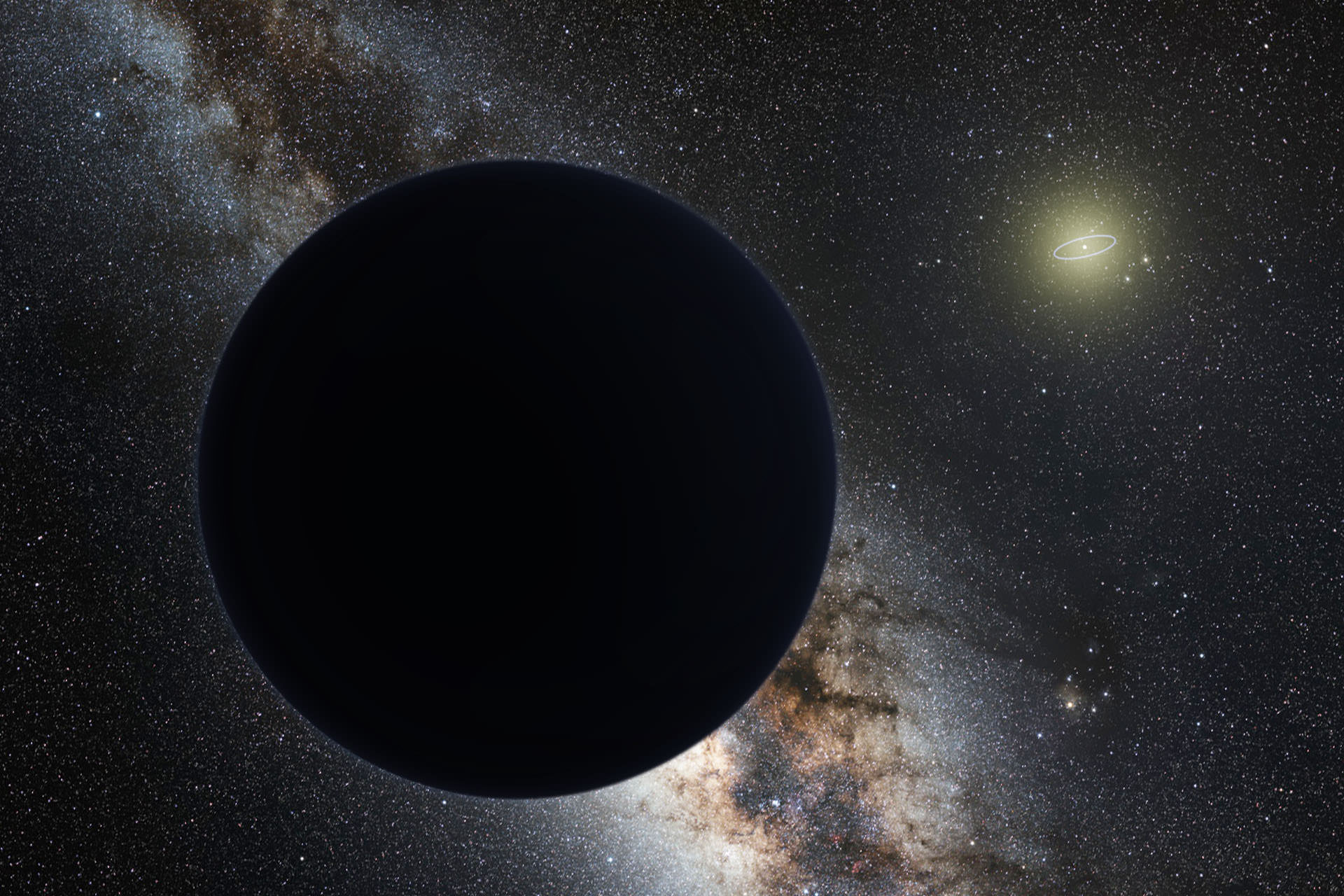
Does another undetected planet languish in our Solar System’s distant reaches? Does it follow a distant orbit around the Sun in the murky realm of comets and other icy objects? For some researchers, the answer is “almost certainly.”
Continue reading “New Evidence for Our Solar System’s Ghost: Planet Nine”New Evidence for Our Solar System’s Ghost: Planet Nine