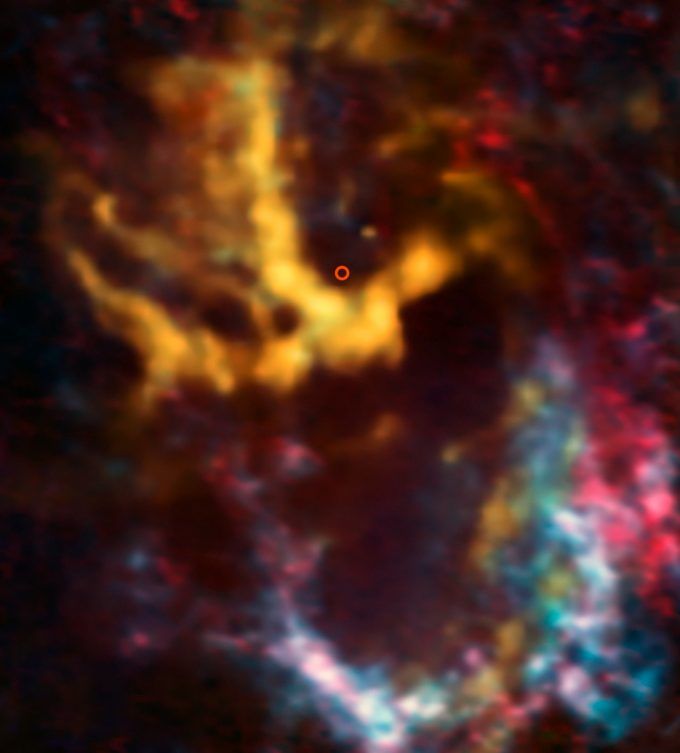
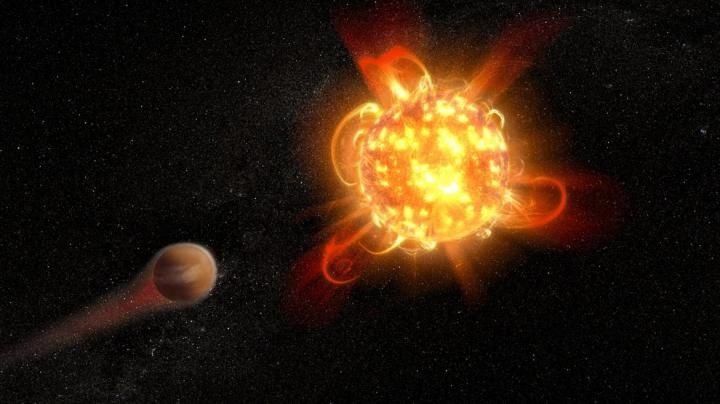
The most common type of star in the galaxy is the red dwarf star. None of these small, dim stars can be seen from Earth with the naked eye, but they can emit flares far more powerful than anything our Sun emits. Two astronomers using the Hubble space telescope saw a red dwarf star give off a powerful type of flare called a superflare. That’s bad news for any planets in these stars’ so-called habitable zones.
Red dwarfs make up about 75% of the stars in the Milky Way, so they probably host many exoplanets. In fact, scientists think most of the planets that are in habitable zones are orbiting red dwarfs. But the more astronomers observe these stars, the more they’re becoming aware of just how chaotic and energetic it can be in their neighbourhoods. That means we might have to re-think what habitable zone means.
“When I realized the sheer amount of light the superflare emitted, I sat looking at my computer screen for quite some time just thinking, ‘Whoa.'” – Parke Loyd, Arizona State University.
Continue reading “A Red Dwarf Blasts off a Superflare. Any Life on its Planets Would Have a Very Bad Day”