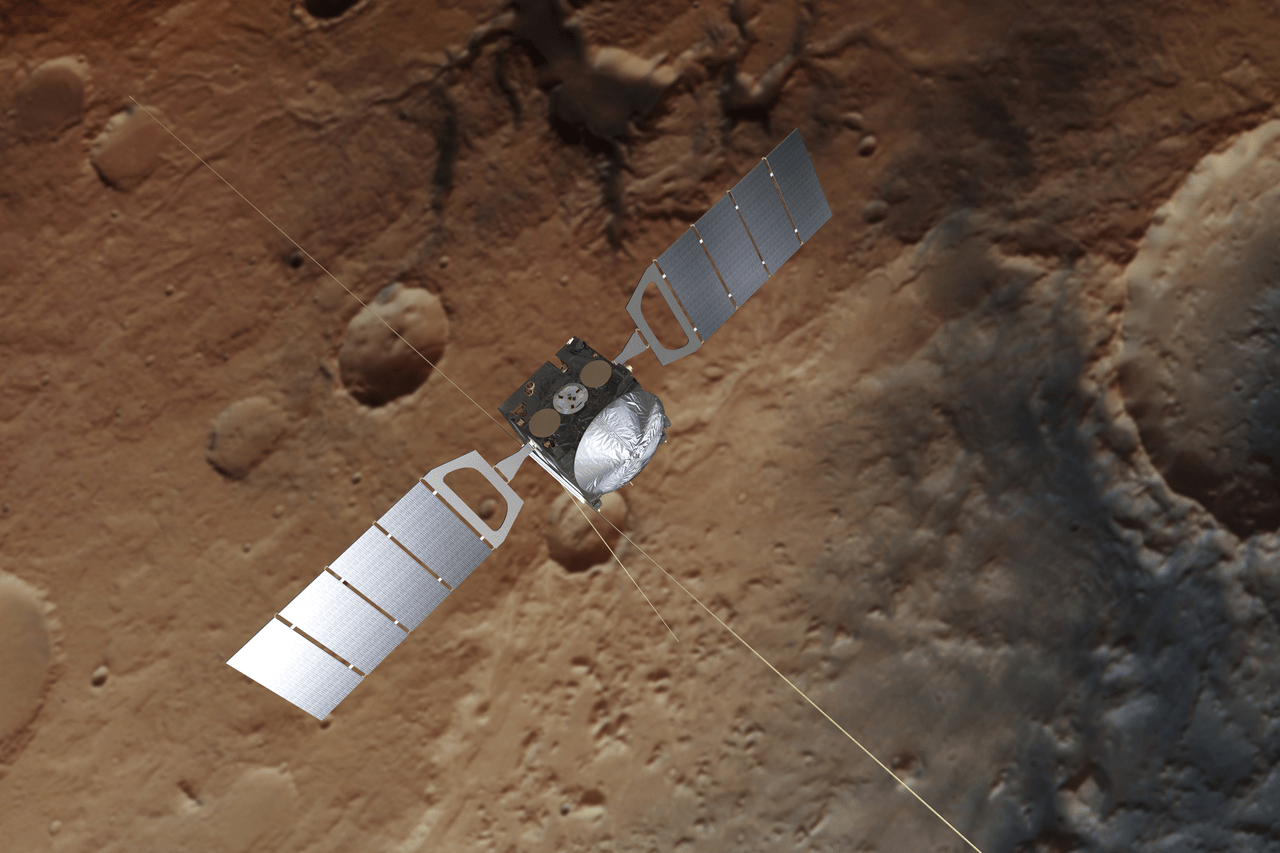
If you’re not a chemist, an astrobiologist, or a scientist of any sort, and that includes most of us, then a tiny, almost imperceptible whiff of methane in the Martian atmosphere might seem like no big deal. But it is, gentle humans. It is.
Why?
Because it could be a signal that some living process is at work. And even we non-scientists have wondered at some point if the only life in the Solar System, or maybe in the entire Universe, is confined here on Earth.
Continue reading “Mars Express Saw the Same Methane Spike that Curiosity Detected from the Surface of Mars”Mars Helicopter Completes More Test Flights. It’s Almost Ready to go to Mars
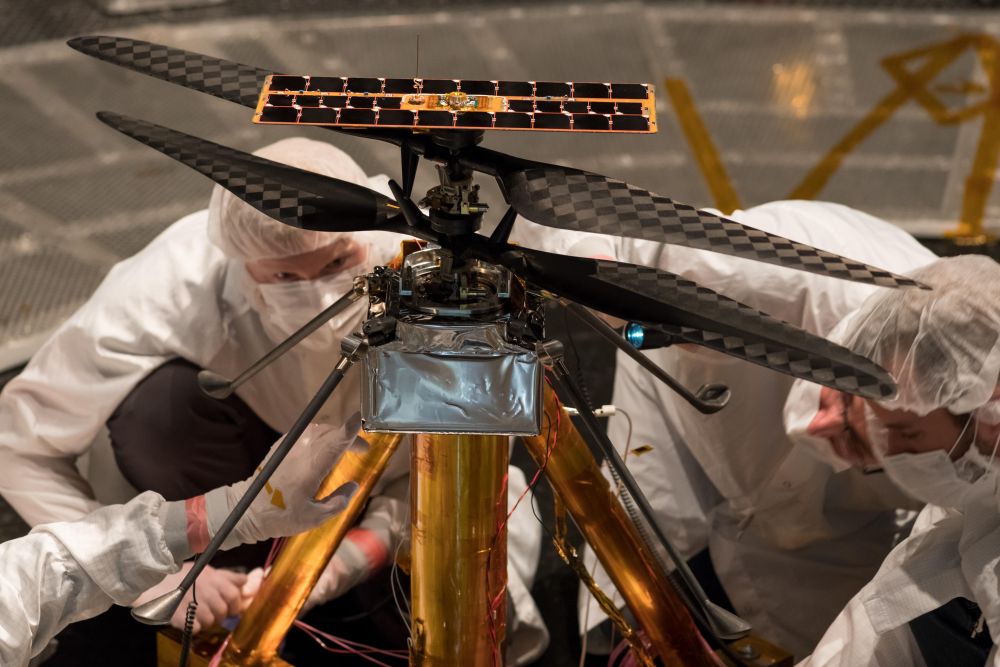

We’ve known for some time that NASA is sending a helicopter to Mars. The vehicle, called the Mars Helicopter, is undergoing flight testing at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. The little helicopter will make its eventual way to Mars as part of the Mars 2020 Rover mission.
The Mars Helicopter is pretty small, less than 1.8 kg (4 lb). It’s made of lightweight carbon fiber, and other materials like aluminum, silicon, and foil. The version being tested is the actual vehicle that will make the trip to Mars.
Continue reading “Mars Helicopter Completes More Test Flights. It’s Almost Ready to go to Mars”The Wait is Almost Over. We’ll Finally See a Picture of a Black Hole’s Event Horizon on April 10th
The rumours you’ve heard are true. And if you haven’t heard the rumours, you should check your internet connection.
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration has set an important press conference for April 10th. They haven’t come right out and said it, but a Media Advisory from the ESO, a partner in the EHT, says they will, “hold a press conference to present a ground-breaking result from the EHT.” If it’s not a black hole, what else would it be?
Continue reading “The Wait is Almost Over. We’ll Finally See a Picture of a Black Hole’s Event Horizon on April 10th”Ground-Based Telescope Directly Observes the Atmosphere of an Extrasolar Planet, and Sees Swirling Clouds of Iron and Silicates
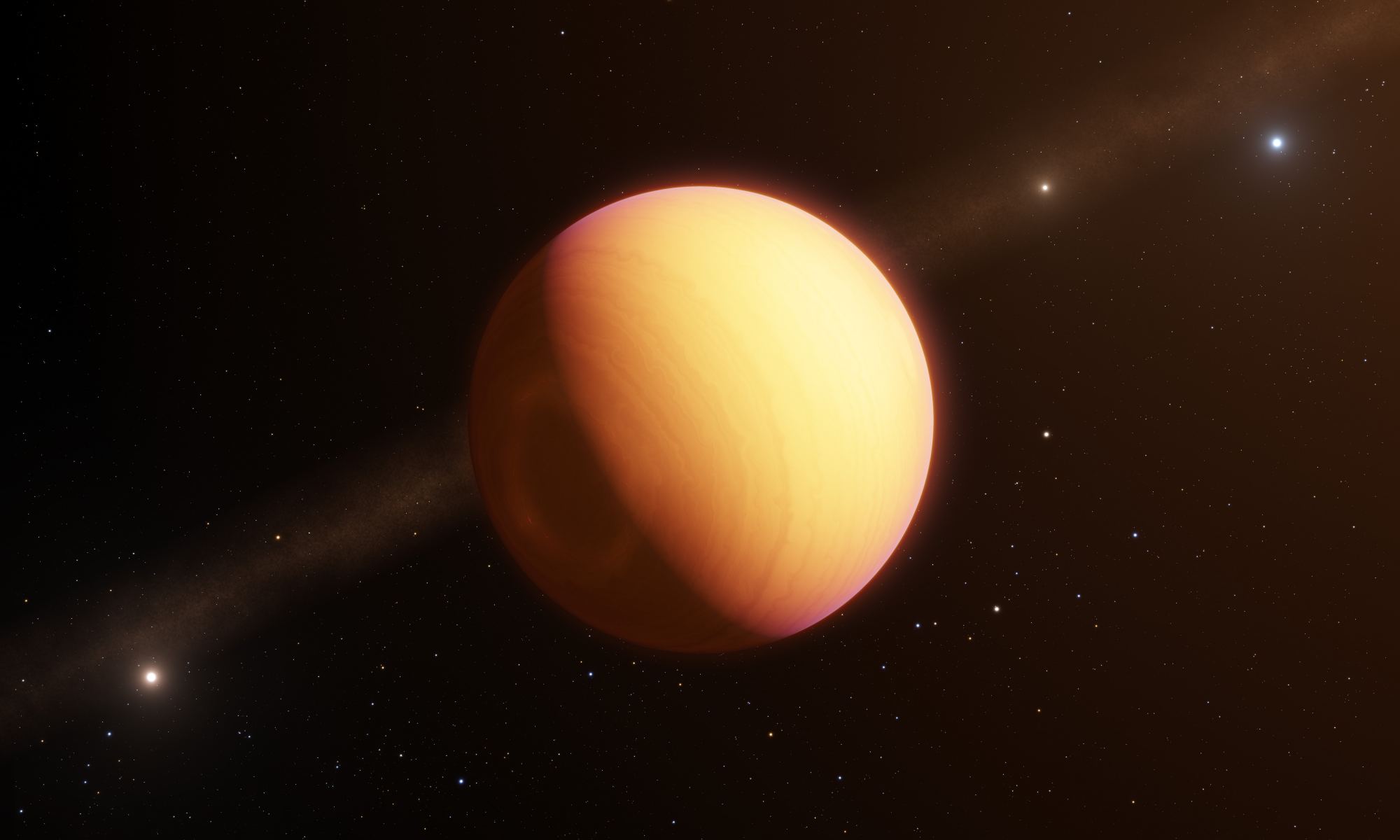

We’ve finally got our first optical look at an exoplanet and its atmosphere, and boy is it a strange place. The planet is called HR8799e, and its atmosphere is a complex one. HR8799e is in the grips of a global storm, dominated by swirling clouds of iron and silicates.
Continue reading “Ground-Based Telescope Directly Observes the Atmosphere of an Extrasolar Planet, and Sees Swirling Clouds of Iron and Silicates”Rivers on Mars Flowed for More Than a Billion Years
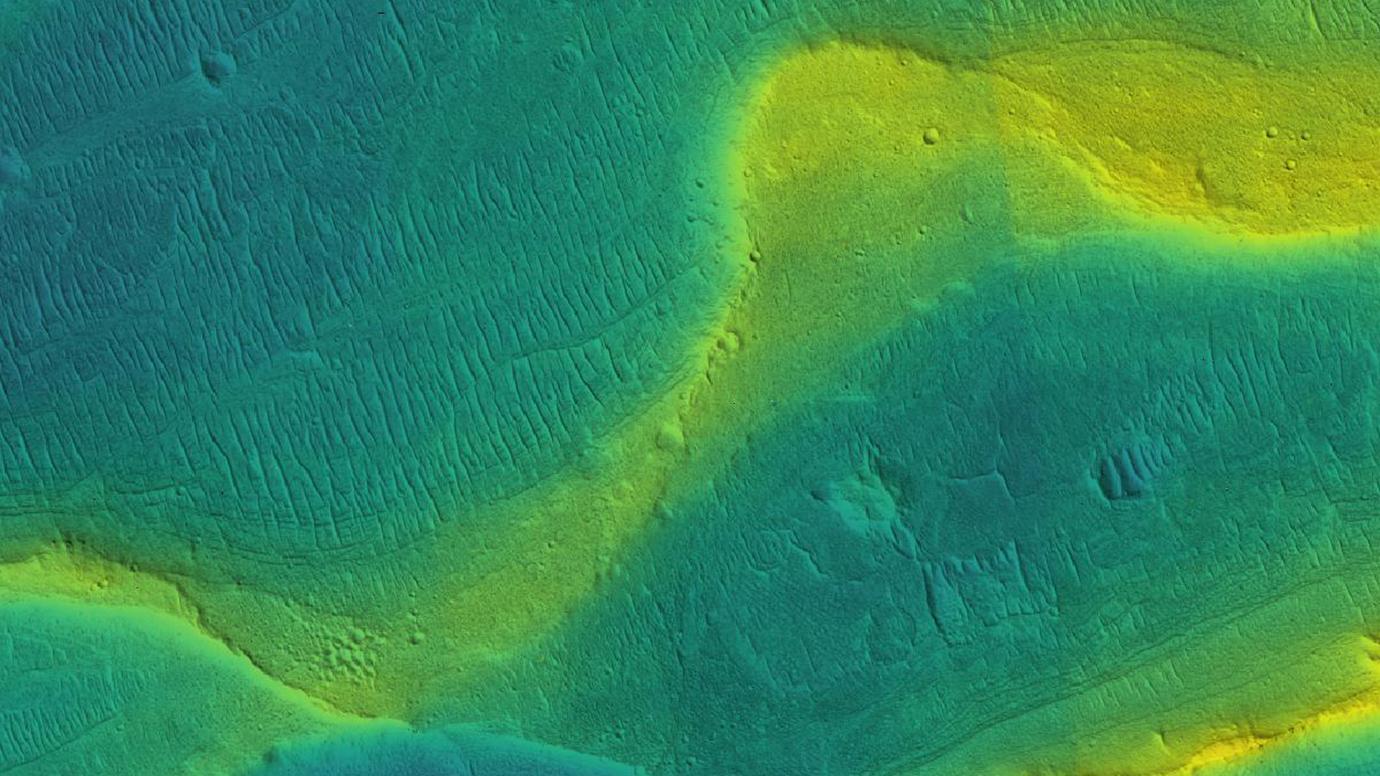

The ancient climate of Mars is a mystery to scientists. Even with all we’ve learned about Mars, it’s still difficult to explain how lakes and rivers existed. A new study shows that Martian rivers were swollen with runoff and that they flowed far later into the planet’s history than previously thought.
The question is, how did the Martian climate create these conditions?
Continue reading “Rivers on Mars Flowed for More Than a Billion Years”


