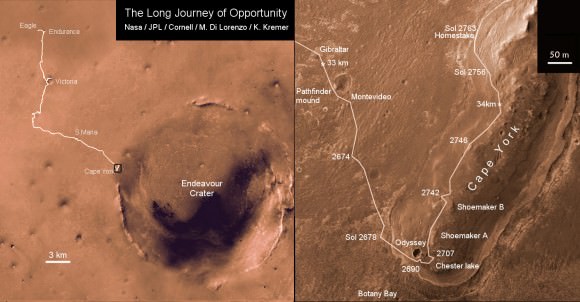
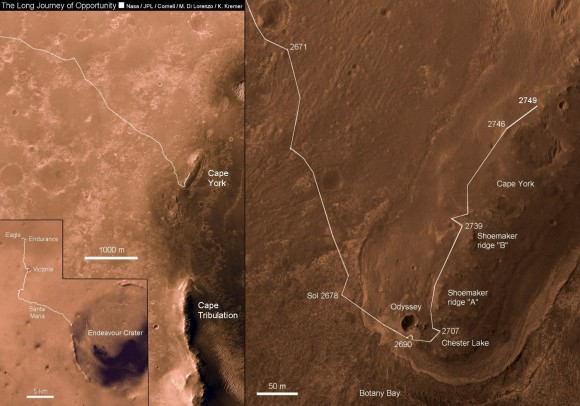
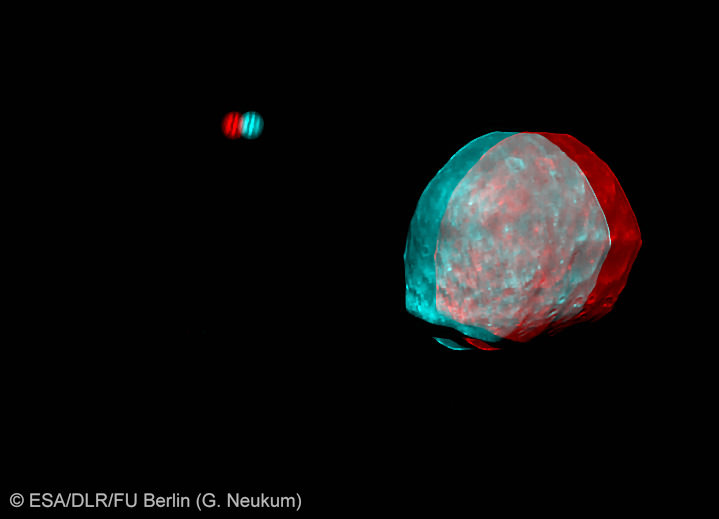
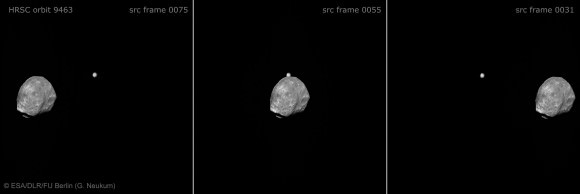
[/caption]
After an absence of almost two decades, Russia is at last on the cusp of resuming an ambitious agenda of interplanetary science missions on Tuesday Nov. 8 3:16 p.m. EST (Nov. 9, 00:16 a.m. Moscow Time) by taking aim at Mars and scooping up the first ever soil and rocks gathered from the mysterious moon Phobos. Russia’s space program was hampered for many years by funding woes after the breakup of the former Soviet Union and doubts stemming from earlier mission failures. The Russian science ramp up comes just as US space leadership fades significantly due to dire NASA budget cutbacks directed by Washington politicians.
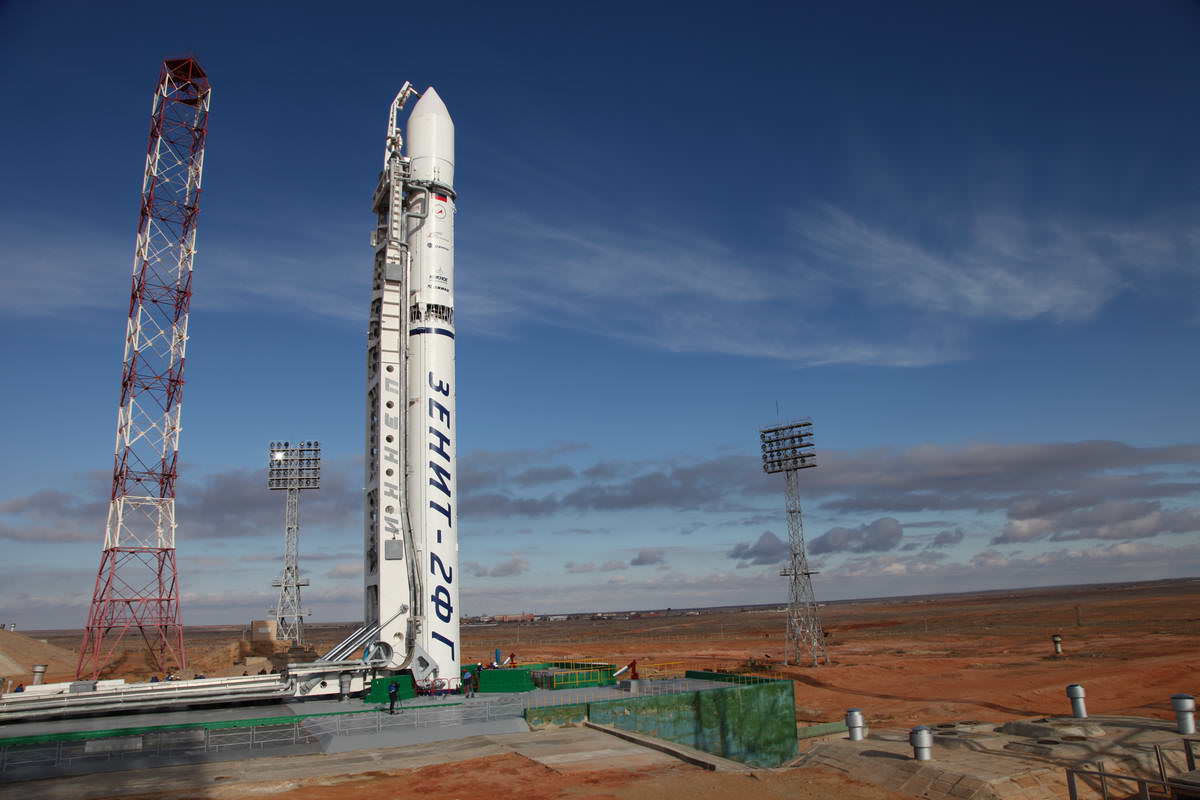
Russia’s daring and highly risky Phobos-Grunt soil sampling robot to the battered Martian moon Phobos now sits poised at the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazahkstan atop a specially upgraded booster dubbed the “Zenit-2SB” rocket according to Alexey Kuznetsov, Head of the Roscosmos Press Office in an exclusive interveiw with Universe Today. Roscosmos is the Russian Federal Space Agency. Watch the awesome Mars mission animation in my article here. See Zenit Rocket rollout video and images below.
“The Phobos-Grunt automatic interplanetary station will launch on November 9, 2011 at 00:26 a.m. Moscow time [Nov. 8, 3:36 p.m. EST],” Kuznetsov confirmed to Universe Today.
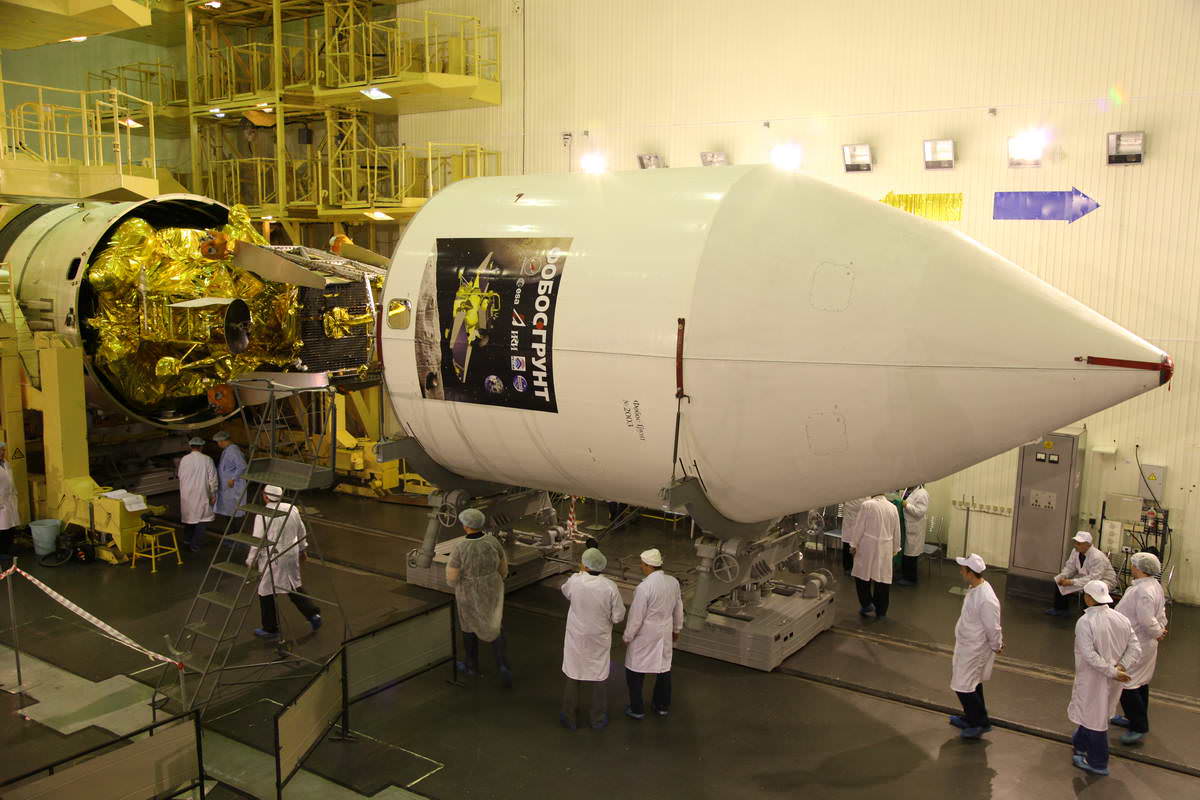
The Roscosmos video and photos here show the Zenit rocket rollout starting from Building 45 where the final prelaunch processing was conducted late last week mounting the nose cone holding the Phobos-Grunt and companion Yinghuo-1 spacecraft to the upgraded Fregat upper stage.

If successful, Phobos Grunt will complete the Earth to Mars round trip voyage in some 34 months and the history making soil samples will plummet through the Earth’s atmosphere in August 2014 to waiting Russian military helicopters.
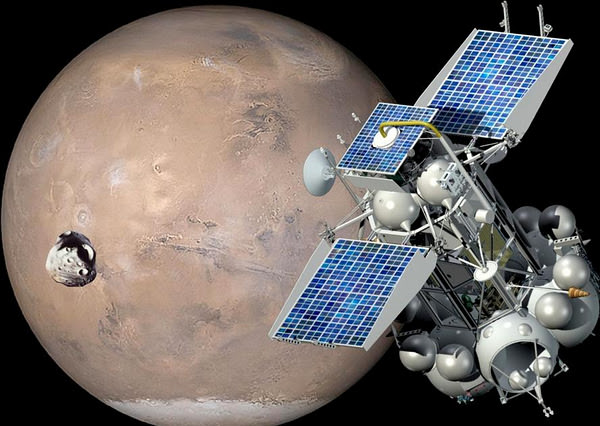
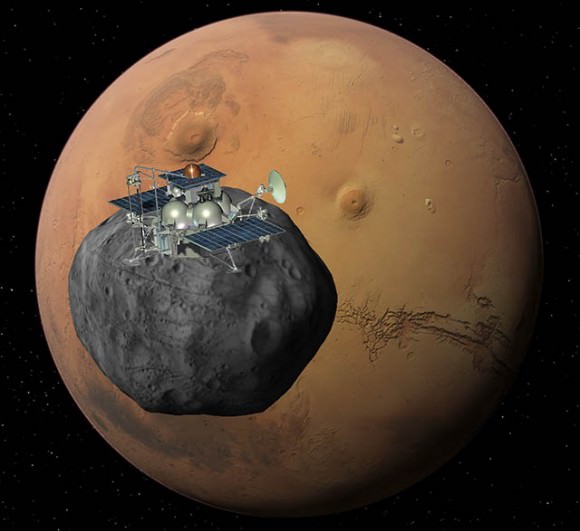
Following an 11 month interplanetary journey, the spaceship will enter Mars orbit and spend several months searching for a suitable landing site on Phobos. The probe is due to touchdown very gently on Phobos surface in Feb. 2013 using radar and precision thrusters accounting for the moon’s extremely weak gravity. After gathering samples with two robotic arms, the soil transferred to the Earth return capsule will take off in the ascent vehicle for the trip back home.
“The Zenit can launch spacecraft from Baikonur into LEO, MEO, HEO and elliptical near-Earth orbits (including GTO and geostationary orbit) and to escape trajectories as well,” Kuznetsov explained.

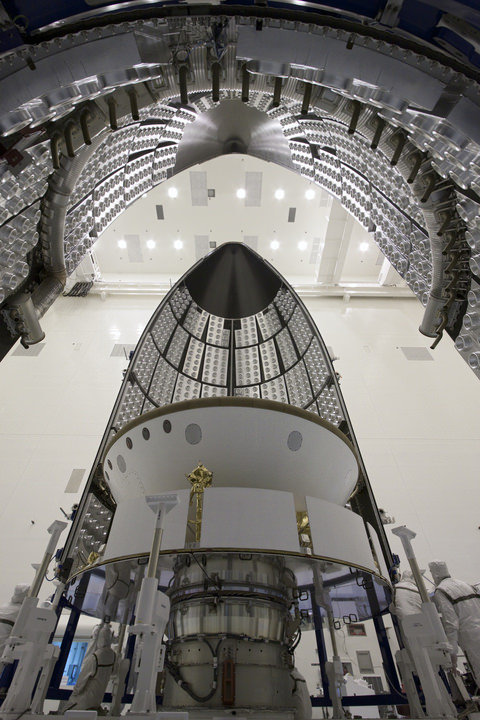
The Zenit-2SB booster with Phobos-Grunt and the piggybacked Yinghuo-1 Mars orbiter from China were rolled out horizontally by train on a railed transporter on Nov. 6, raised and erected vertically into launch position at Launch Pad 45 at Baikonur.
“The ‘Zenit-2SB’ rocket belongs to the rocket family using nontoxic fuel components – liquid oxygen and kerosene,” Kuznetsov elaborated. “The Zenit was manufactured by the A.M. Makarov Yuzhny Machine-Building Plant in Ukraine.”
“This “Zenit-2” rocket modification has significant improvements,” Kuznetsov told me. “The improvements include a new navigation system, a new generation on-board computer, and better performance by mass reduction and increase in thrust of the second stage engine.”

Likewise the upper stage was upgraded for the historic science flight.
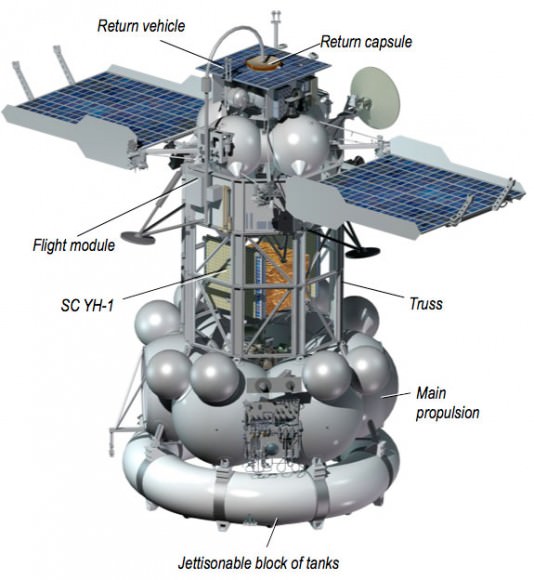
“The Zenit’s Fregat upper stage has also been modified. The “Phobos Grunt” automatic interplanetary station cruise propulsion system was built onto the base of the “Fregat-SB” upper stage. Its main task is to insert the automatic interplanetary station onto the Mars flight path and accomplish the escape trajectory.”
“The “Phobos Grunt” automatic interplanetary station mission was constructed by the Russian Academy of Sciences Space Research Institute in Moscow and the spacecraft was manufactured by NPO Lavochkin in Moscow,” Kuznetsov told me.
The 12,000 kg Phobos-Grunt automatic interplanetary station is equipped with a powerful 50 kg payload of some 20 science instruments provided by a wide ranging team of international scientists and science institutions from Europe and Asia.
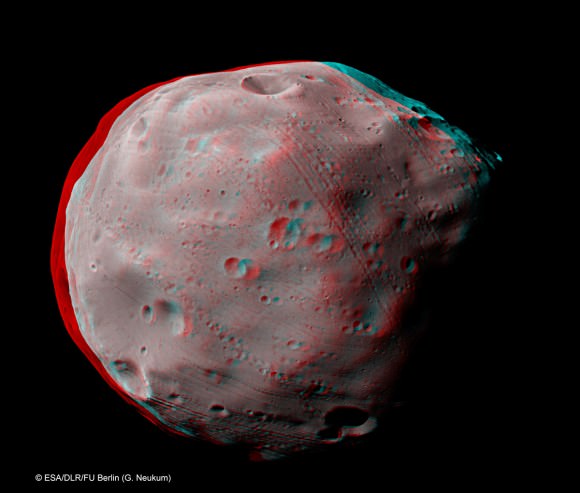
The audacious goal is to bring back up to 200 grams of pristine regolith and rocks that help unlock the mysteries of the origin and evolution of Phobos, Mars and the Solar System



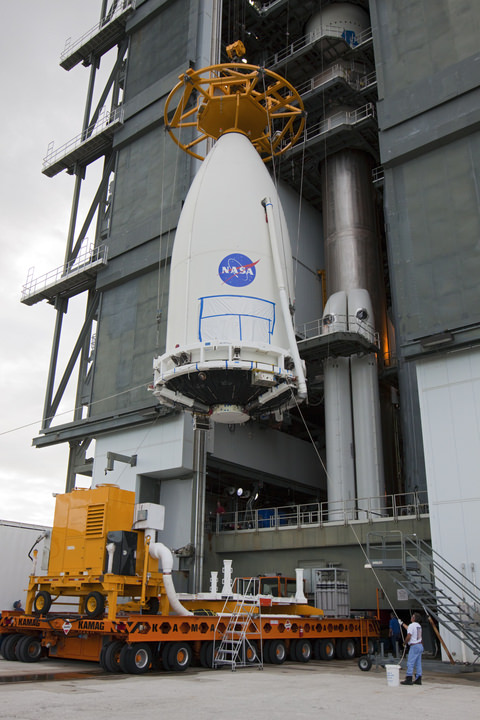
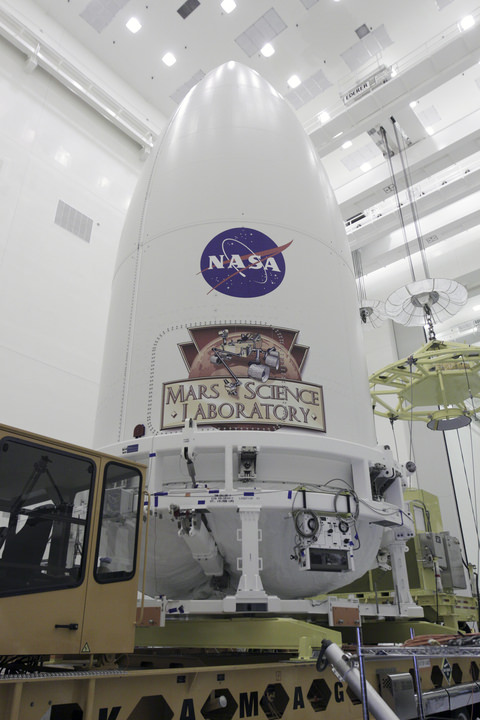
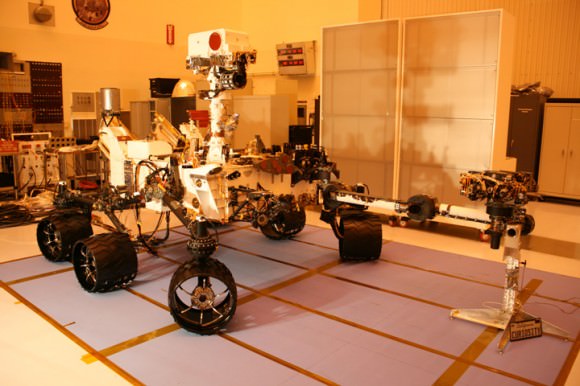
NASA’s Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Rover has also arrived at her Florida launch pad awaiting Nov. 25 liftoff.
Join me in wishing all the best to Roscosmos and NASA for this duo of fabulous Mars missions in 2011 that will help unravel our place in the Universe – like never before!
Read Ken’s continuing features about Phobos-Grunt upcoming Nov 9 launch here:
Awesome Action Animation Depicts Russia’s Bold Robot Retriever to Mars moon Phobos
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghuo-1 Encapsulated for Voyage to Mars and Phobos
Phobos and Jupiter Conjunction in 3 D and Amazing Animation – Blastoff to Martian Moon near
Russia Fuels Phobos-Grunt and sets Mars Launch for November 9
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghou-1 Arrive at Baikonur Launch Site to tight Mars Deadline
Phobos-Grunt: The Mission Poster
Daring Russian Sample Return mission to Martian Moon Phobos aims for November Liftoff