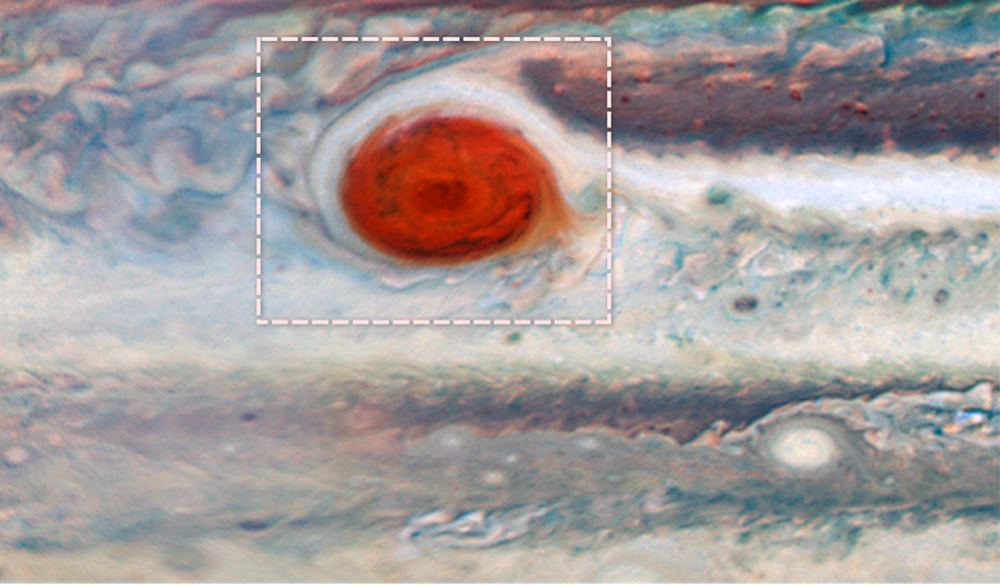
It’s difficult to imagine the magnitude of storms on Jupiter. The gas giant’s most visible atmospheric feature, the Great Red Spot, may be getting smaller, but one hundred years ago, it was about 40,000 km (25,000 miles) in diameter, or three times Earth’s diameter.
Jupiter’s atmosphere also features thunderheads that are five times taller than Earth’s: a whopping 64 km (40 miles) from bottom to top. Its atmosphere is not entirely understood, though NASA’s Juno spacecraft is advancing our understanding. The planet may contain strange things like a layer of liquid metallic hydrogen.
Now a group of scientists are combining the power of the Hubble Space Telescope, the Gemini Observatory and the Juno spacecraft to probe Jupiter’s atmosphere, and the awe-inspiring storms that spawn there.
Continue reading “Spacecraft and Ground Telescopes Work Together to Give us Stunning New Pictures of Jupiter”