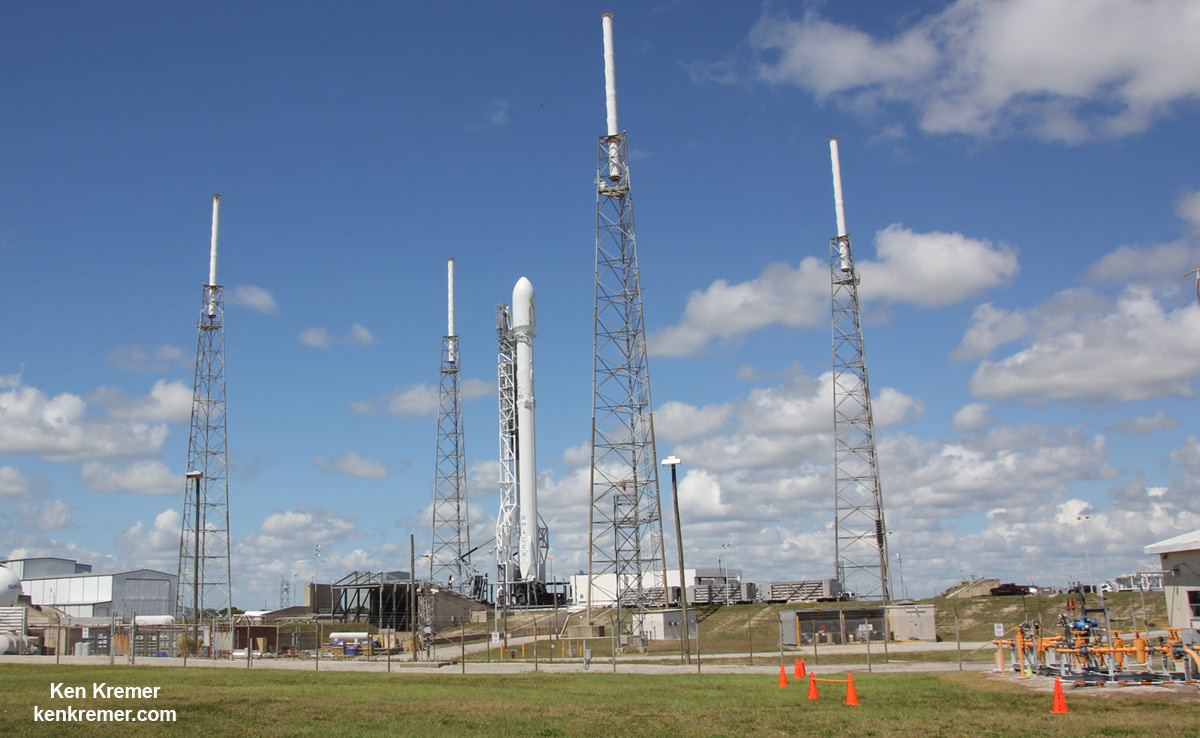
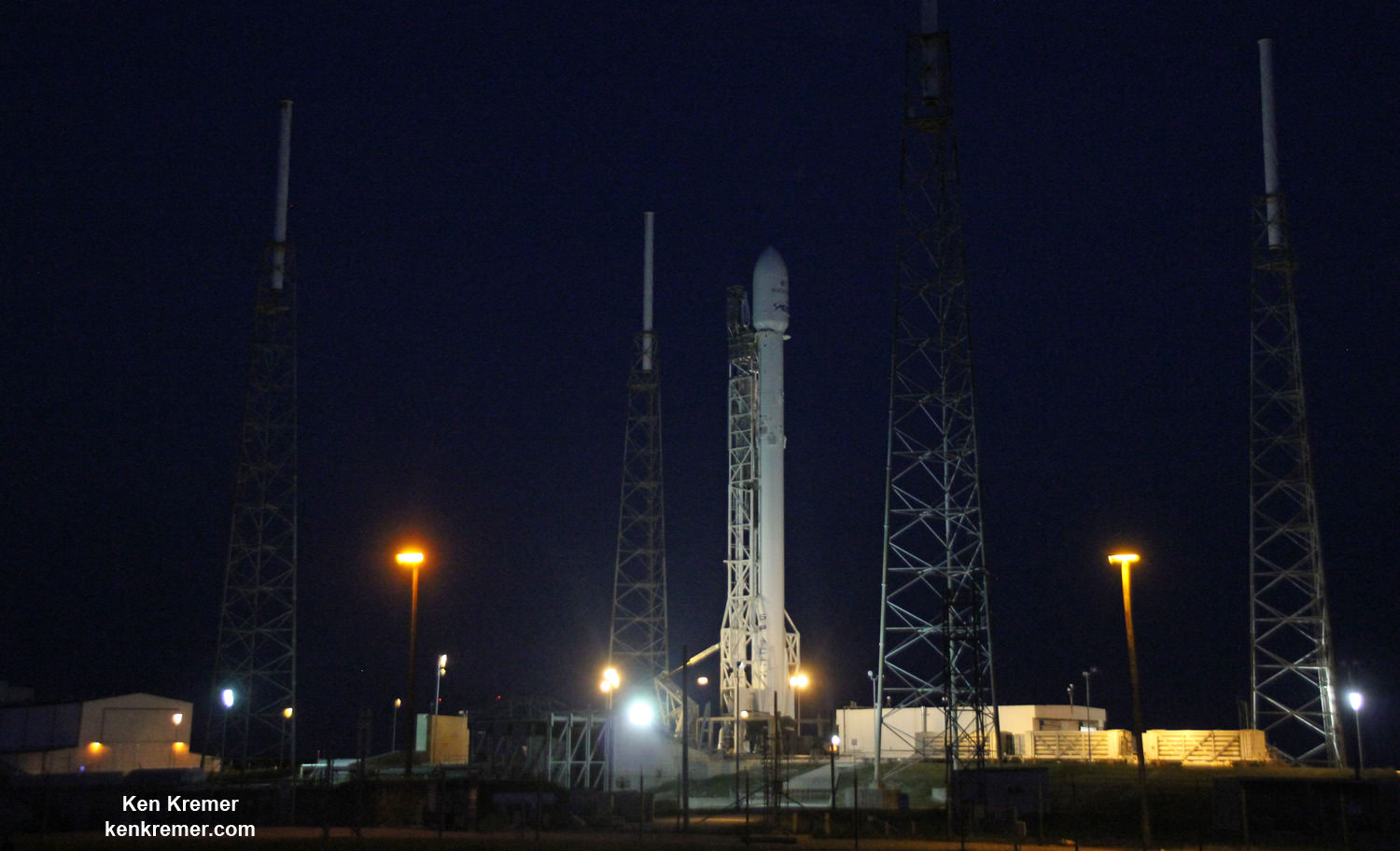
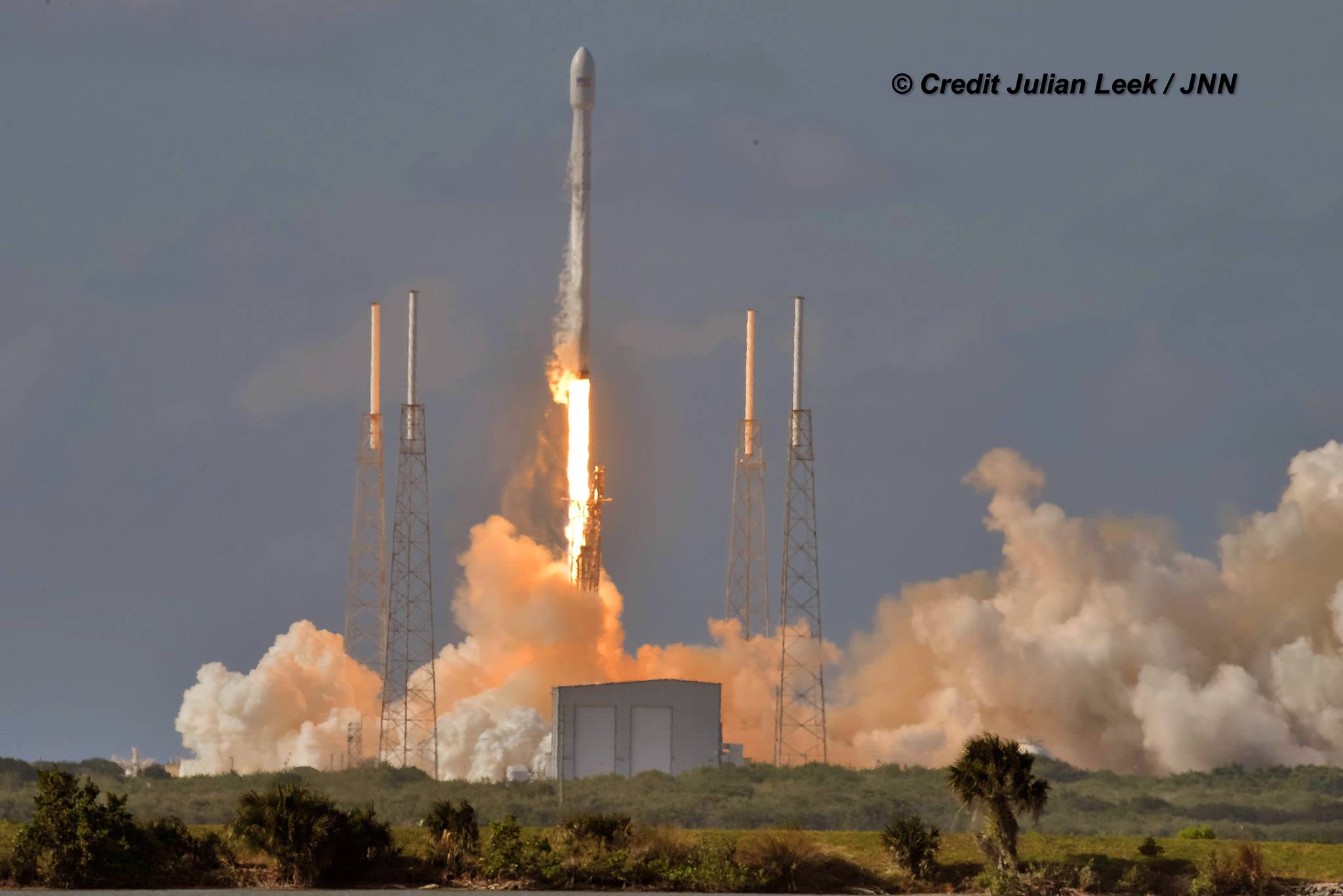
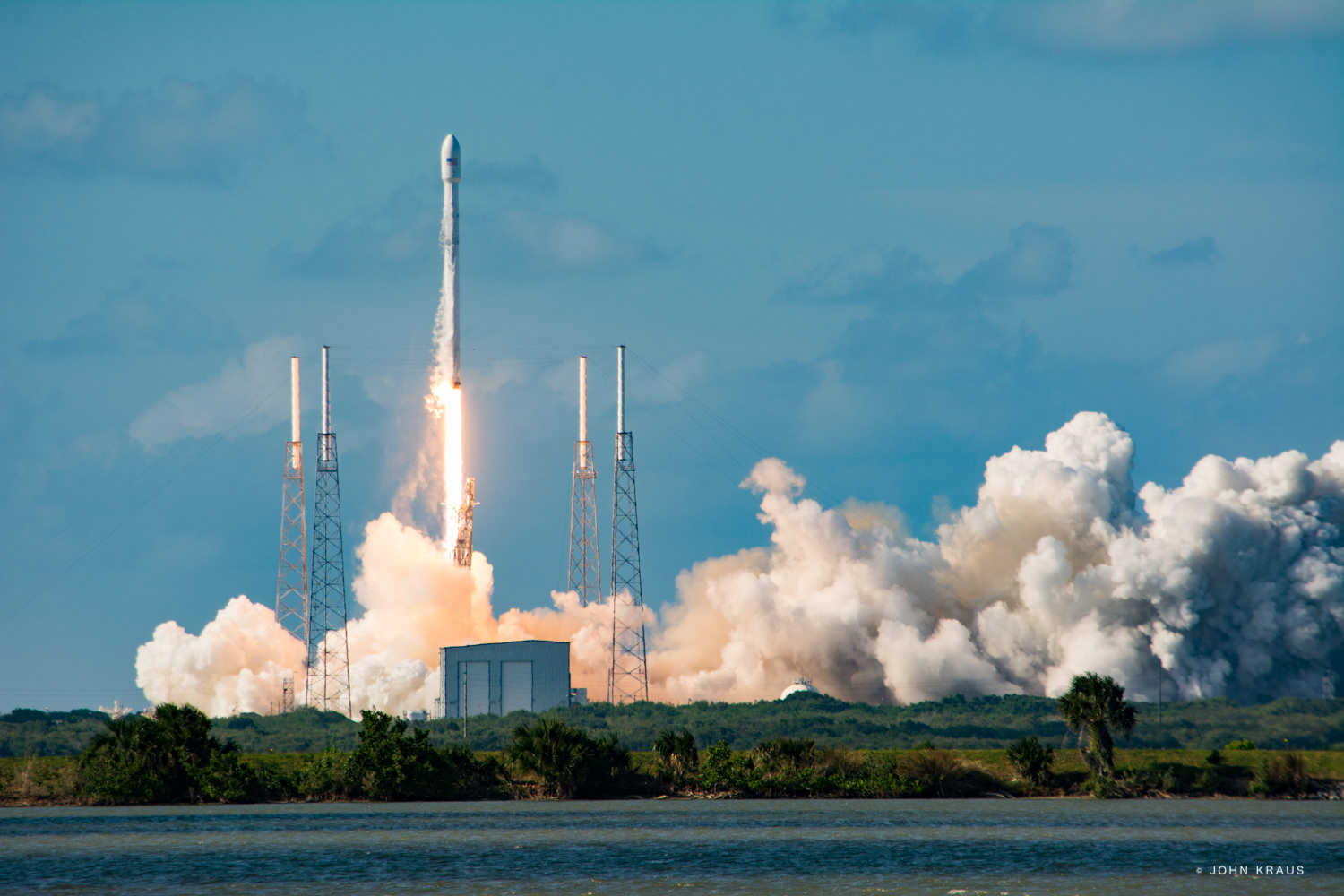
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, FL — Less than three weeks after their last successful launch and landing attempt involving a Thai payload, SpaceX is set to continue the firms rapid fire pace of satellite deliveries to orbit with a new mission involving a stacked pair of all-electric propulsion commercial comsats that are due to liftoff tomorrow, Wednesday morning.
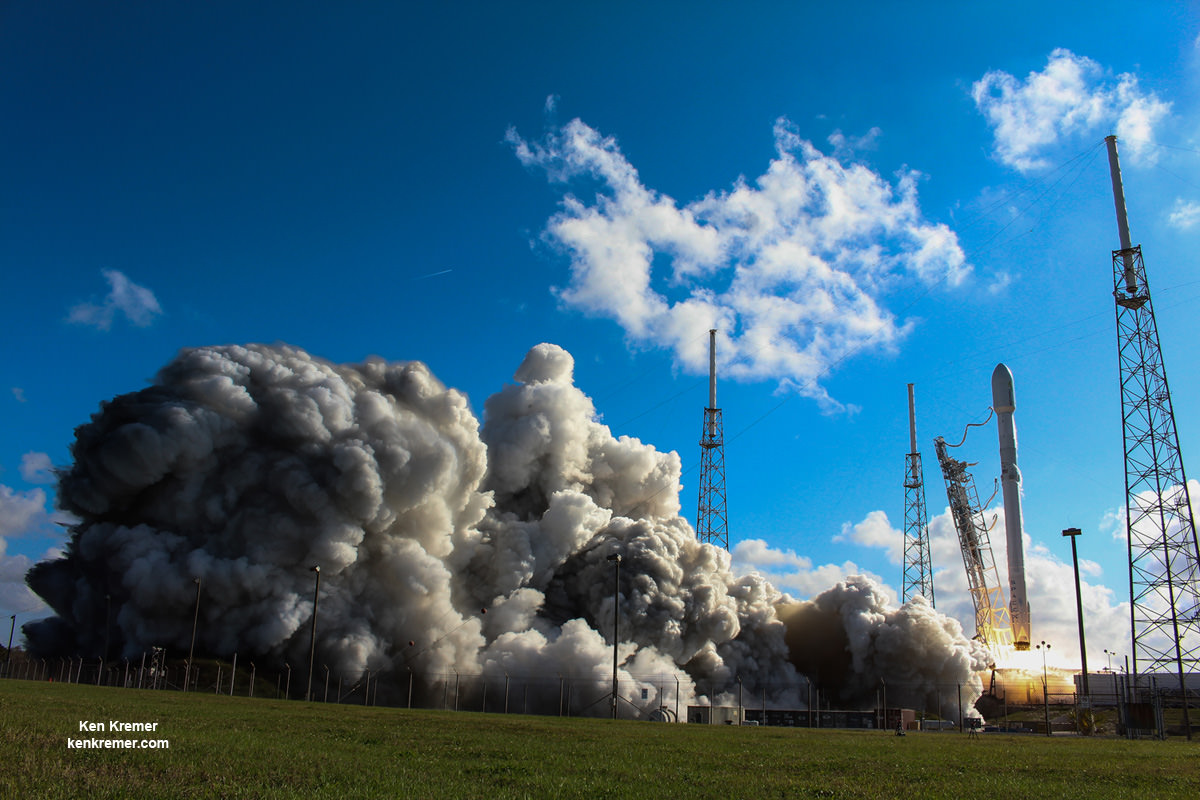
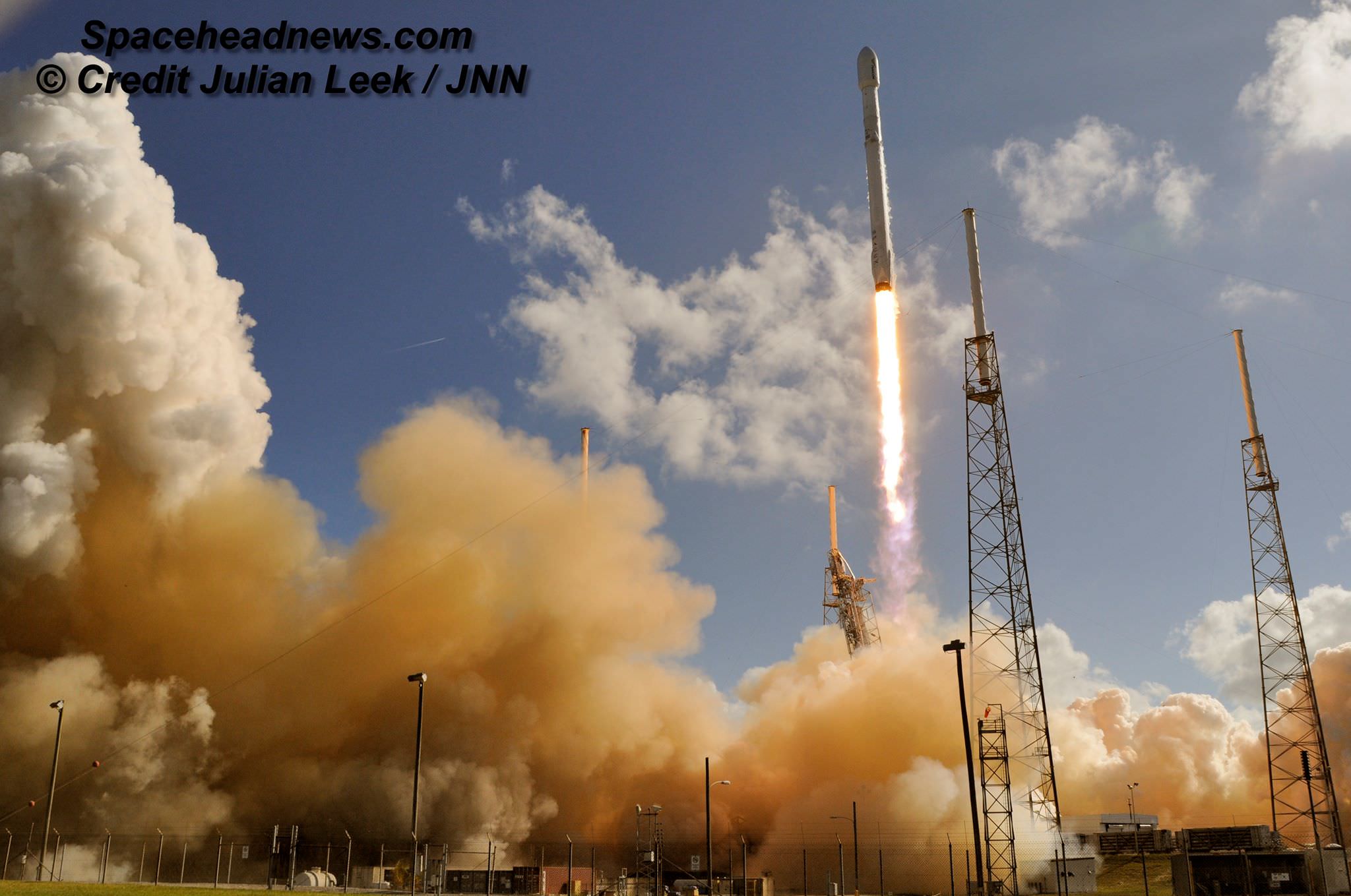
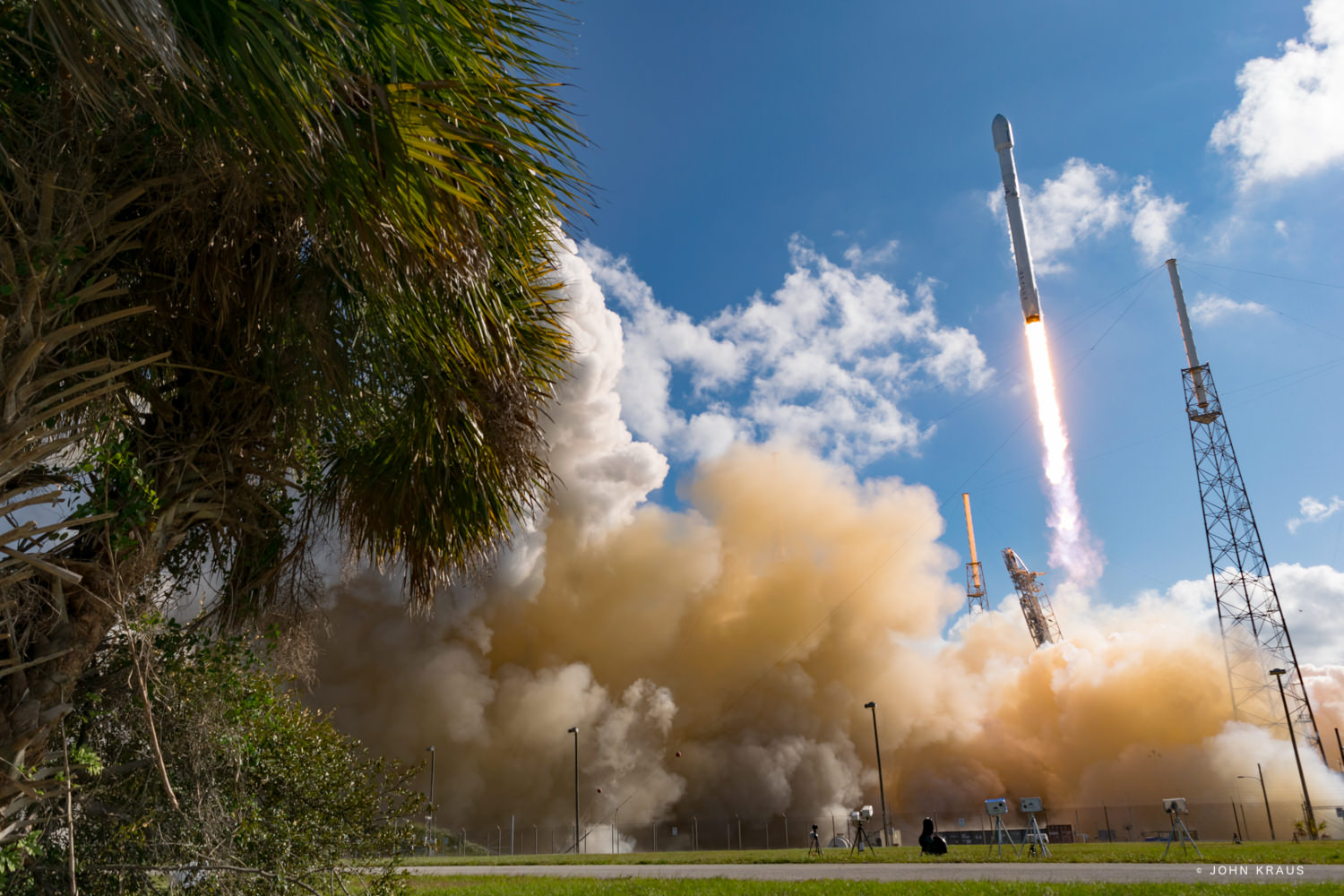
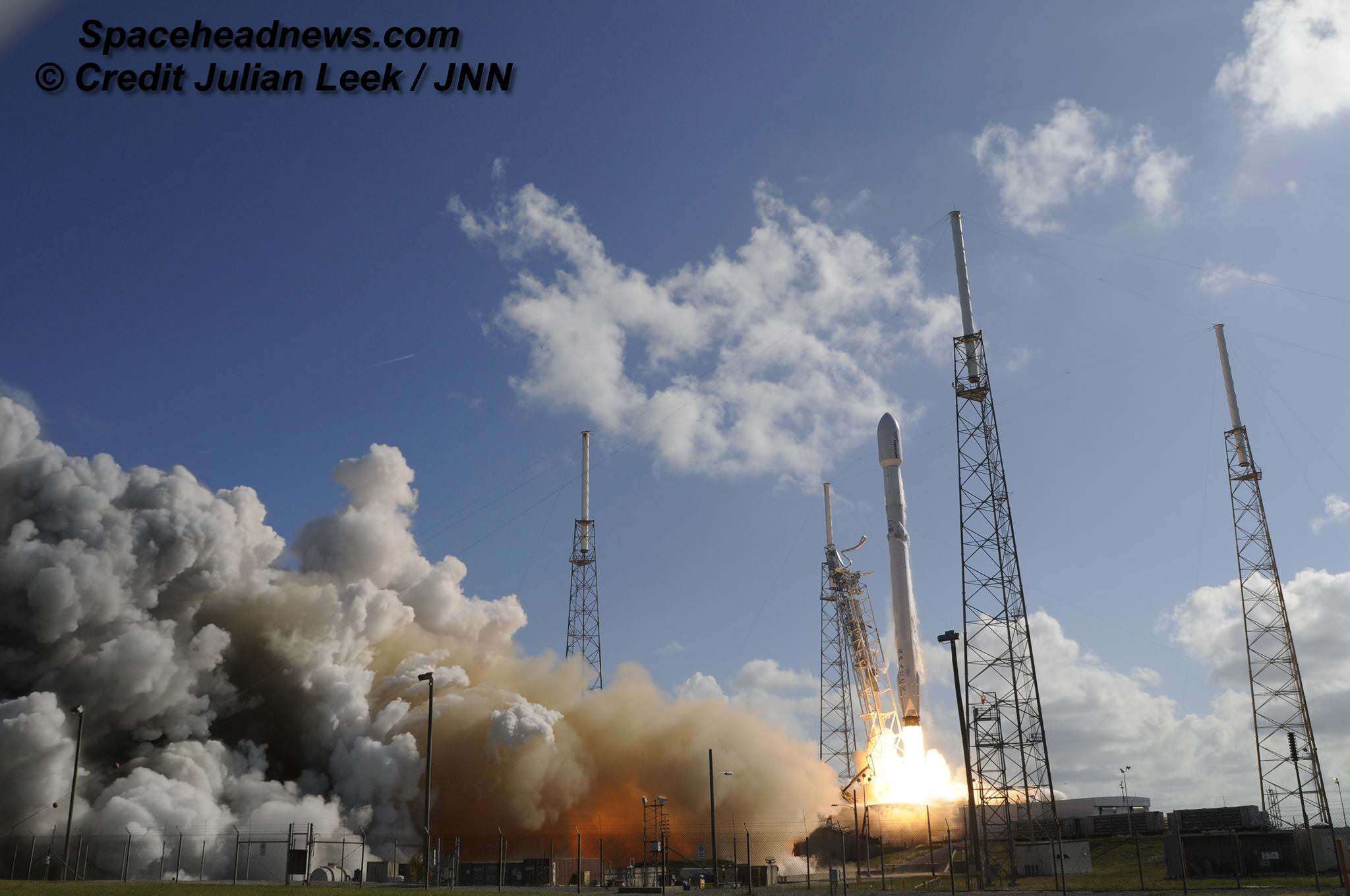
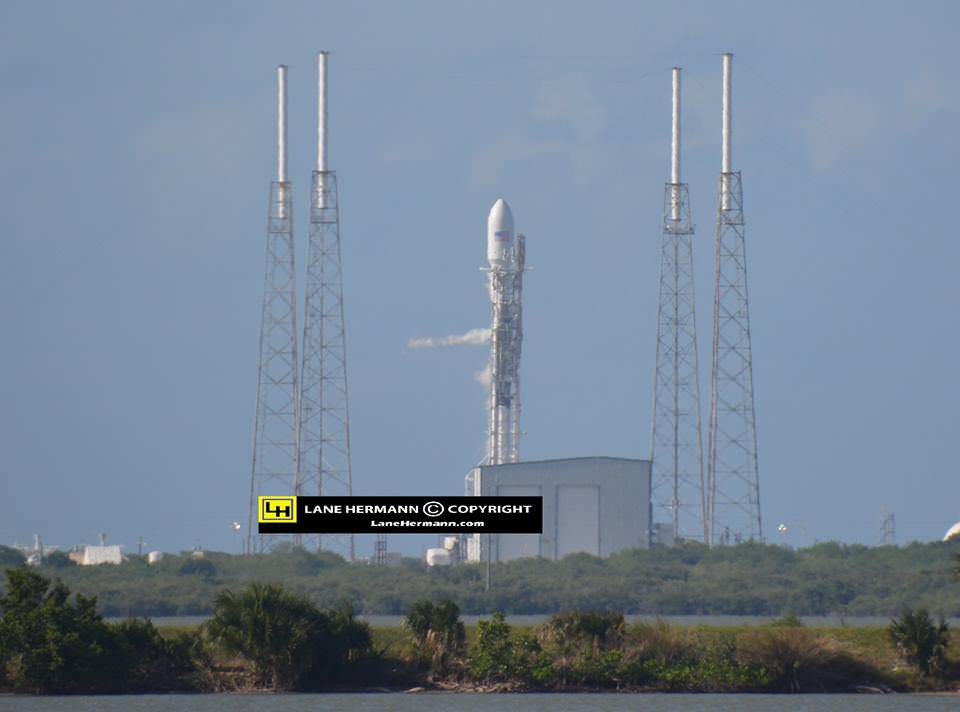
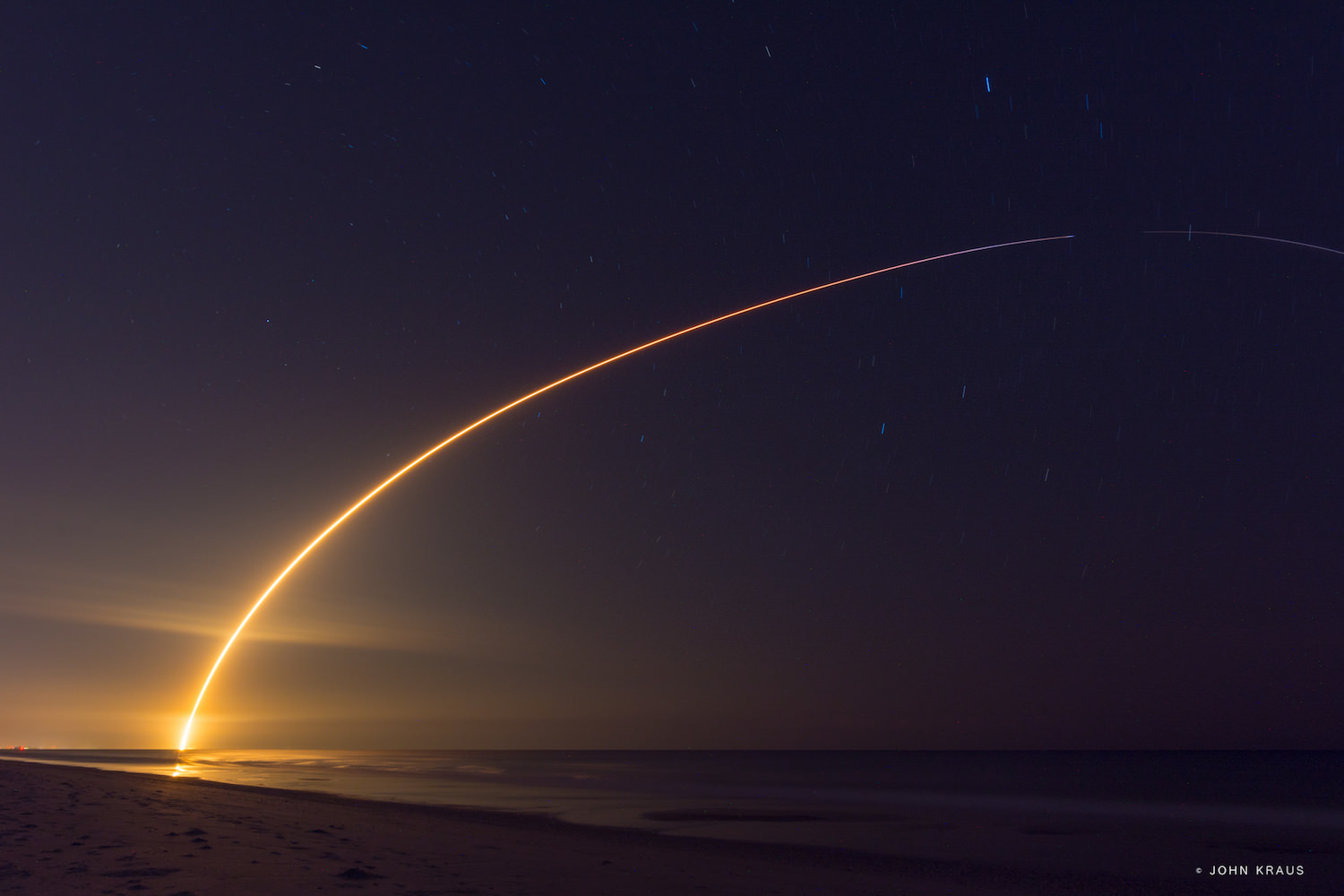
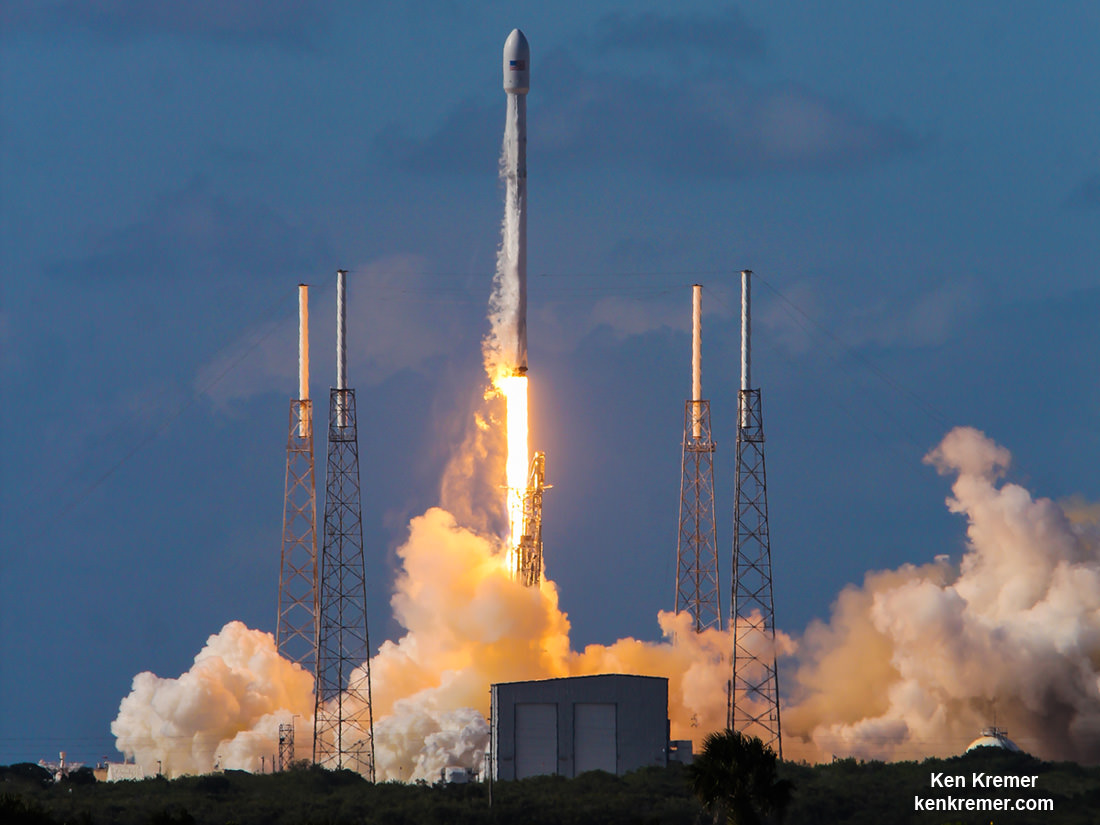
Working off a hefty back log of lucrative launch contracts SpaceX is targeting Wednesday, June 15 for the launch of the Boeing-built EUTELSAT 117 West B and ABS-2A satellites for Latin American and Asian customers from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on an upgraded Falcon 9 rocket.
SpaceX is aiming to launch at the opening of Wednesday’s launch window at 10:29 a.m. EDT (2:29 UTC) which closes at 11:13 a.m. EDT.
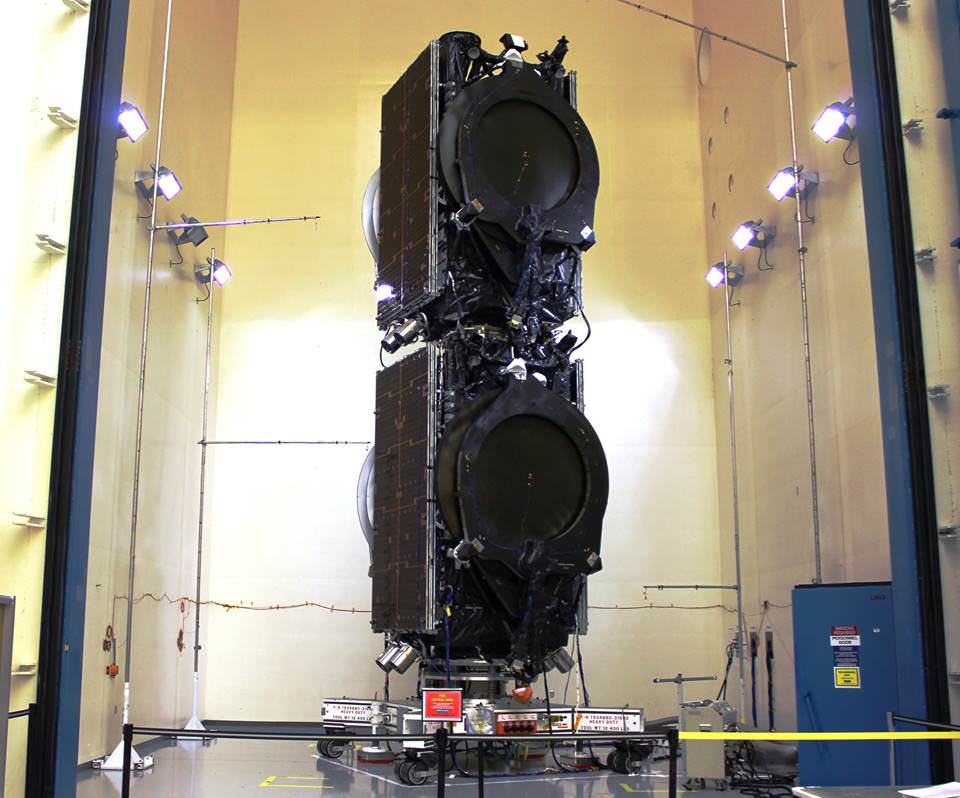

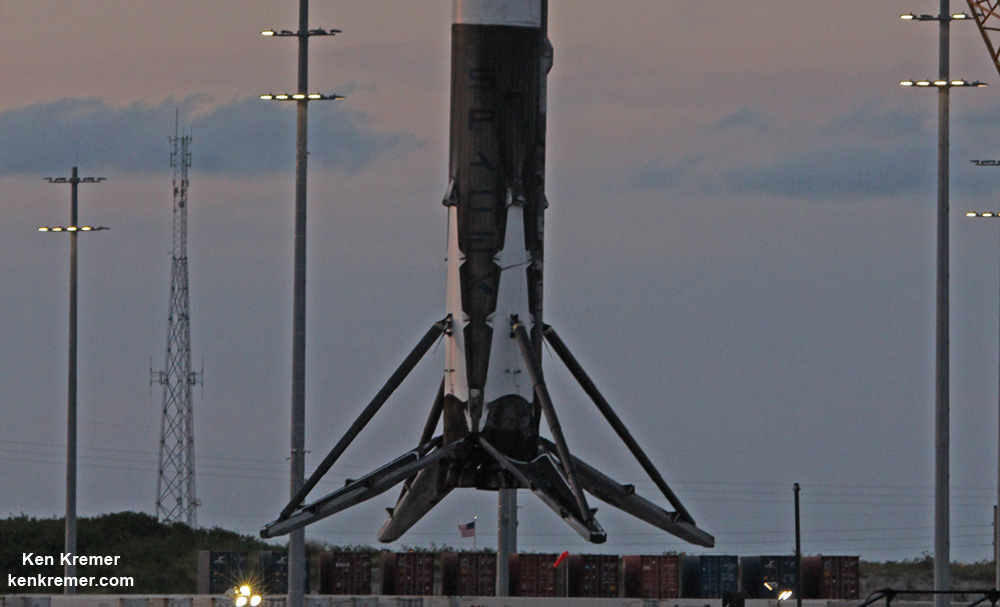
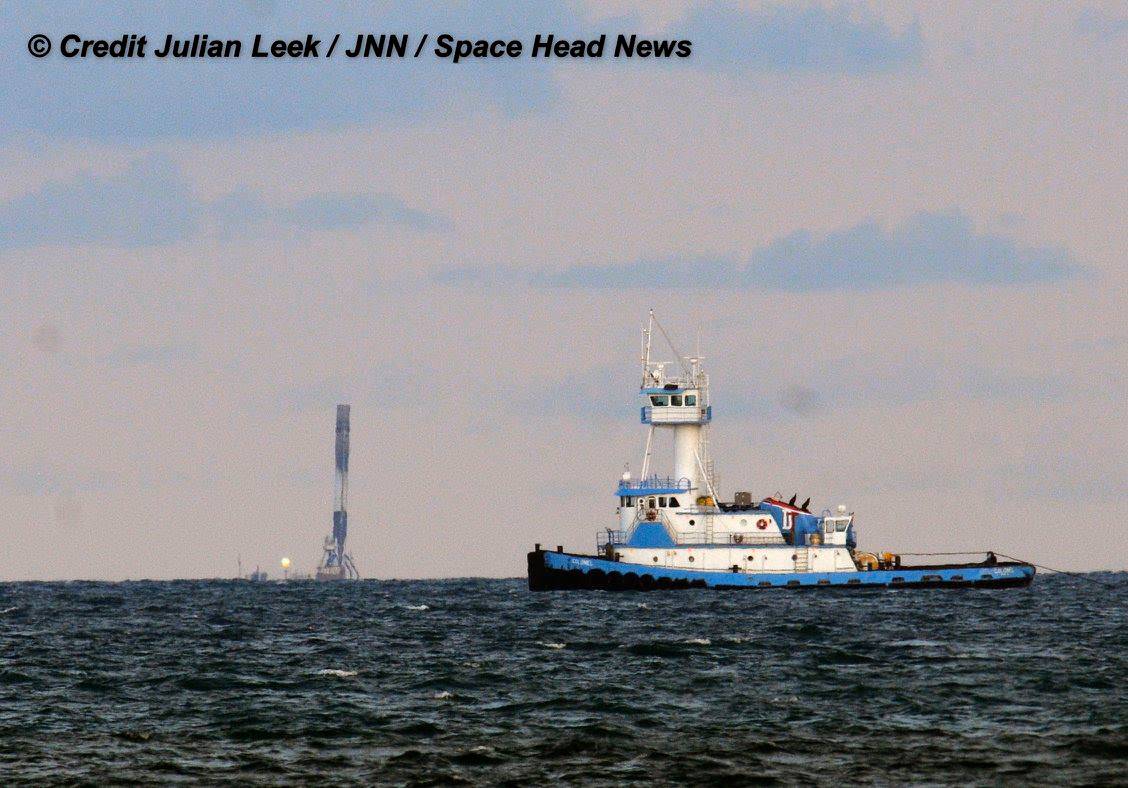
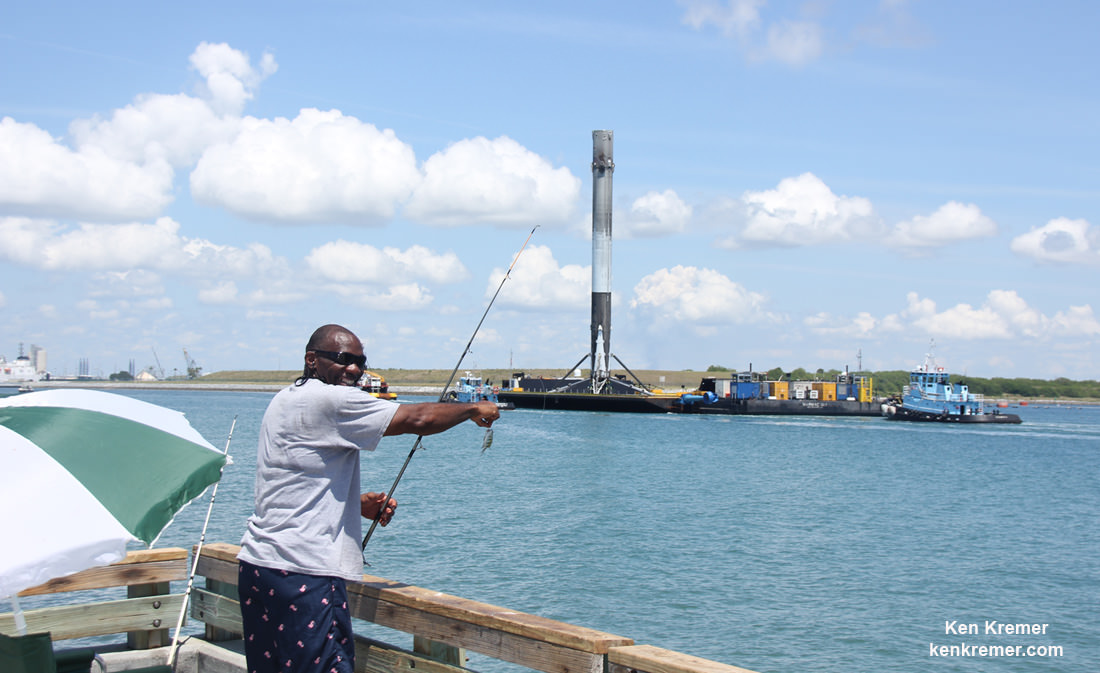
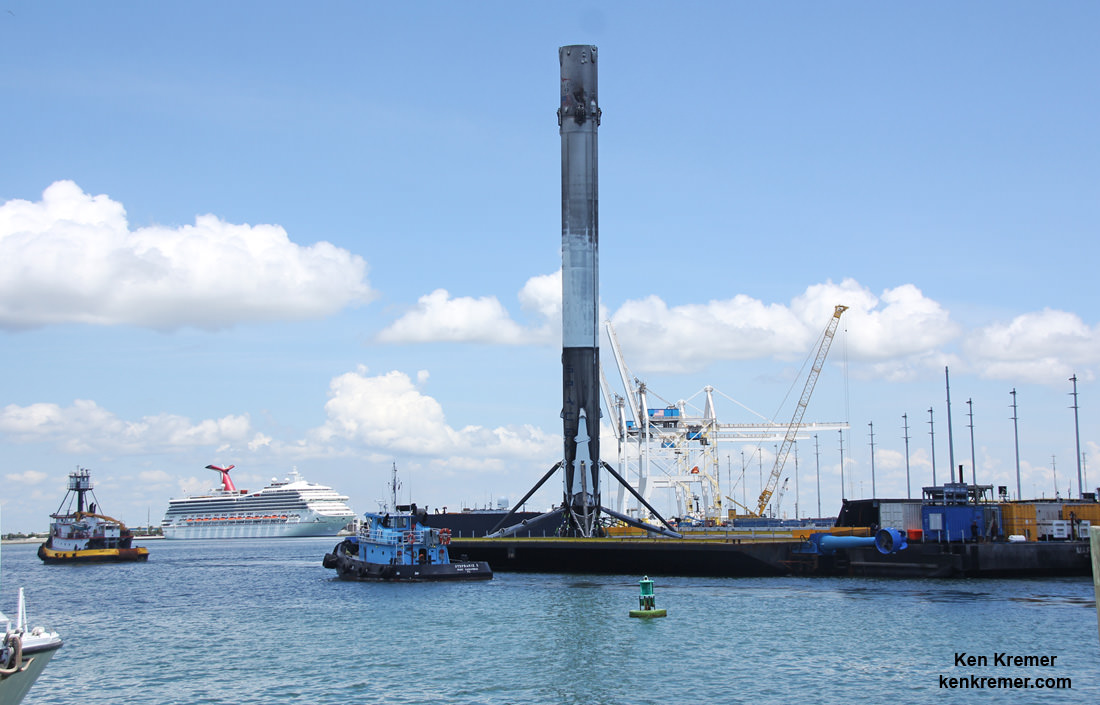
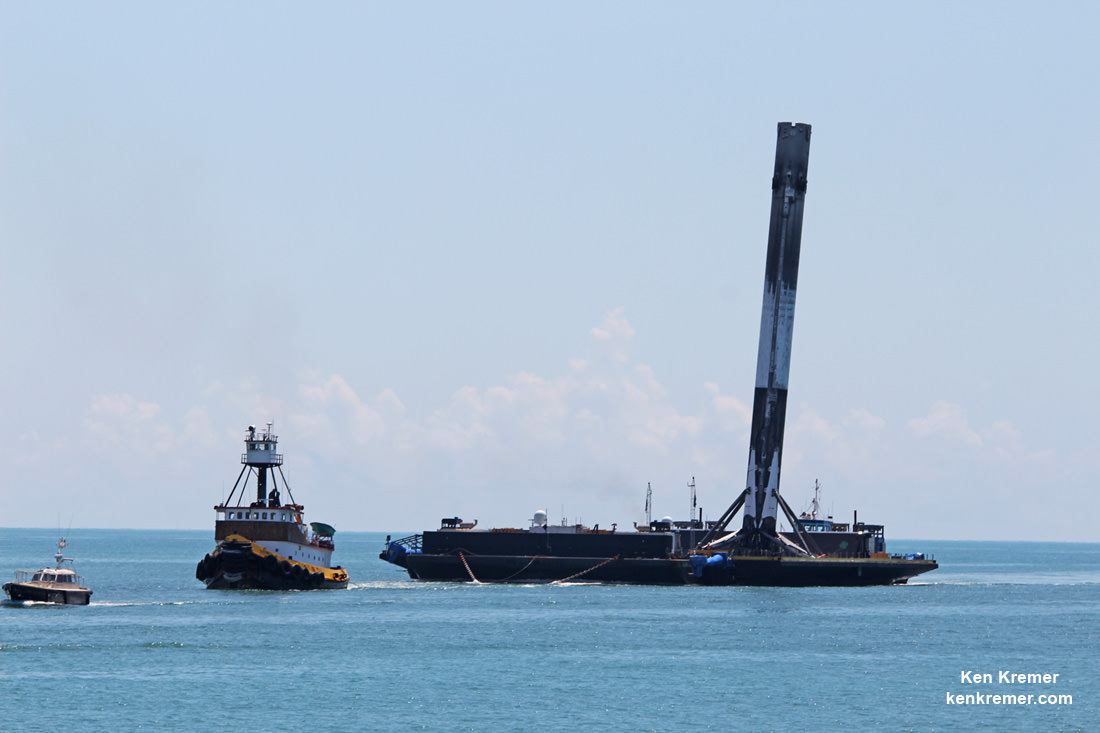
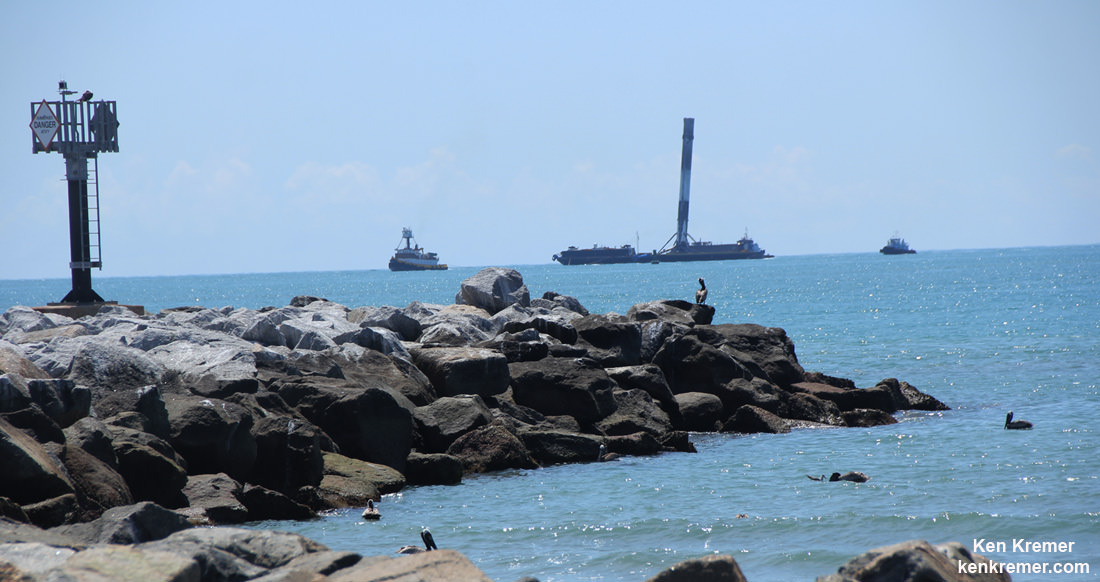
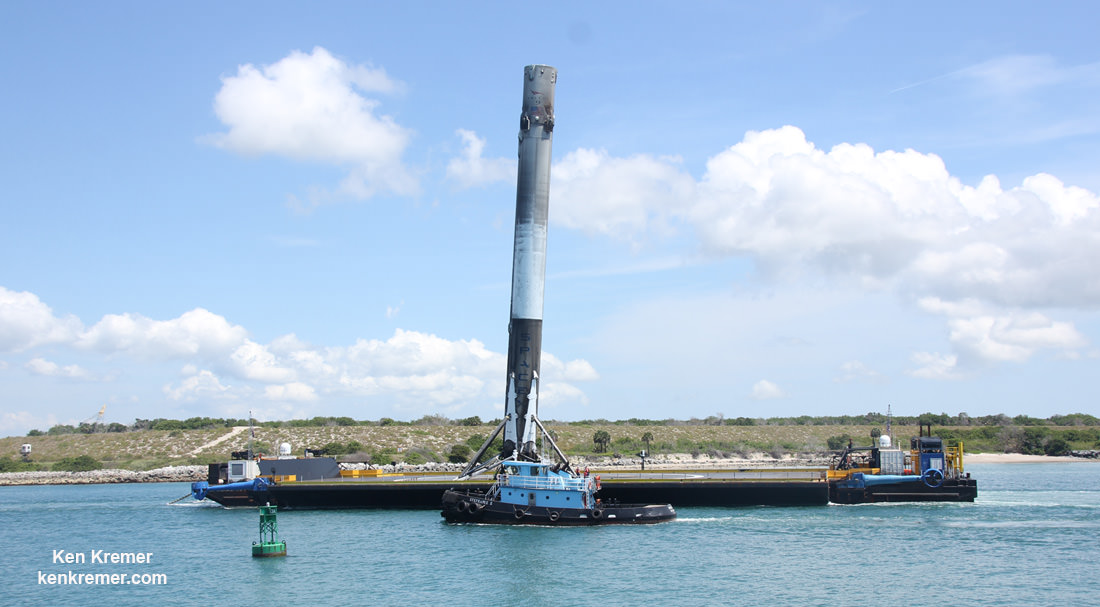
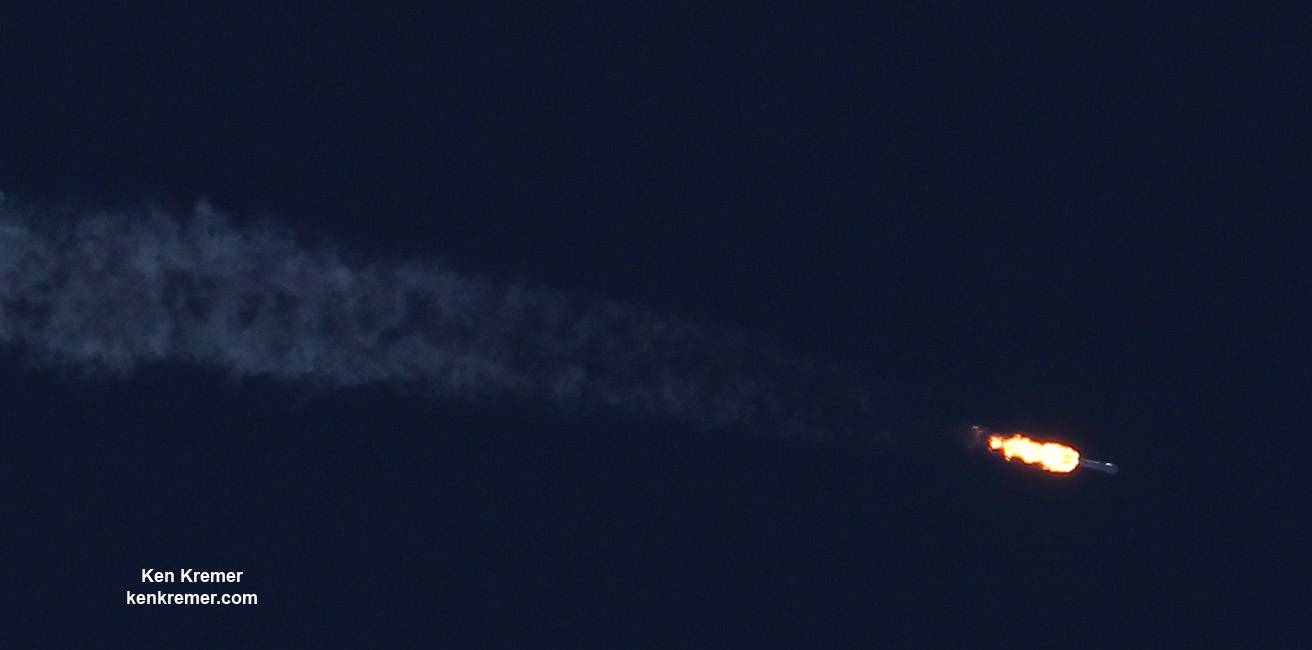
SpaceX most recently scored a stellar success with the double headed launch of Thaicom-8 and sea based first stage landing on May 27 – as I reported here from the Cape.
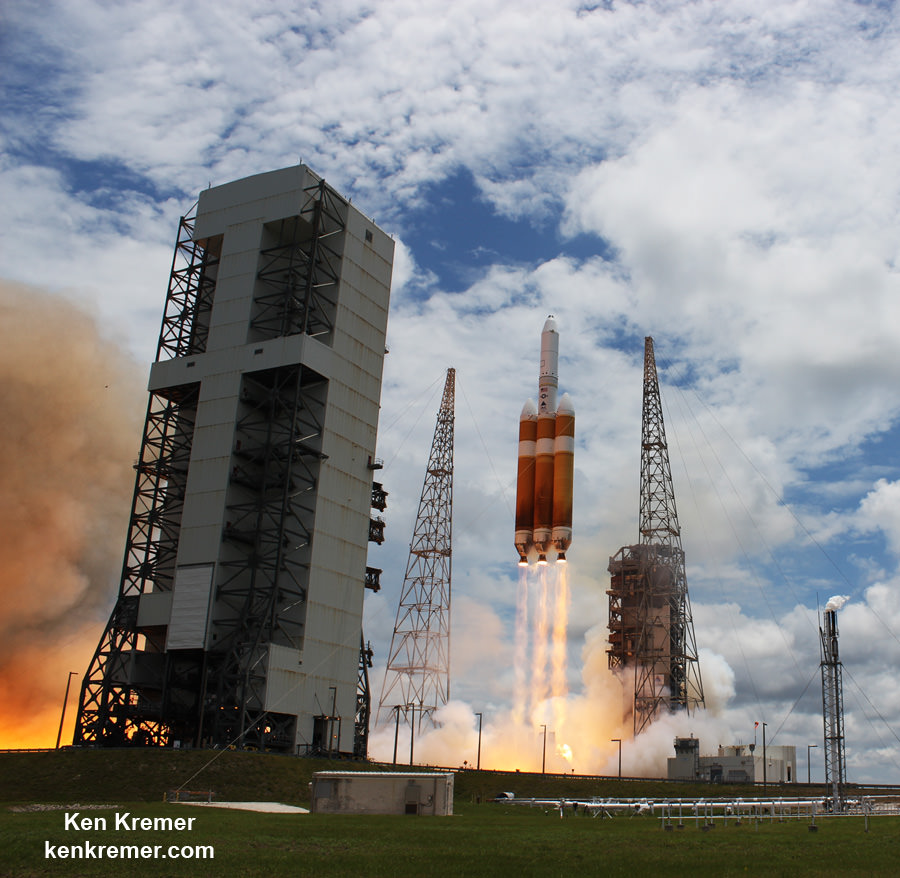
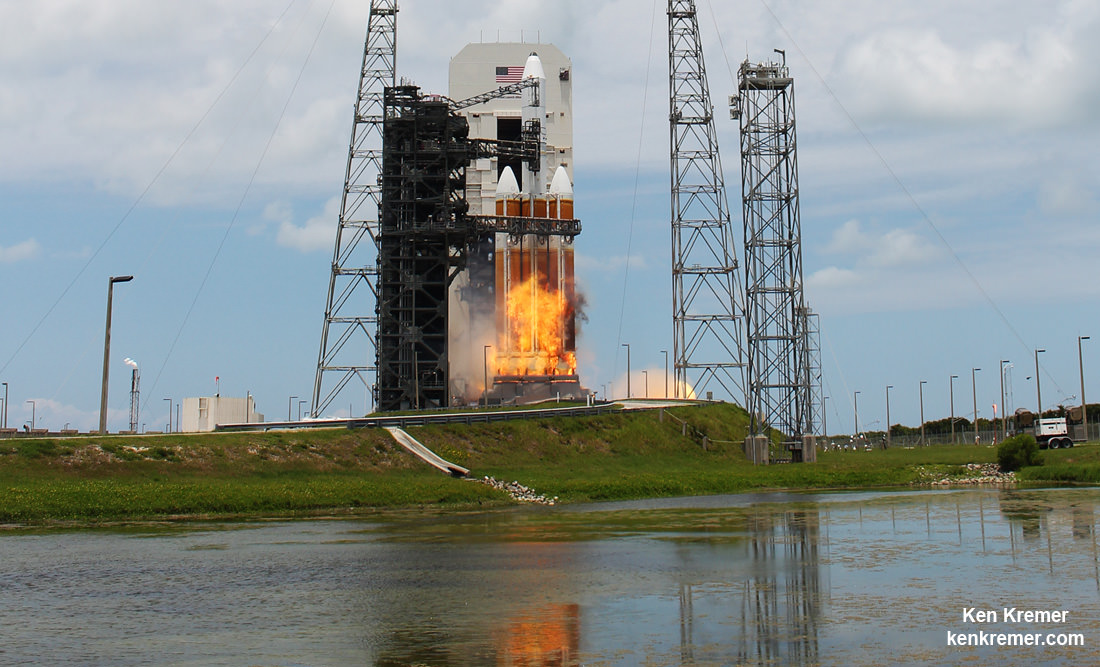
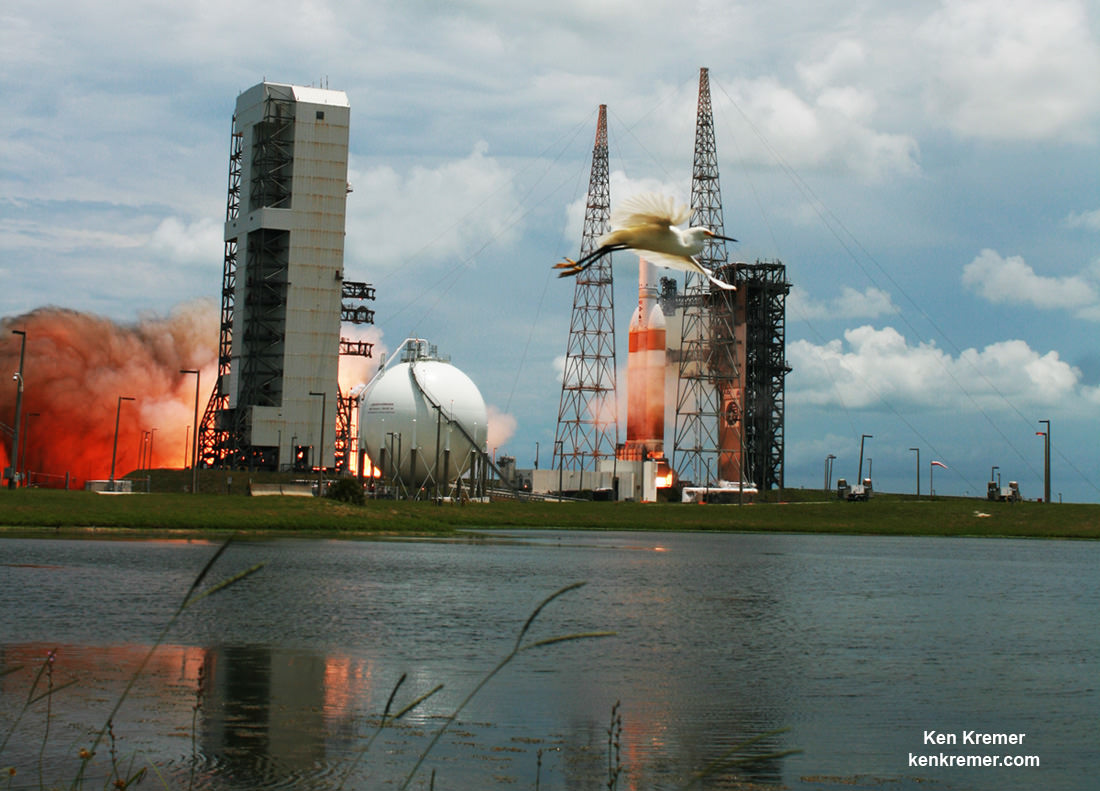
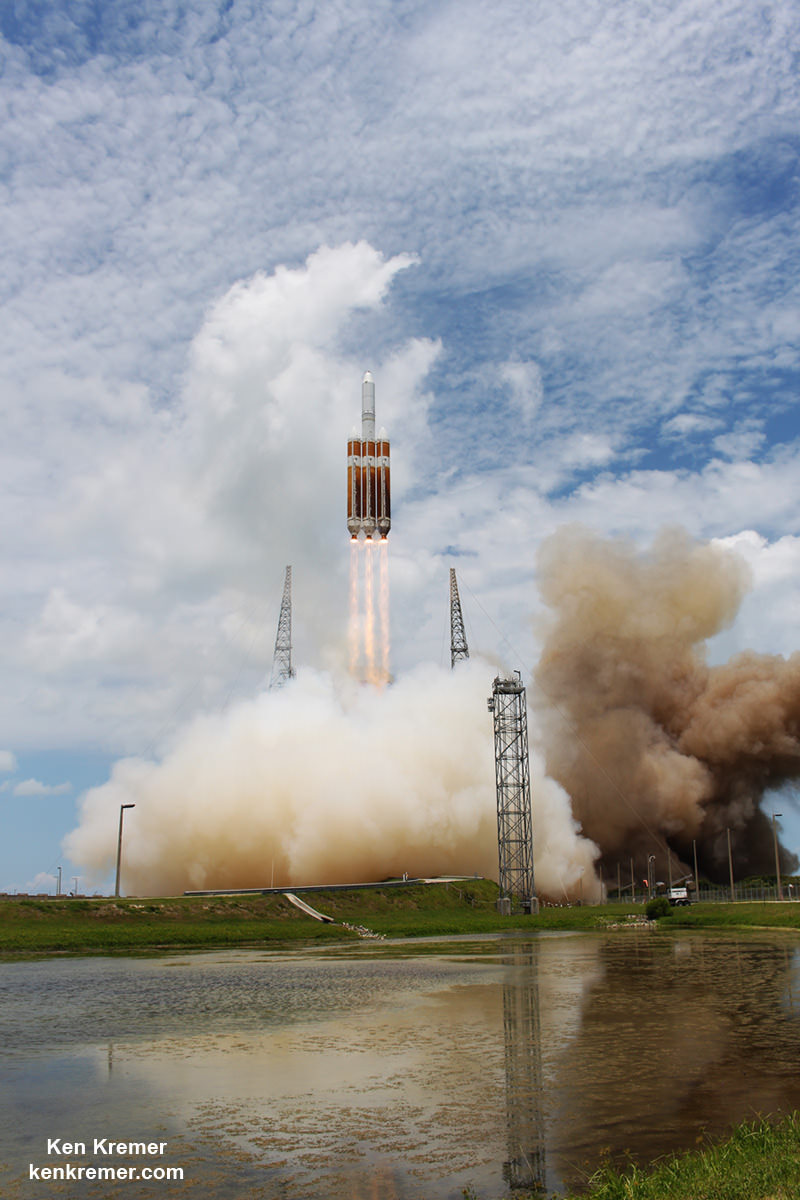
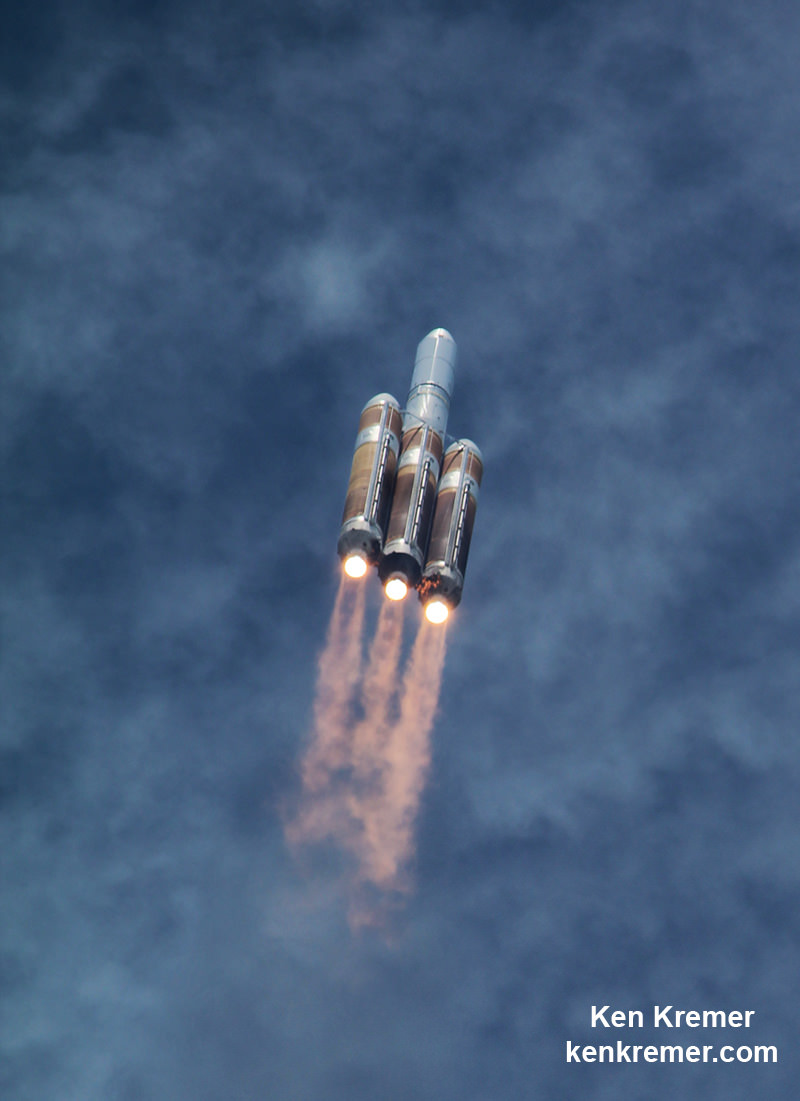
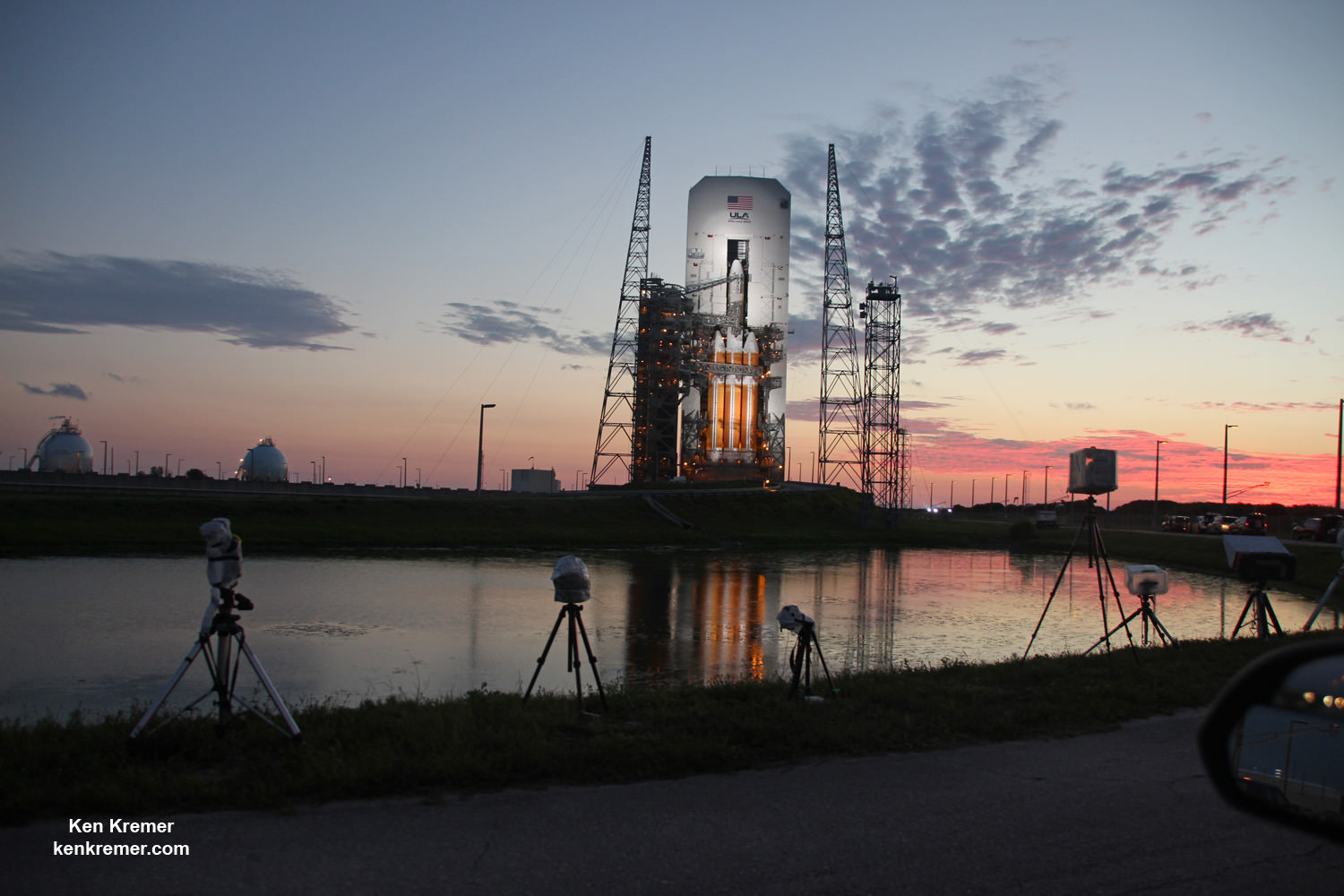
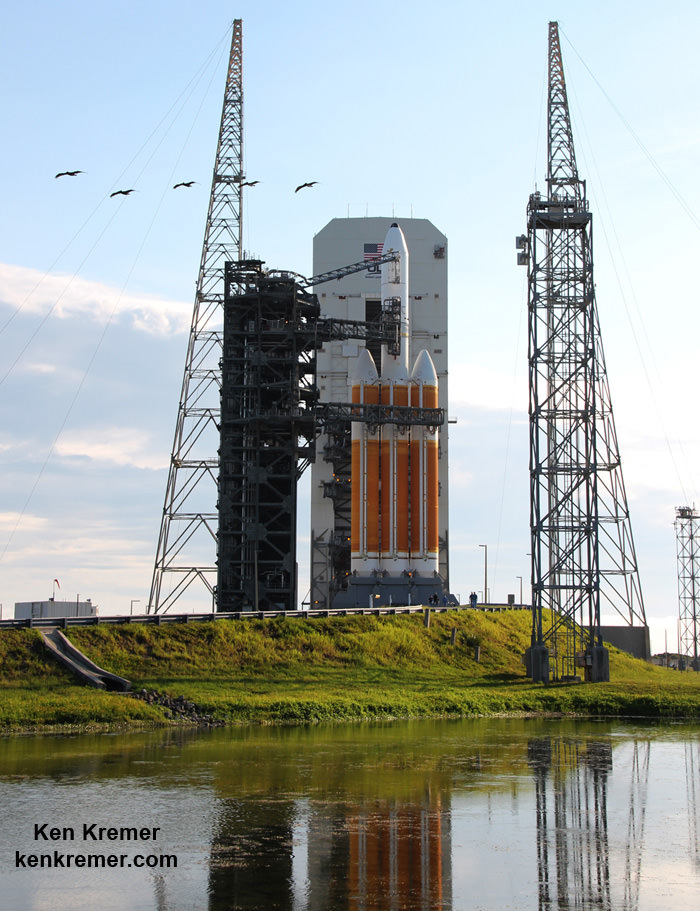
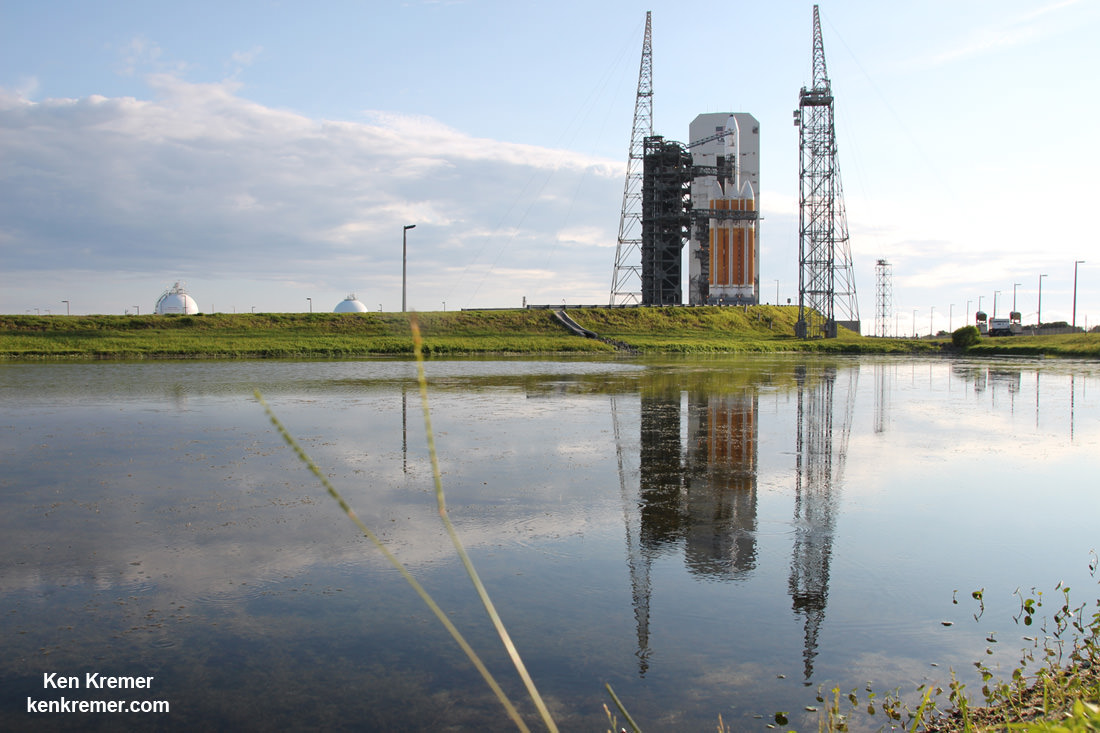
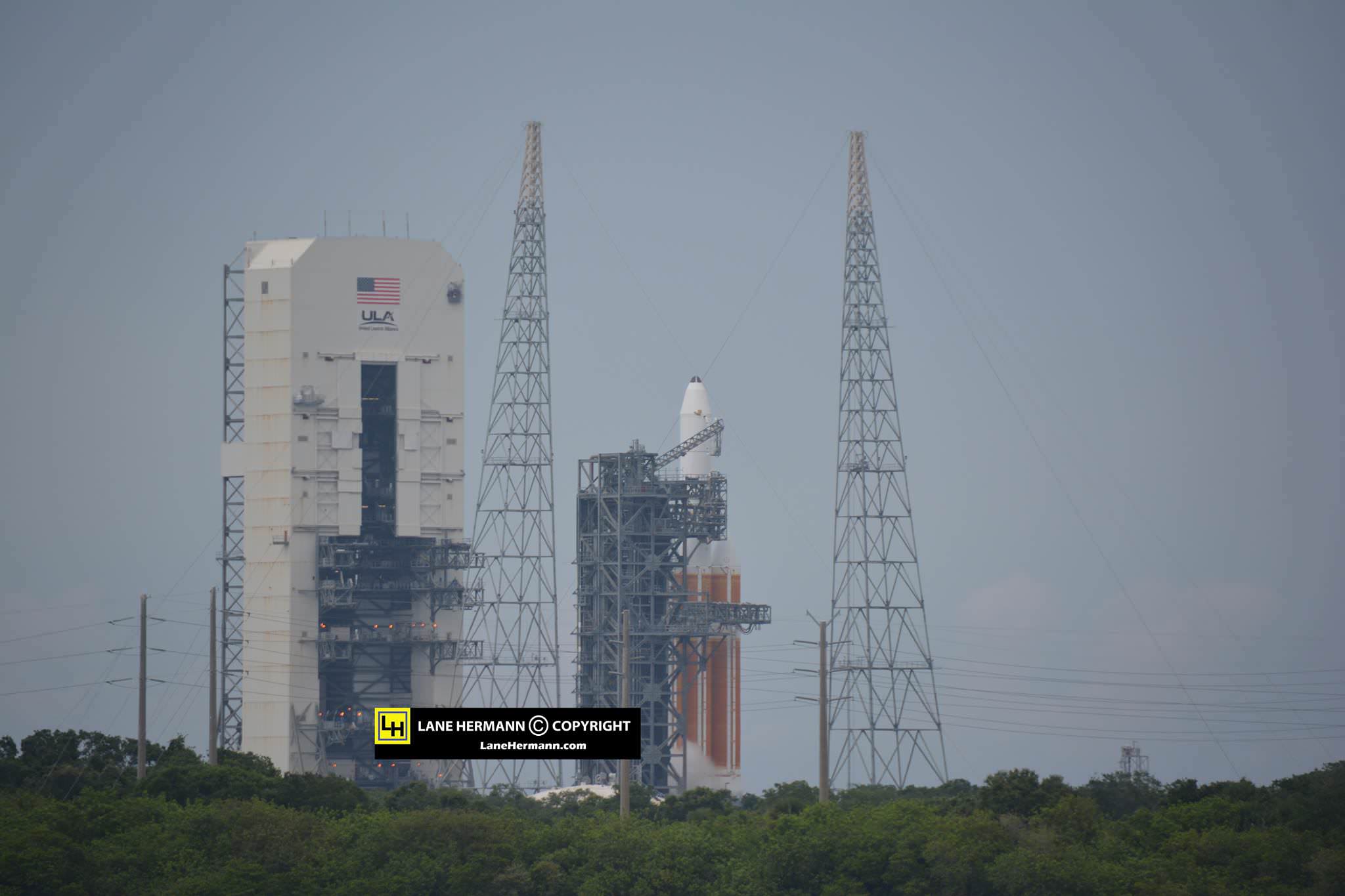
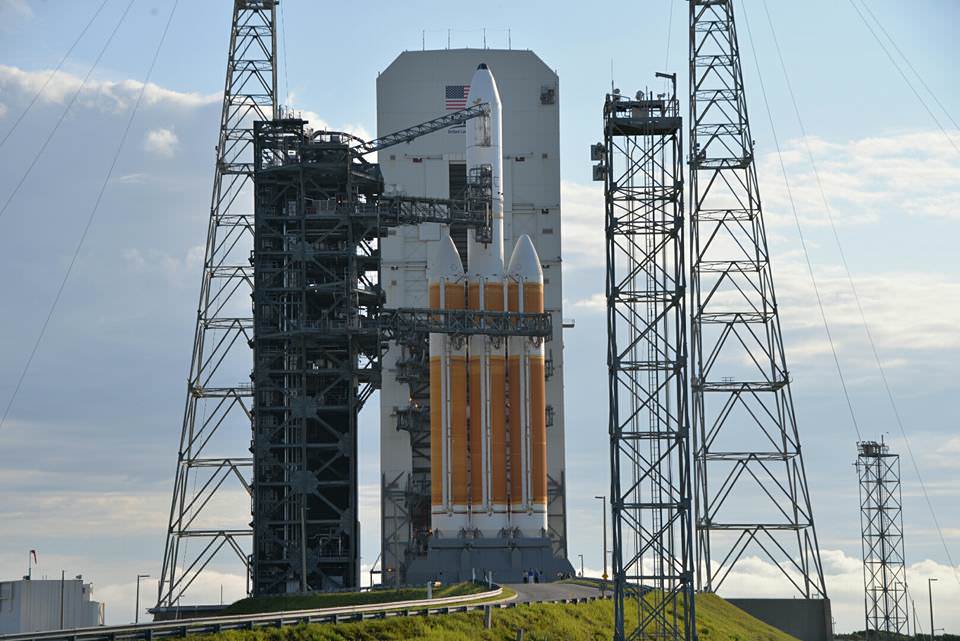
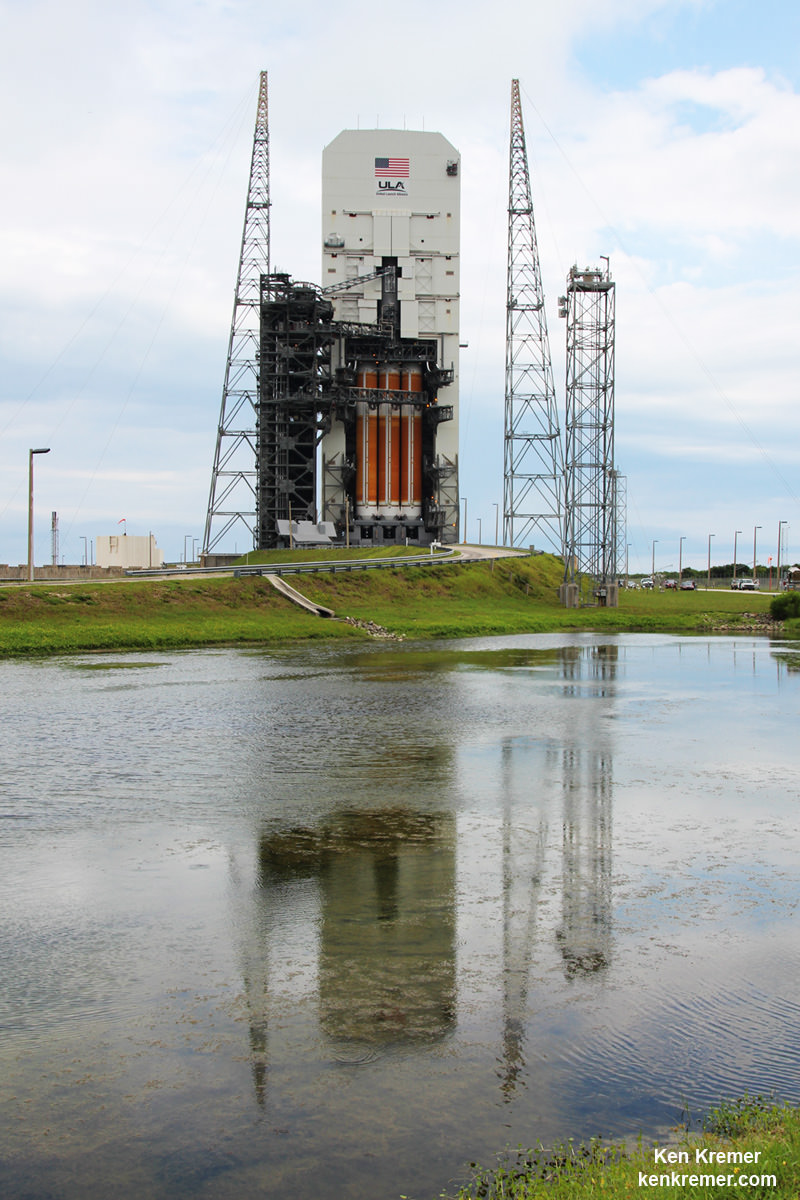
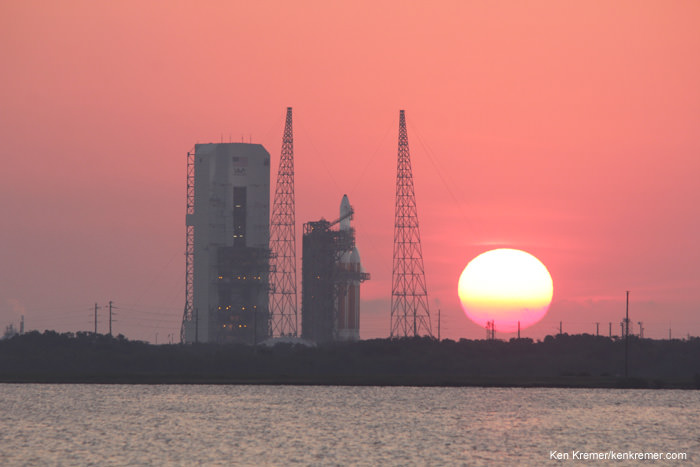
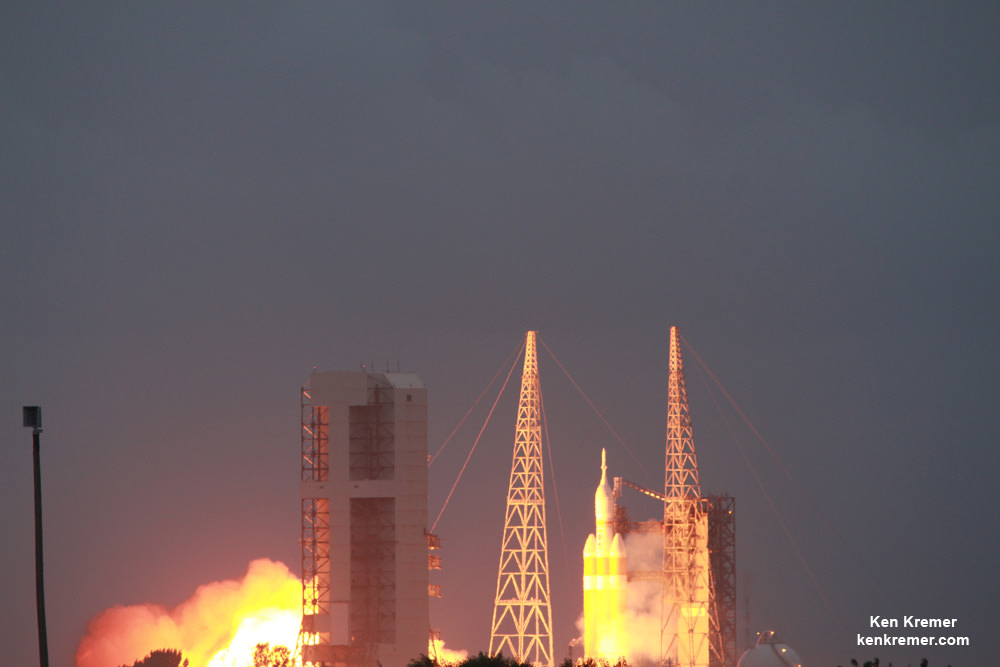
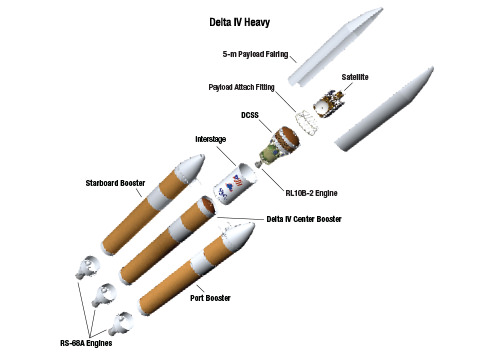
And Wednesday’s launch comes just 5 days after Saturday’s (June 11) launch from the Cape of the world’s most powerful rocket – the Delta 4 Heavy – which delivered a huge spy satellite to orbit for the NRO in support of US national defense.
Indeed what makes this flight especially interesting is that the satellites are based on Boeing’s 702SP series program and were the first all-electric propulsion satellites when Boeing introduced it in 2012, a Boeing spokesperson Joanna Climer told Universe Today.
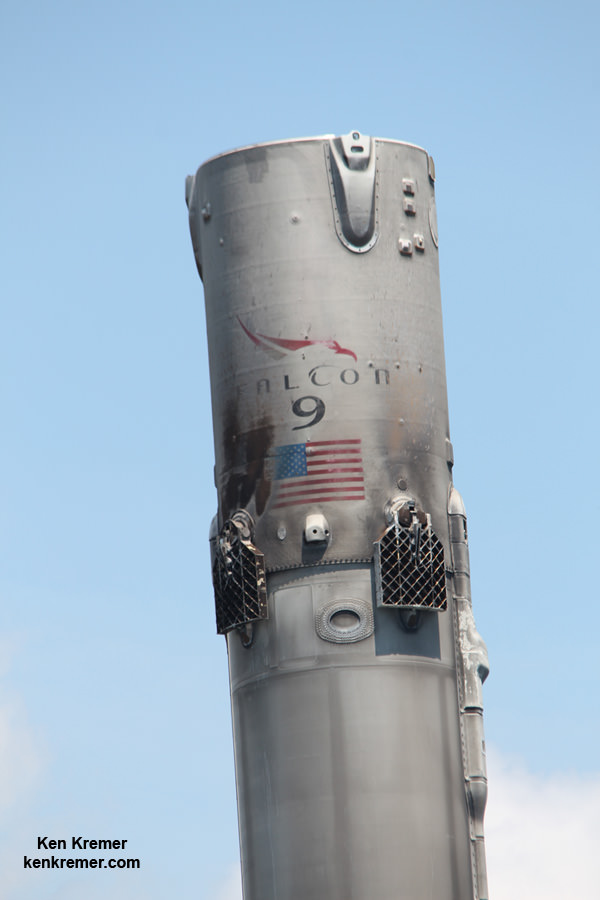
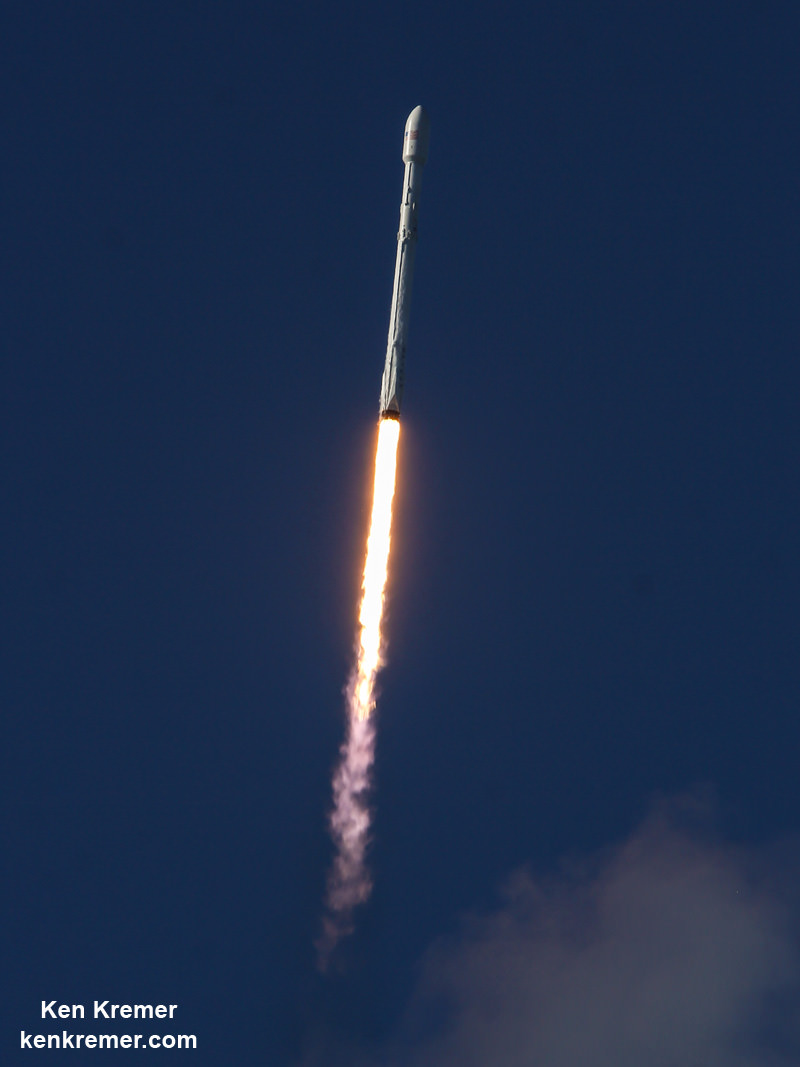
The 229 foot-tall (70 meter) Falcon 9 will deliver the roughly 5000 pound commercial telecommunications satellites to a Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) for Eutelsat based in Paris and Asia Broadcast Satellite of Bermuda and Hong Kong.

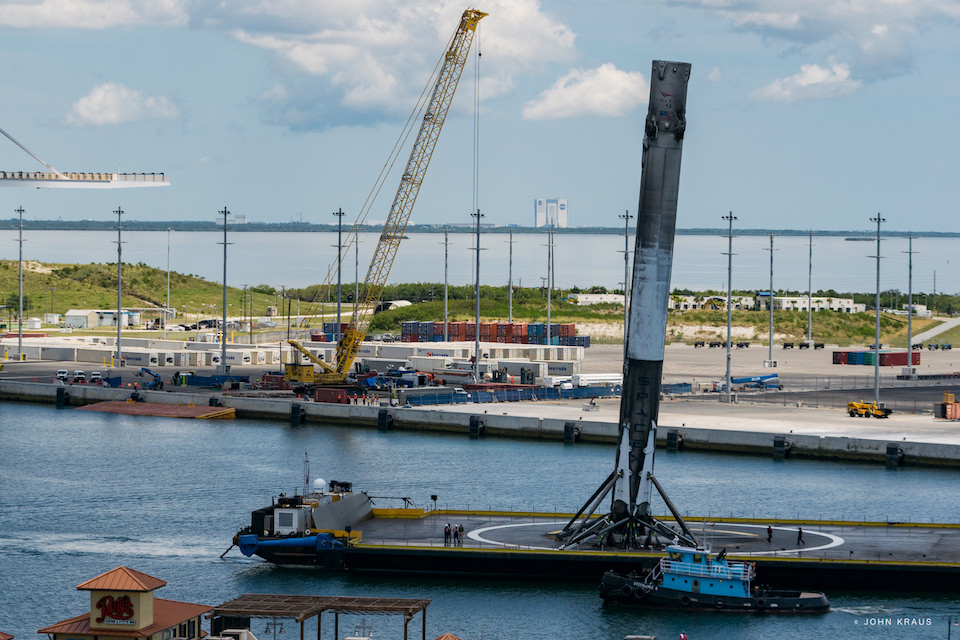
For the fourth time in a row, the spent first stage booster will again attempt to propulsively soft land on a platform at sea some nine minutes later.
You can watch the Falcon launch live on Wednesday via a special live webcast directly from SpaceX HQ in Hawthorne, Ca.
The SpaceX webcast will be available starting about 20 minutes before liftoff, at approximately 10:09 a.m. EDT at SpaceX.com/webcast
The two stage Falcon 9 rocket has a 44-minute long launch window that extends until 11:13 a.m. EDT on Wednesday, June 15.
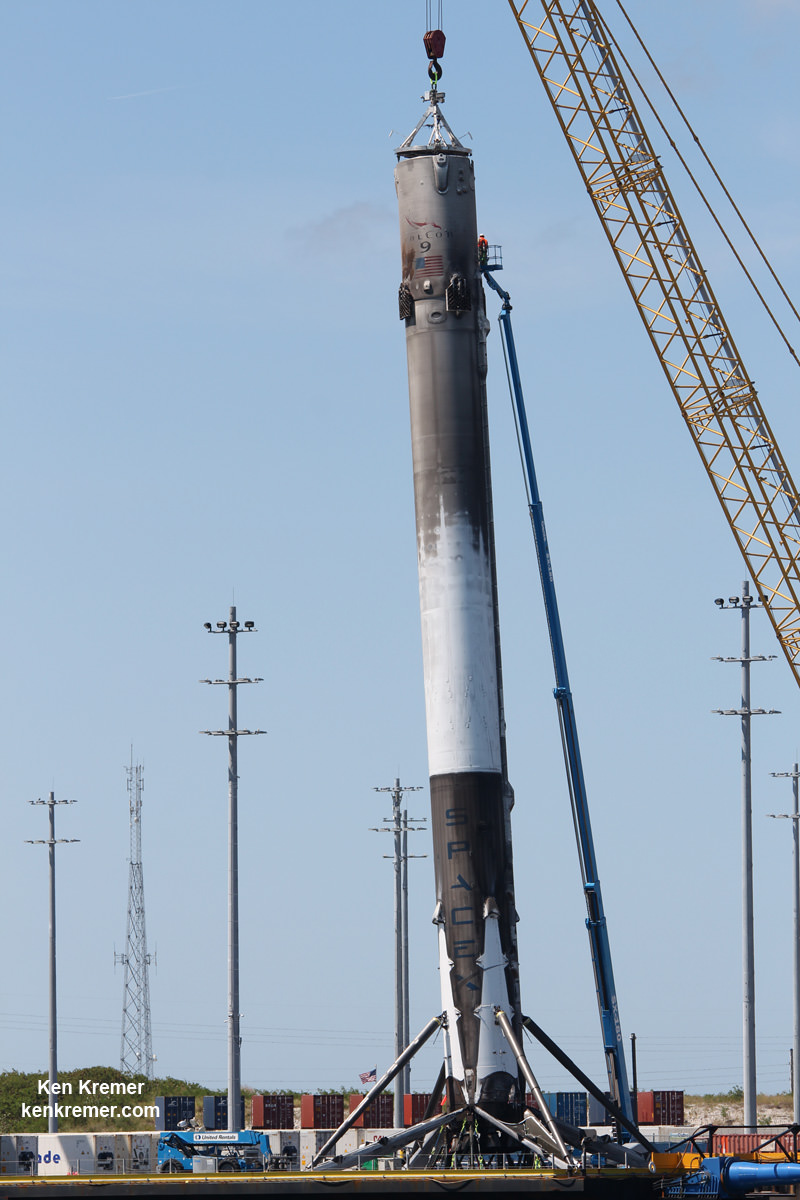
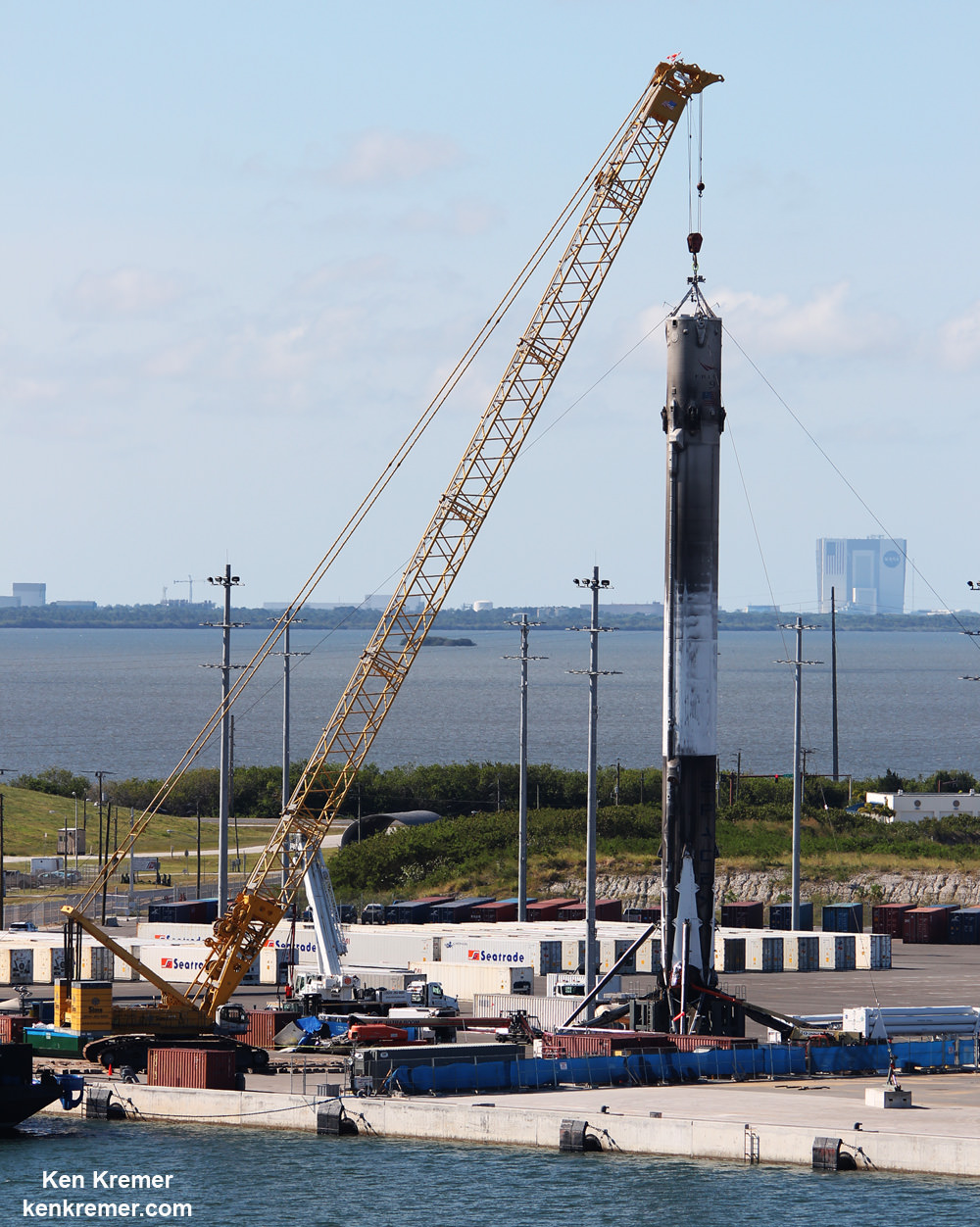
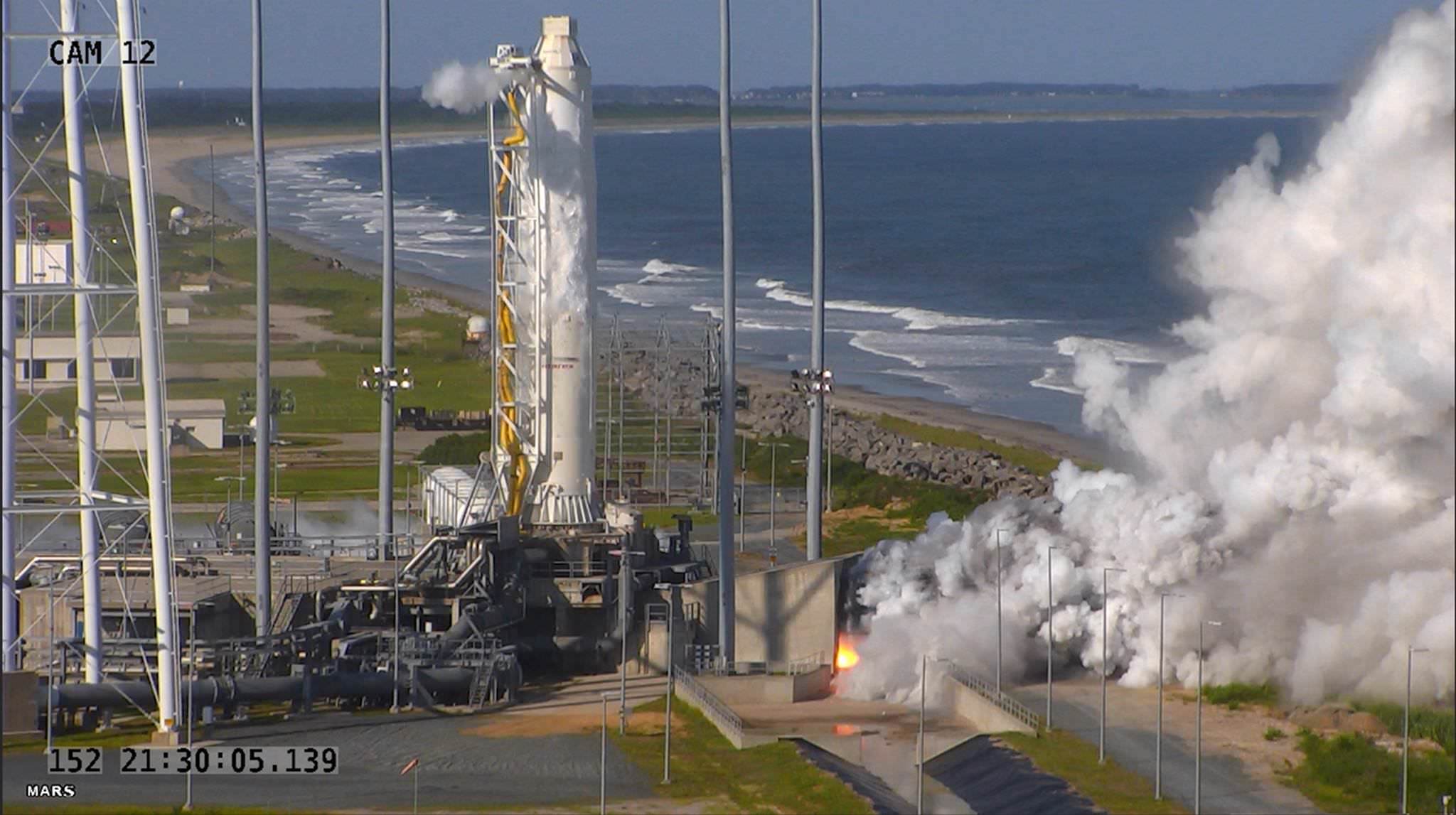
The path to launch was cleared after SpaceX engineers successfully carried out a brief static fire test of the first stages engines with the rocket erect at pad 40. The customary test lasts a few seconds and was conducted headless – without the two satellites bolted on top.
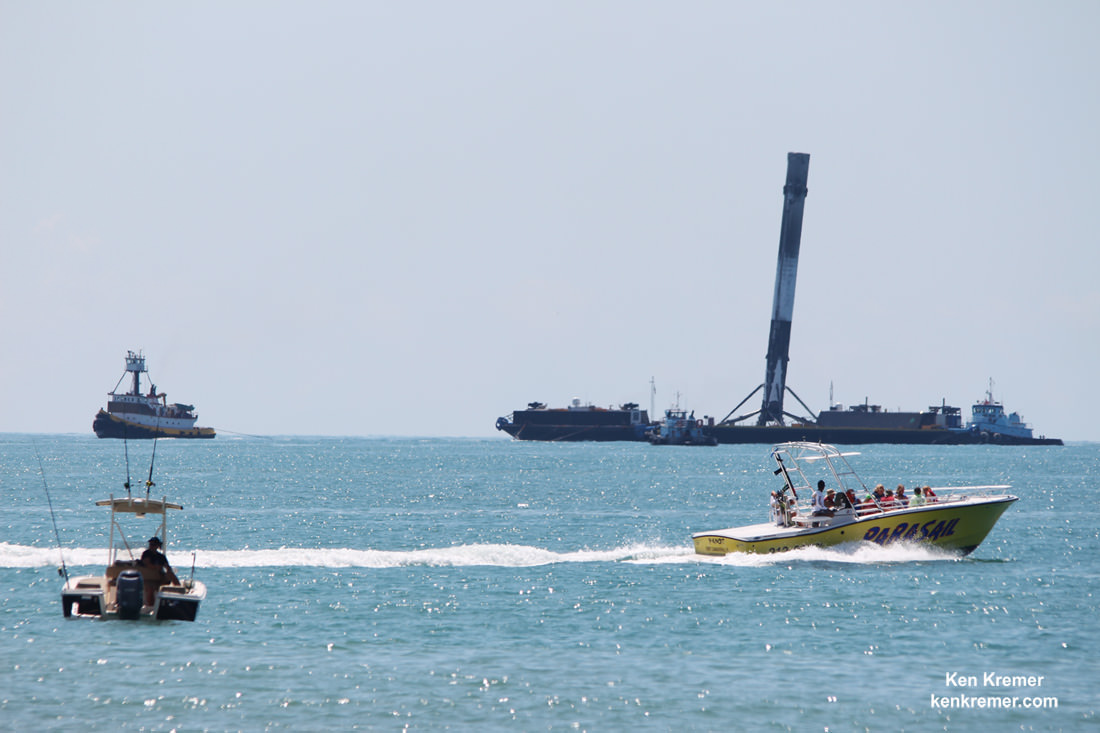

The vertically stacked pair of comsats are “very similar, but not identical,” Climer told me.
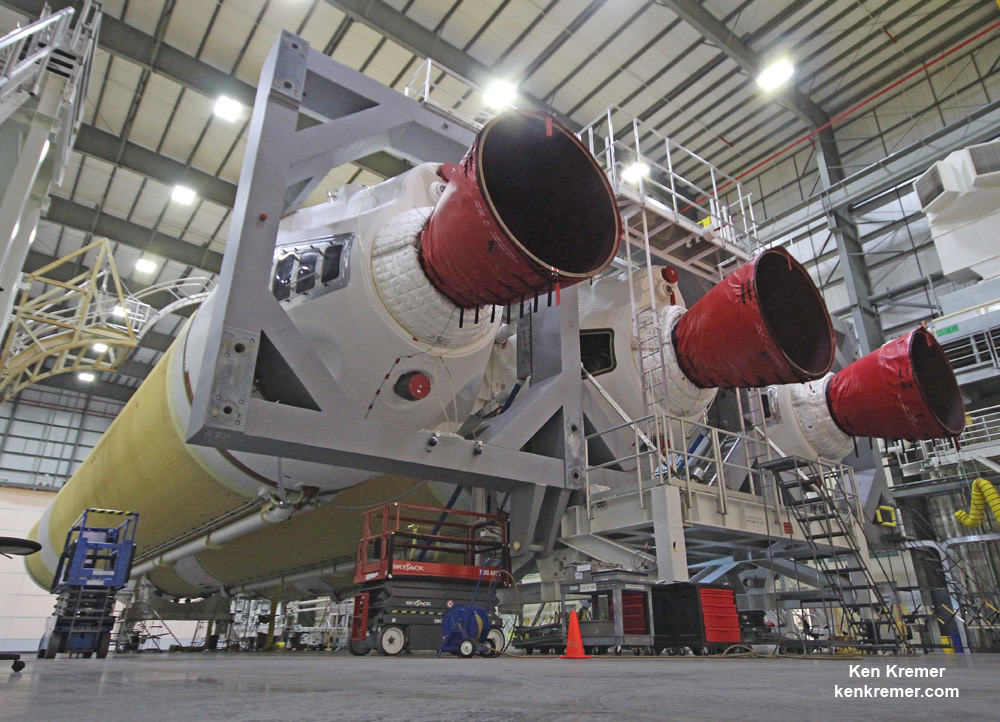
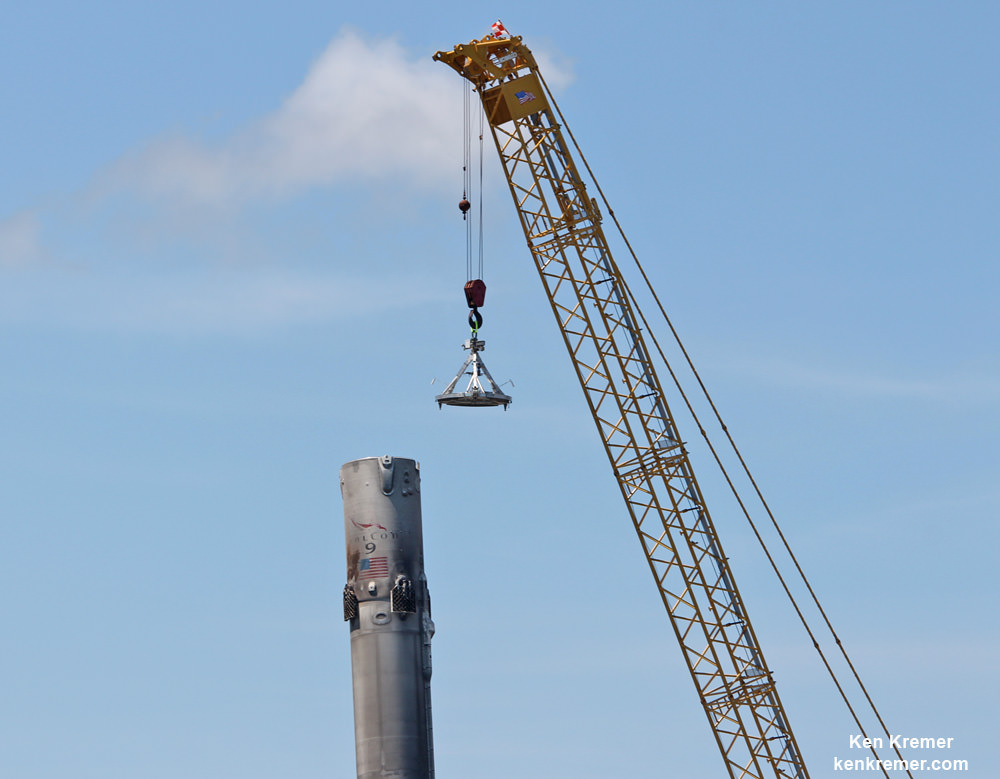
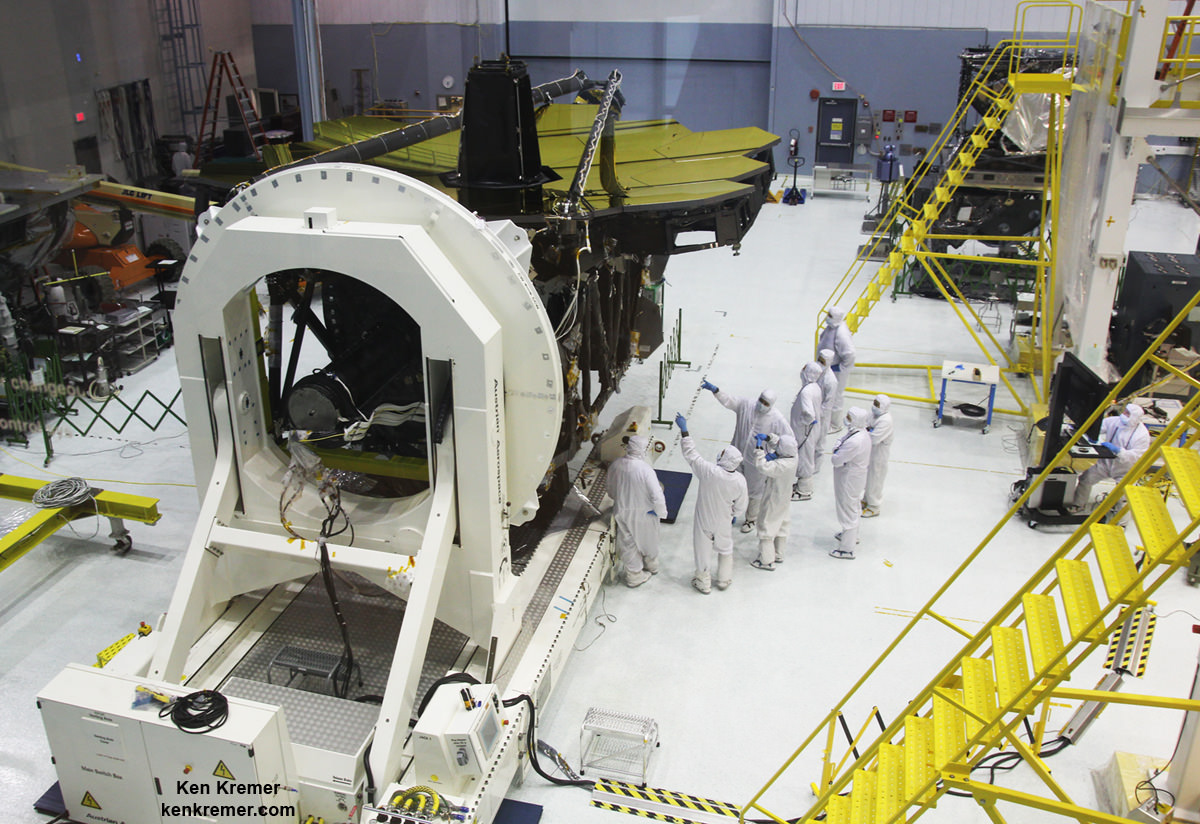
They are already encased inside the Falcon 9 payload fairing and stacked in a Boeing-patented and customized interface configuration – as seen in the photo herein.
They were tested at the Boeing Satellite Development Center in El Segundo, Calif., to ensure they could withstand the rigors of the launch environment. They have a design lifetime of a minimum of 15 years.
“They vary slightly in mass, but have similar payload power. The satellite on top weighs less than the one on the bottom.”
The Eutelsat satellite is carrying a hosted payload for the FAA.
They will detached and separate from one another in space. The top satellite will separate first while the pair are still attached to the second stage. Then the bottom satellite will detach completing the spacecraft separation event.
They will be deployed at about 30 minutes and 35 minutes after liftoff.
Eutelsat 117 West B will provide Latin America with video, data, government and mobile services for Paris-based Eutelsat.
ABS 2A will distribute direct-to-home television, mobile and maritime communications services across Russia, India, the Middle East, Africa, Southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean region for Asia Broadcast Satellite of Bermuda and Hong Kong.
The satellites have no chemical thrusters. They will maneuver to their intended orbit entirely using a use xenon-based electric thruster propulsion system known as XIPS.
XIPS stands for xenon-ion propulsion system.
“XIPS uses the impulse generated by a thruster ejecting electrically charged particles at high velocities. XIPS requires only one propellant, xenon, and does not require any chemical propellant to generate thrust,” according to Boeing officials.
“XIPS is used for orbit raising and station-keeping for the 702SP series.”
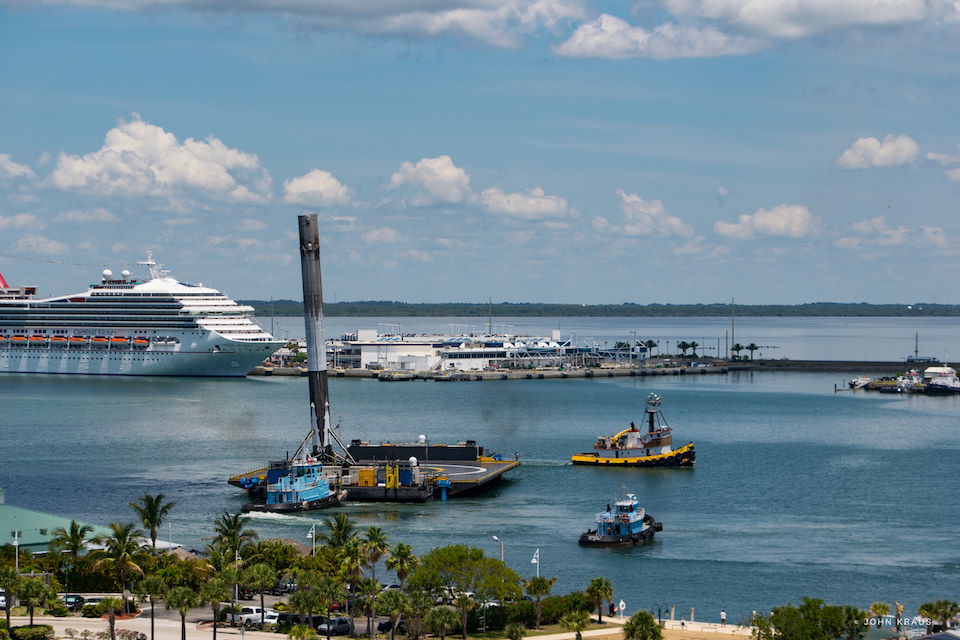
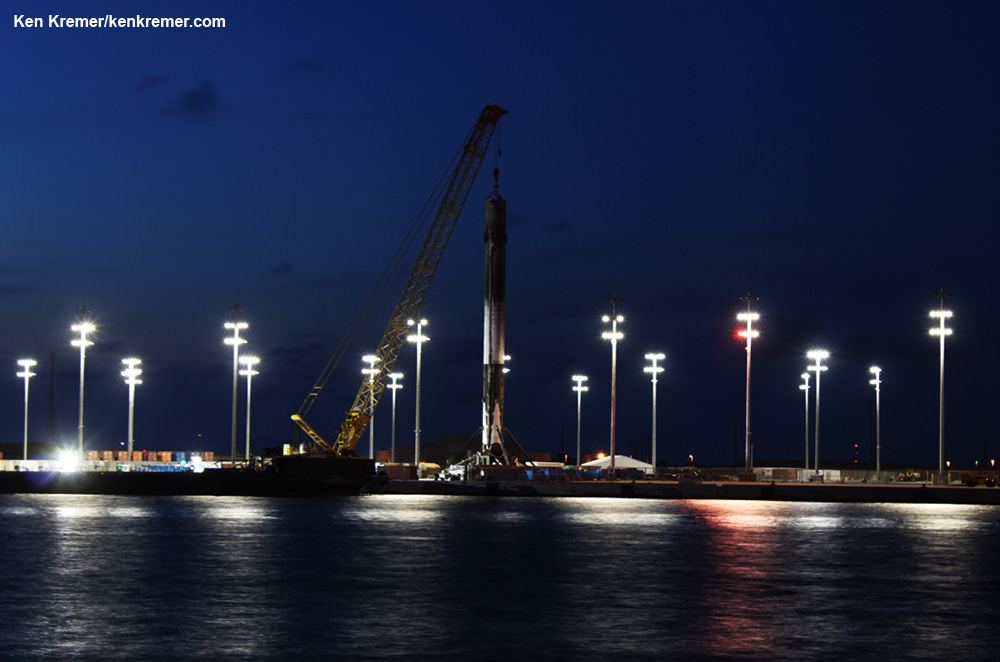
The ASDS drone ship landing platform known as “Of Course I Still Love You” or OCISLY was already dispatched several days ago.
It departed Port Canaveral for the landing zone located approximately 420 miles (680 kilometers) off shore and east of Cape Canaveral, Florida surrounded by the vastness of the Atlantic Ocean.
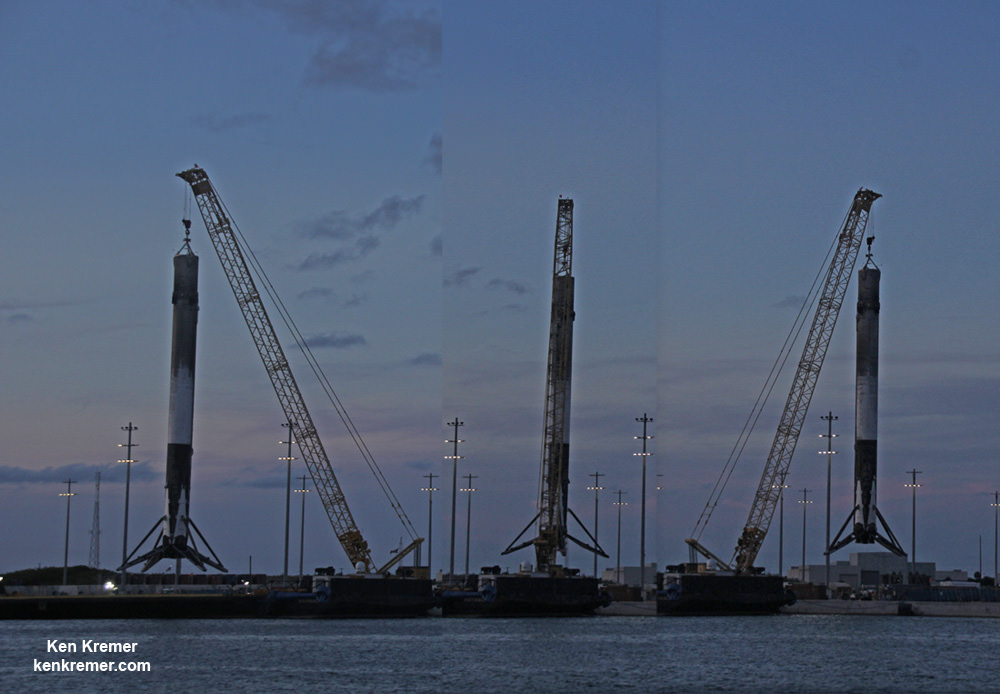
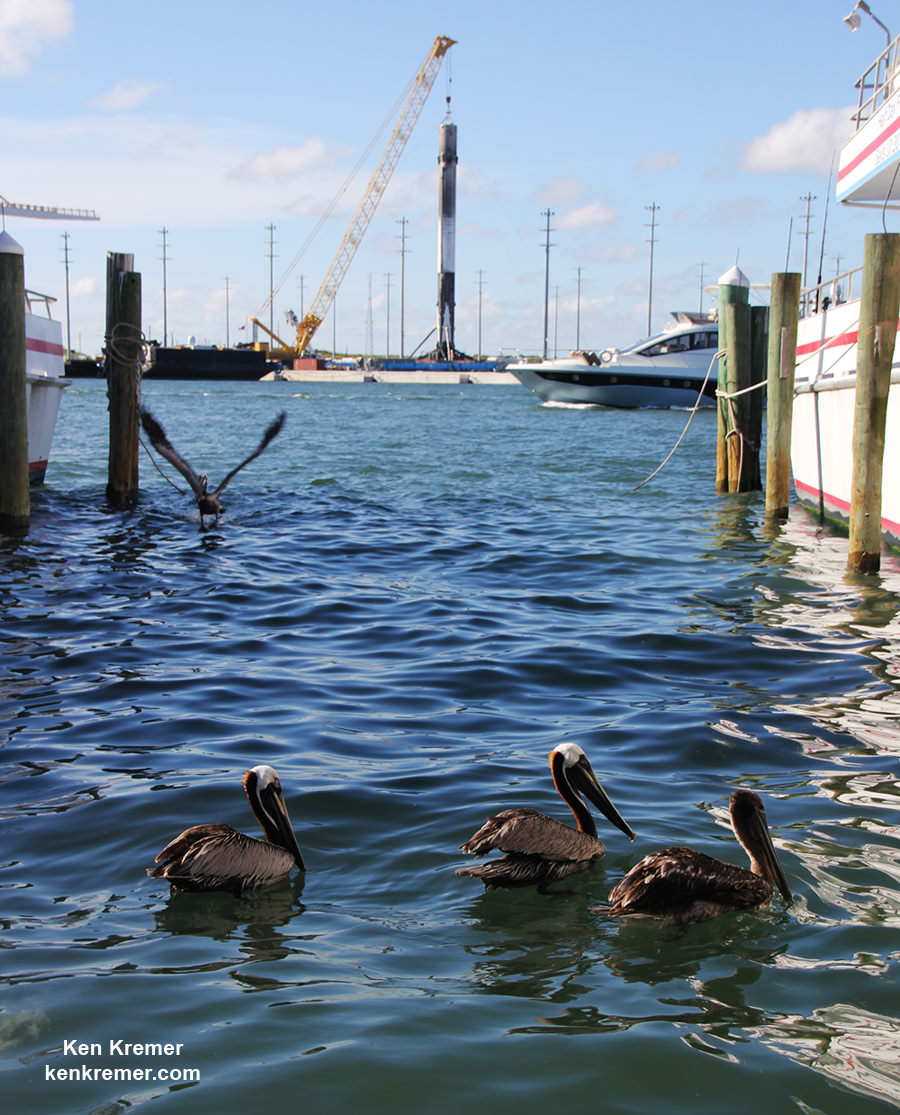
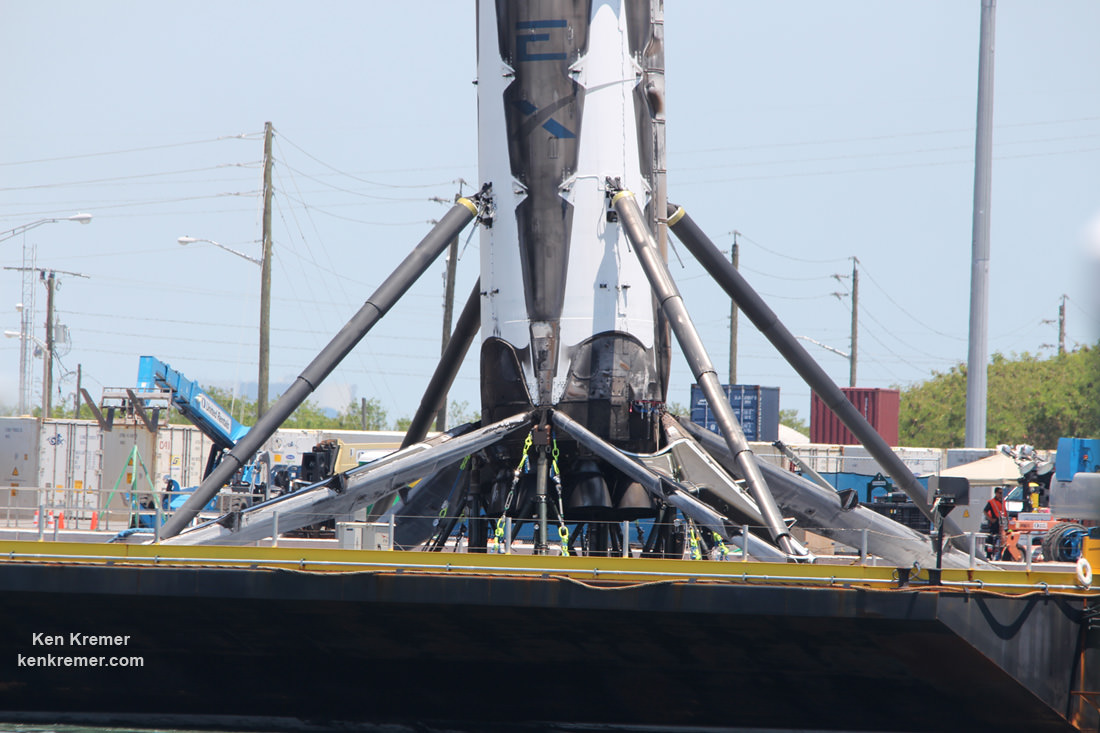
As I witnessed and reported here first hand, the Thaicom-8 first stage arrived on OCISLY six days after the ocean landing, in a tilted configuration. It was craned off the drone ship onto a ground support cradle two days later.
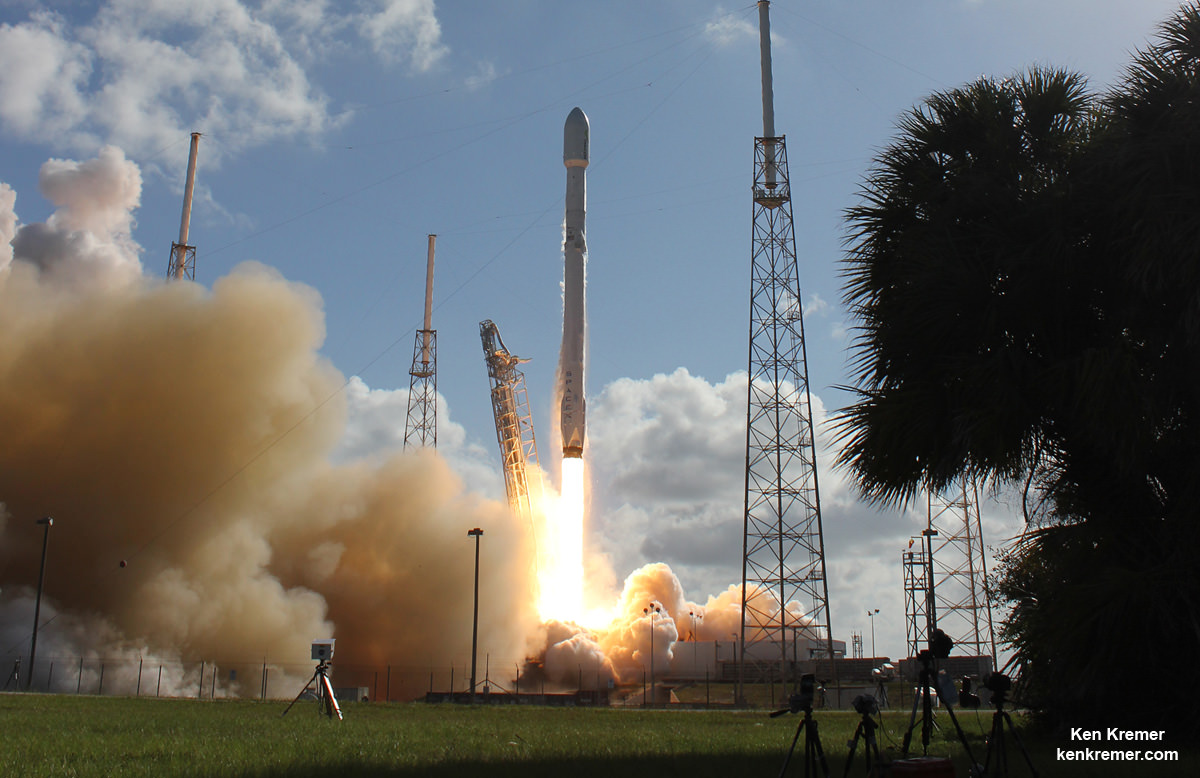

Watch for Ken’s continuing on site reports direct from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and the SpaceX launch pad.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
………….
Learn more about ULA Atlas and Delta rockets, SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Orbital ATK Cygnus, ISS, Boeing, Space Taxis, Mars rovers, Orion, SLS, Antares, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
June 14/15: “ULA Delta 4 Heavy spy satellite, SpaceX, SLS, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, Pluto and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings