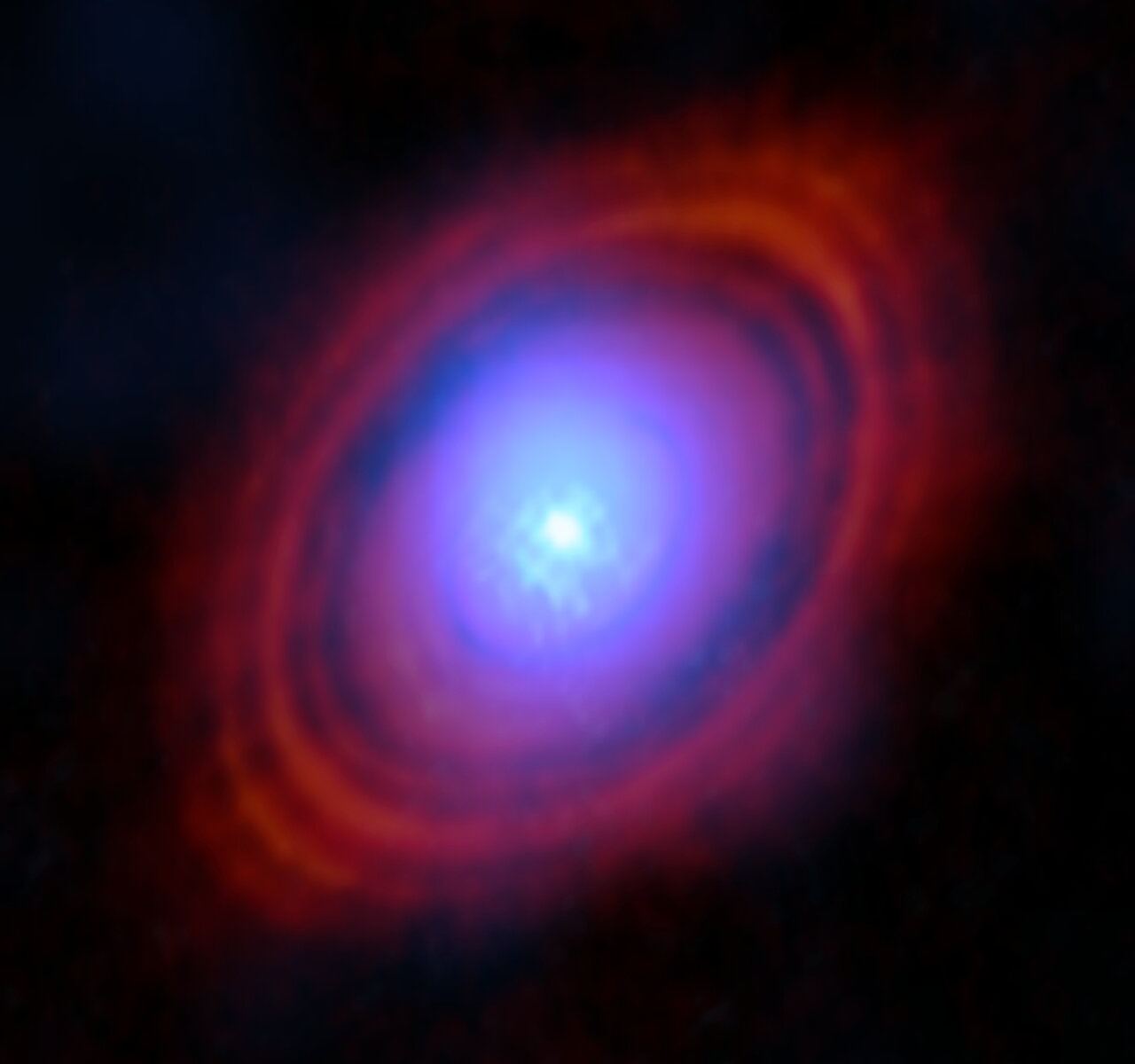
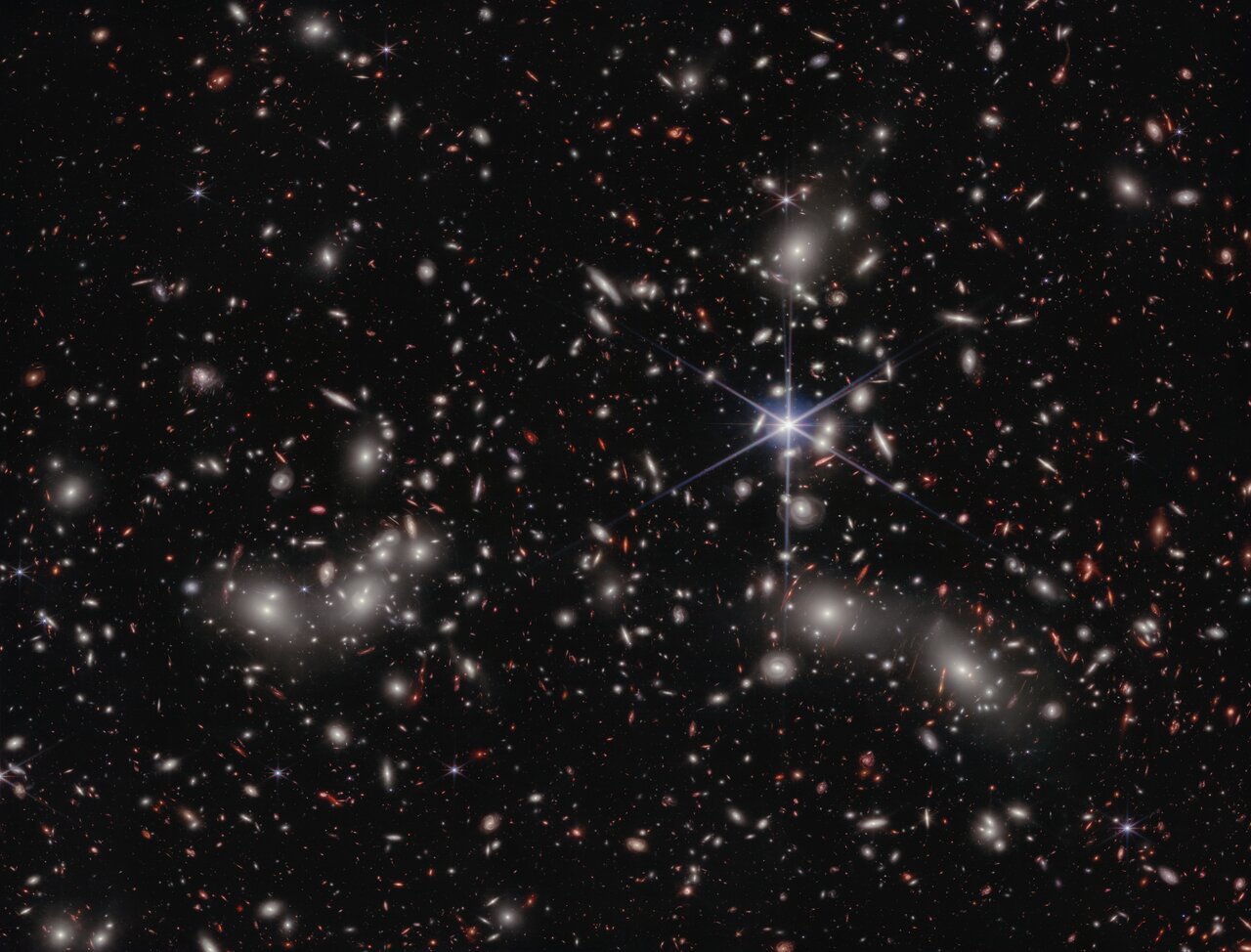
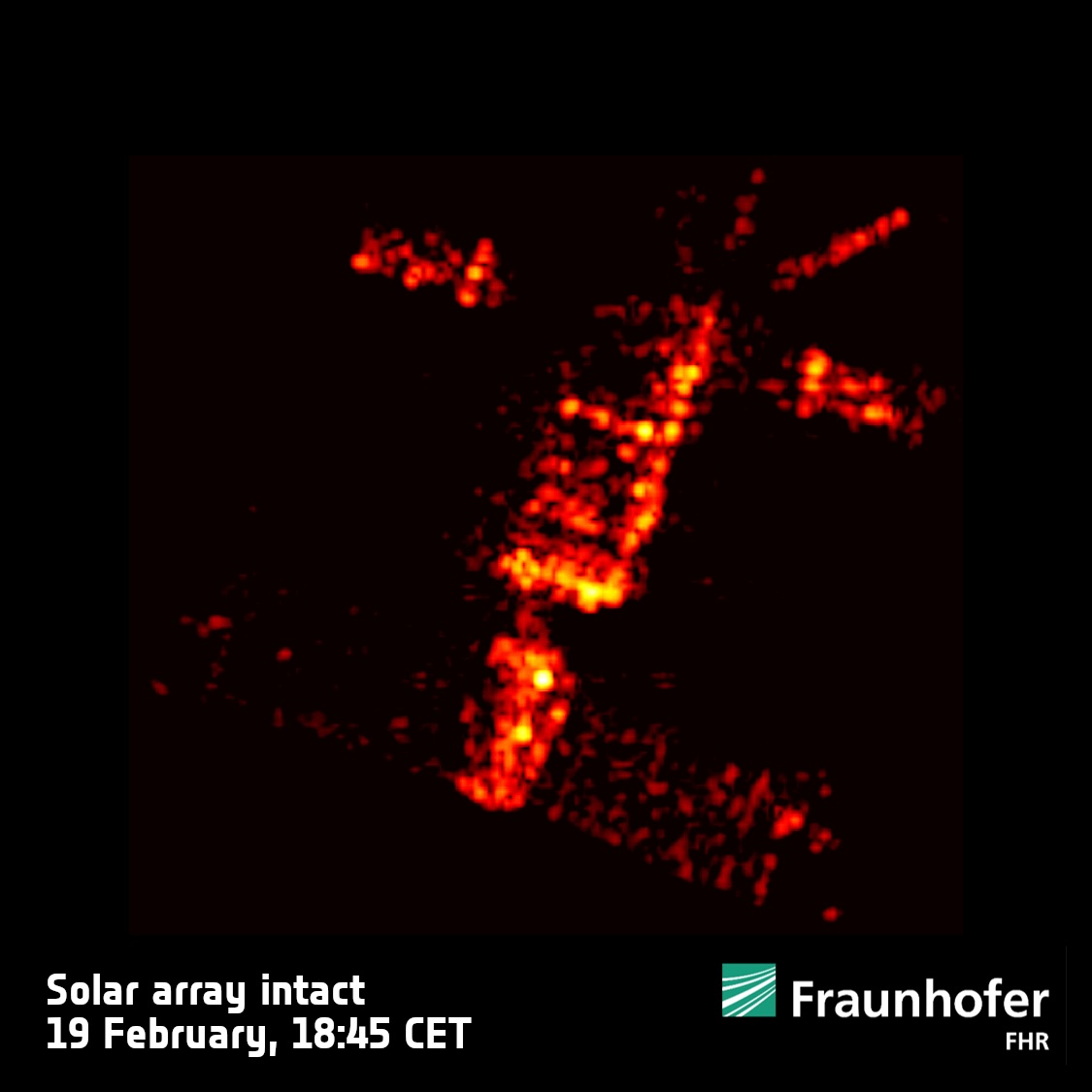
Stars shape their solar systems. It’s true of ours, and it’s true of others. But for some massive stars, their power to shape still-forming systems is fateful and final.
Continue reading “Massive Stars Have the Power to Shape Solar Systems”Massive Stars Have the Power to Shape Solar Systems