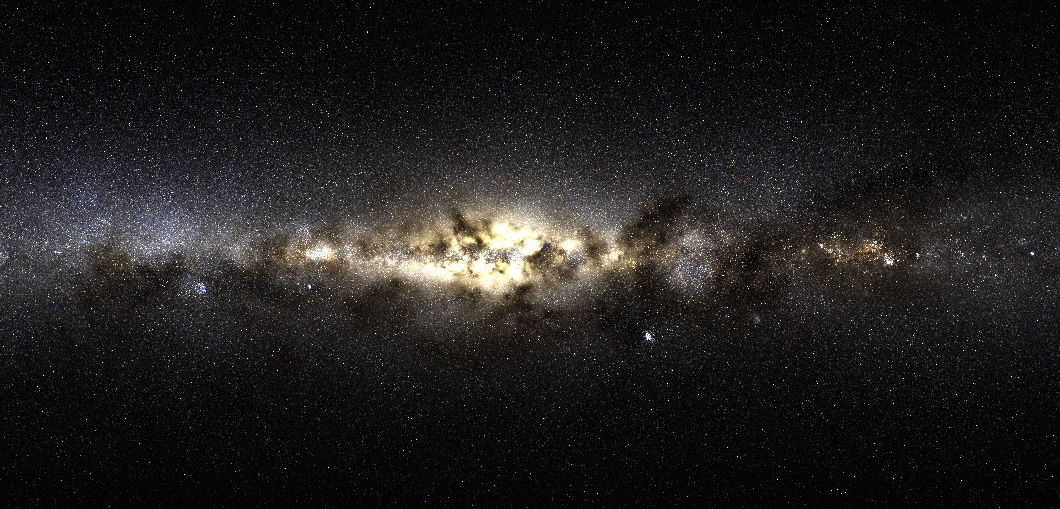
Modern professional astronomers aren’t much like astronomers of old. They don’t spend every suitable evening with their eyes glued to a telescope’s eyepiece. You might be more likely to find them in front of a super-computer, working with AI and deep learning methods.
One group of researchers employed those methods to find a whole new collection of stars in the Milky Way; a group of stars which weren’t born here.
Continue reading “A Stellar Stream of Stars, Stolen from Another Galaxy”