[/caption]
It may be visible to the naked eye, but it took the unblinking gaze of NASA’s Kepler space telescope to reveal the true triple nature of this star system.
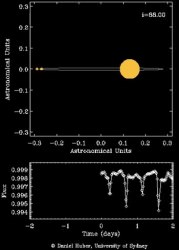
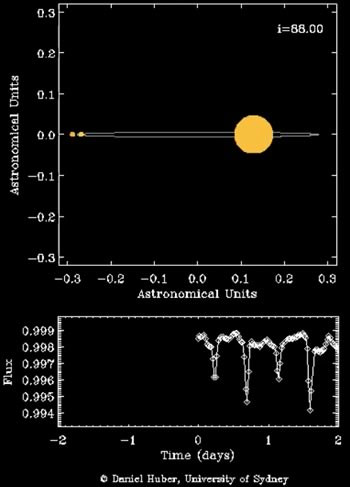
Unofficially dubbed “Trinity”, object HD 181068 is a multiple star system comprised of three stars: a red giant more than twelve times the diameter of the Sun and two red dwarf stars each slightly smaller than the Sun. The red dwarfs orbit each other in tight rotation around a central point, which in turn orbits the red giant. The smaller stars complete a full orbit around the giant every 45.5 days and, from our point of view, pass directly in front of and behind the huge star.
The orbital eclipse events of HD 181068 last about 2 days. What’s surprising is that during these eclipses the brightness of the system is not affected very much. This is because the surface brightnesses of the three stars are very similar. The current metaphor is a “white rabbit in a snowfall”, wherein the two red dwarfs effectively become invisible when they pass in front of the red giant. It wasn’t until the Kepler mission that we had an observational tool precise enough to detect the structure of this intriguing star system, located 800 light-years away from our own.
“The intriguing nature of this unique system remained unnoticed until now despite the fact that it is nearly bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. We really needed Kepler with its unprecedentedly precise and uninterrupted photometric monitoring to uncover such a rare gem.”
– Aliz Derekas, Eotvos University and Konkoly Observatory, Budapest, Hungary
Another unexpected feature of Trinity is its “quiet” nature. Astronomers have known that red giant stars exhibit seismic oscillations, as does our own Sun. But these oscillations are not present in Trinity’s red giant. Scientists speculate that the two red dwarfs may be creating some sort of gravitational offset, effectively negating the red giant’s vibrations. More research will be needed to determine if this is in fact the case.
Find out more about HD 181068 and other recent Kepler discoveries on NASA’s mission site or in the press release issued by the Ames Research Center, or read the published report on Science.
Image credit: NASA/KASC