[/caption]
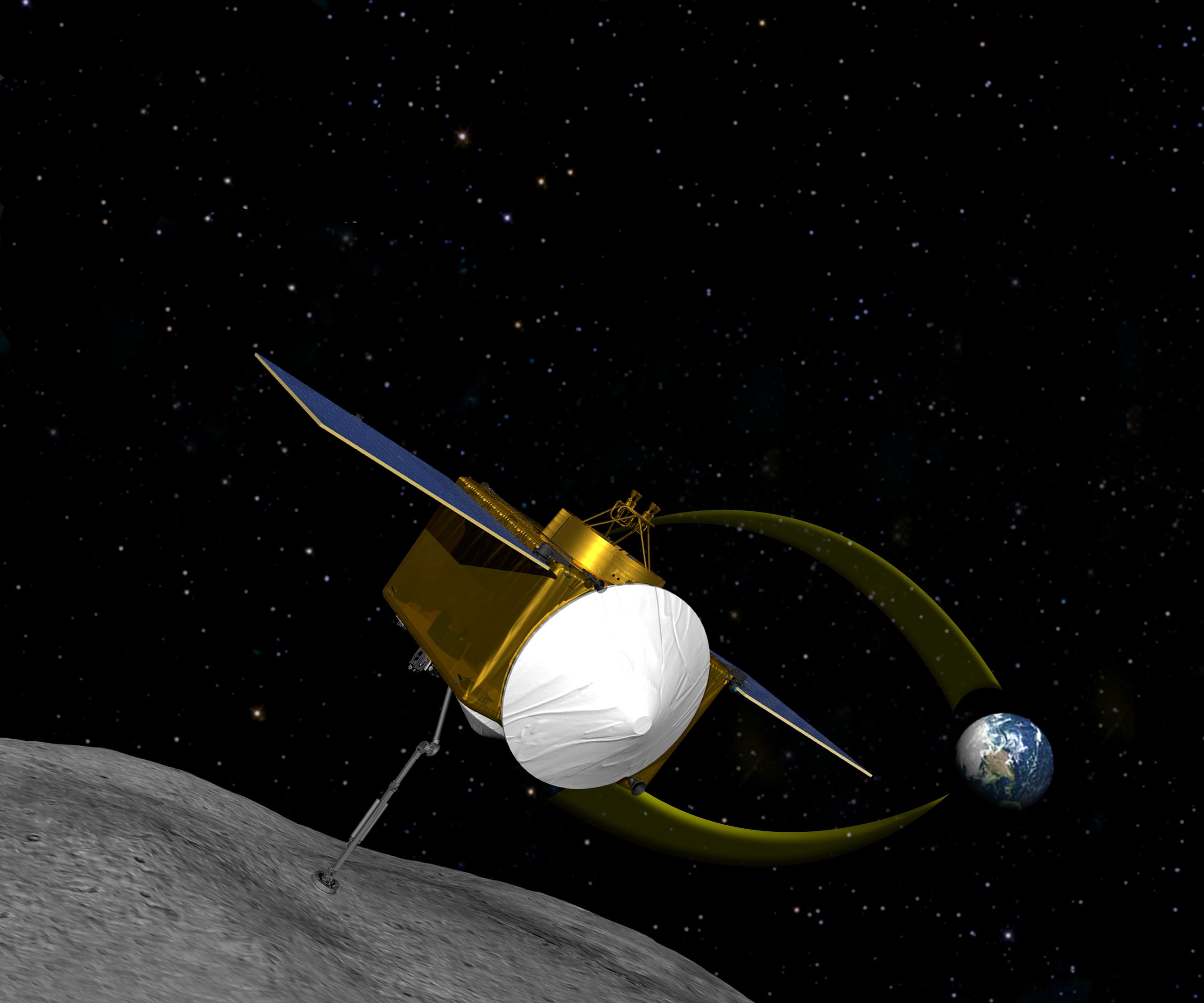
NASA officials announced the selection of OSIRIS-Rex as the next US robotic planetary science mission and which will pave the way for an eventual manned mission to an asteroid. OSIRIS-Rex will be the first US mission to collect and return samples of an asteroid to Earth.
OSIRIS-Rex is planned for launch to the near Earth asteroid designated as 1999 RQ36 in September 2016 and will return up to four pounds of prisitine asteroidal material to Earth in 2023. The precious sample would land arrive at Utah’s Test and Training Range in a sample return canister similar to the one for the Stardust spacecraft.
“We are absolutely delighted to announce the selection of OSIRIS-Rex,” said Jim Green, director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, at a briefing for reporters.
“This asteroid is a time capsule from the birth of our solar system and ushers in a new era of planetary exploration. The knowledge from the mission also will help us to develop methods to better track the orbits of asteroids.”
OSIRIS-Rex is the acronym for Origins-Spectral Interpretation-Resource Identification-Security-Regolith Explorer.
The asteroid is an unchanged remnant from the collapse of the solar nebula and birth of our solar system some 4.5 billion years ago, little altered over time.
Asteroid 1999 RQ36 is likely rich in carbon, the key constituent of organic molecules and one of the building blocks of life. Organic molecules have been found in meteorite and comet samples, which indicates that some of life’s ingredients can be created in space.
The science team will determine if organics also are present on RQ36.

Asteroids like 1999 RQ36 may have seeded Earth billions of years ago with organic molecules that are the building blocks of life and perhaps eventually led to living organisms. Samples from the asteroids may help scientists unlock the mysteries of the origin of life on Earth.
Three years after launch, OSIRIS-Rex would arrive at Asteroid 1999 RQ36 in 2020 and study the 1900 foot wide space rock in detail for at least six months of comprehensive surface examinations with four science instruments.
The science team will also use the time – perhaps up to one year – to look for the optimal place to touch the surface and collect a sample of at least two ounces of surface material with a robotic arm.
“We are bringing back what we believe is the type of material that led to the building blocks of life, that led to us,” said Michael Drake, principal investigator of the OSIRIS-REx mission from the University of Arizona.

Credit: NASA/Goddard/University of Arizona
“OSIRIS-REx will explore our past and help determine our destiny,” said Drake. “It will return samples of pristine organic material that scientists think might have seeded the sterile early Earth with the building blocks that led to life. Such samples do not currently exist on Earth. OSIRIS-REx will also provide the knowledge that will guide humanity in deflecting any future asteroid that could collide with Earth, allowing humanity to avoid the fate of the dinosaurs.”
The small asteroid RQ36 has also attracted interest because there is a 1-in-1,800 chance of impacting the Earth in the year 2182.
Drake added that the team will carefully practice the sample collection before conducting the actual retrieval of a surface material of a mixture of soil and rocks with a pogo stick like device. He said it would be more like “kissing” the surface than a actual landing of the spacecraft.
The sampling device at the end of the robot arm looks like a car air filter. It will haul in the pristine regolith into the sample acquisition mechanism within 5 seconds in a “touch and go” maneuver as the spacecraft slowly descends at 0.1 m/sec. Up to 3 attempts are possible.
Check the sampling sequence video below.
Because the samples are expected to possess organic molecules, they will be subject to stringent planetary protection protocols. The OSIRIS-REx sample capsule will be stored for analysis at a special curation facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. By returning the asteroid samples to Earth, they can be studied by the most advanced science equipment available.
“I think we’ll get some much needed info on the composition and physical properties of asteroid surface material. I’m particularly interested in water content for future resource use. The photos should be spectacular,” said former Astronaut Tom Jones in exclusive comments for Universe Today.
“This is a critical step in meeting the objectives outlined by President Obama to extend our reach beyond low-Earth orbit and explore into deep space,” said NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden in a statement. “It’s robotic missions like these that will pave the way for future human space missions to an asteroid and other deep space destinations.”
When the mission is complete, the spacecraft is expected to have sufficient fuel reserves to be retargeted to a new destination according to Michael Drake.
OSIRIS-Rex is expected to cost $800 million according to Jim Green, minus the cost of the launch vehicle which he said has not yet been determined. This is the third mission in NASA’s New Frontiers Program following the Pluto-Charon mission and the Juno Jupiter Orbiter.
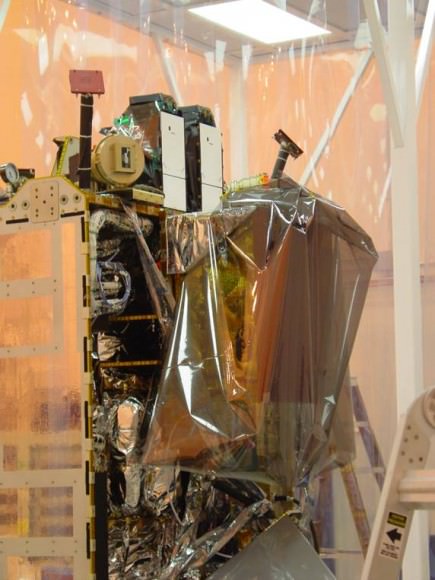
Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver is building the spacecraft. Overall mission management will be provided by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.